|
Halmyros
Almyros or Halmyros (, ) is a town and a municipality of the regional unit of Magnesia, region of Thessaly, Greece. It lies in the center of prosperous fertile plain known as 'Krokio Pedio', which is crossed by torrents. Almyros is an important agricultural and commercial center of Magnesia, and is also developing as a tourist center for the area. The main agricultural products are tomatoes, cotton, wheat, almonds, peanuts and pistachio nuts. History The history of Almyros begins with the ancient city of Halos (about 10 km .2 misouth of Almyros), the ruins of which can still be visited. Halos was a very important and populous town, famous for its port and for its role in the Persian Wars. After the Byzantine Empire, because of pirate raids, they built the town in the place that it is today. Ancient Halos was still mentioned in the works of Stephanus of Byzantium (6th century). The medieval successor settlement of Halmyros is first mentioned in the 11th century, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalan Company
The Catalan Company or the Great Catalan Company (; , , , or ) was a company of mercenaries led by Roger de Flor in the early 14th century and hired by Byzantine Emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos to combat the increasing power of the Anatolian beyliks. It was formed by '' almogavar'' veterans of the War of the Sicilian Vespers, who had remained unemployed after the signing in 1302 of the Peace of Caltabellotta between the Crown of Aragon and the French dynasty of the Angevins. Origin The military demands of the Reconquista stimulated the formation of the elite light infantry known as the '' almogavars'' on the Iberian peninsula during the 13th century. These troops were used quite effectively by the Crown of Aragon for other imperial ventures in the Mediterranean, particularly the War of the Sicilian Vespers. They were typically organised in companies (''societates'') of 20 to 50 men, following a chief of recognized military skill. The signing of the Peace of Caltabellotta i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitio Terrarum Imperii Romaniae
The ''Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae'' (Latin for "Partition of the lands of the empire of ''Romania'' .e., the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire, or ''Partitio regni Graeci'' ("Partition of the kingdom of the Greeks"), was a treaty signed among the crusaders after the sack of the Byzantine capital, Constantinople, by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. It established the Latin Empire and arranged the nominal partition of the Byzantine territory among the participants of the Crusade, with the Republic of Venice being the greatest titular beneficiary. However, because the crusaders did not in fact control most of the Empire, local Byzantine Greek nobles established a number of Byzantine successor kingdoms (Empire of Nicaea, Empire of Trebizond, Despotate of Epirus). As a result, much of the crusaders' declared division of the Empire amongst themselves could never be implemented. The Latin Empire established by the treaty would last until 1261, when the Empire of Nicaea reconquered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
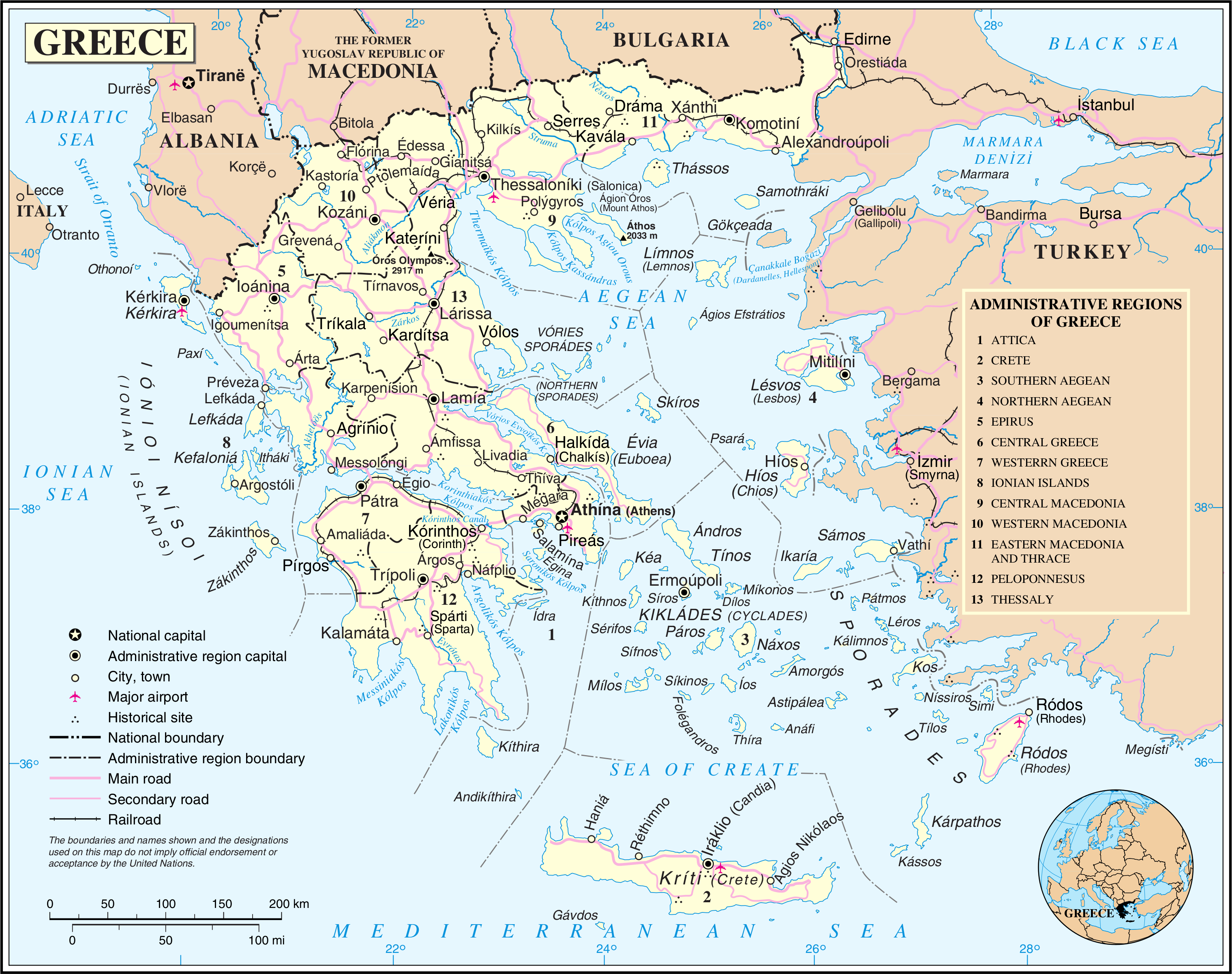
Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia (, ), and appears thus in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Thessaly Convention of Constantinople (1881), became part of the modern Greek state in 1881, after four and a half centuries of Ottoman Greece, Ottoman rule. Since 1987 it has formed one of the country's 13 Modern regions of Greece, regions and is further (since the Kallikratis reform of 2011) sub-divided into five regional units of Greece, regional units and 25 municipalities of Greece, municipalities. The capital of the region is Larissa. Thessaly lies in northern central Greece and borders the regions of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia to the north, Epirus (region), Epirus to the west, Central Greece (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece () are the country's thirteen second-level administrative divisions of Greece, administrative entities, counting decentralized administrations of Greece as first-level. Regions are divided into regional units of Greece, regional units, known as prefectures of Greece, prefectures until 2011. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the Prefectures of Greece, prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad geographic regions of Greece, historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Jews In The Byzantine Empire
Jews were numerous and had significant roles throughout the history of the Byzantine Empire. Background and legal standing After the decline of the Greek-speaking Hellenistic Judaism in ancient times, the use of the Greek language and the integration of Greek culture into Judaism continued to be an integral part of life in Jewish communities in the Byzantine Empire. The legal standing of the Jews of the Byzantine Empire was unique throughout the empire’s history. They did not belong to the Christian Eastern Orthodox faith, which was the state church of the Byzantine Empire, nor were they, in most circumstances, grouped together with heretics and pagans. They were placed in a legal position somewhere between the two. The place along the spectrum of social freedom in which Byzantine Jews found themselves varied somewhat, though far from drastically, over time. This status was shaped largely by three factors: the theological aim of the state to preserve Jews as a living testame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme (Byzantine District)
The themes or (, , singular: , ) were the main military and administrative divisions of the middle Byzantine Empire. They were established in the mid-7th century in the aftermath of the Slavic migrations to Southeastern Europe and Muslim conquests of parts of Byzantine territory, and replaced the earlier provincial system established by Diocletian and Constantine the Great. In their origin, the first themes were created from the areas of encampment of the field armies of the East Roman army, and their names corresponded to the military units that had existed in those areas. The theme system reached its apogee in the 9th and 10th centuries, as older themes were split up and the conquest of territory resulted in the creation of new ones. The original theme system underwent significant changes in the 11th and 12th centuries, but the term remained in use as a provincial and financial circumscription until the very end of the Empire. History Background During the late 6th and ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael II Of Epirus
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * he He ..., a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect)">Michael (surname)">he He ..., a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (fashion designer), Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian football ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Of Hungary
Margaret of Hungary (''Margit'' in Hungarian; b. 1175 – d. after 1229) was a Hungarian princess from the House of Árpád. She was a Byzantine Empress by marriage to Isaac II Angelos (d. 1204), and Queen of Thessalonica by marriage to Boniface of Montferrat (d. 1207). She was regent of Thessalonica during the minority of her son Demetrius of Montferrat, from 1207 to 1216. In later years (c. 1223) she governed some of the most southern regions of the Kingdom of Hungary, with her domains being centered in the region of Syrmia. Early life Margaret was the eldest daughter of Béla III of Hungary and his first wife Agnes of Antioch. She was a younger sister of Emeric, King of Hungary. Her younger siblings were Andrew II of Hungary and Constance of Hungary. Two other siblings, Solomon and Stephen, are mentioned in the standard reference work on the genealogy of medieval European aristocracy, "Europäische Stammtafeln" (1978–1995) by Detlev Schwennicke. They reportedly died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Of Larissa
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will or Wil, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, Billie, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie). Female forms include Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic name is a compound of *''wiljô'' "will, wish, desire" and *''helmaz'' "helm, helmet".Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boniface I, Marquis Of Montferrat
Boniface I, usually known as Boniface of Montferrat (; ; c. 1150 – 4 September 1207), was the ninth Marquis of Montferrat (from 1192), a leader of the Fourth Crusade (1201–04) and the king of Thessalonica (from 1205). Early life Boniface was the third son of William V of Montferrat and Judith of Babenberg, born after his father's return from the Second Crusade. He was a younger brother of William "Longsword", Count of Jaffa and Ascalon, and of Conrad I of Jerusalem. His youthful exploits in the late 1170s are recalled in the famous "epic letter", ''Valen marques, senher de Monferrat'', by his good friend and court troubadour, Raimbaut de Vaqueiras. These included the rescue of the heiress Jacopina of Ventimiglia from her uncle Count Otto, who was intending to deprive her of her inheritance and send her to Sardinia. Boniface arranged a marriage for her. When Albert of Malaspina (husband of one of Boniface's sisters) abducted Saldina de Mar, a daughter of a prominent G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrosyne Doukaina Kamatera
Euphrosyne Doukaina Kamaterina or better Kamatera (, – 1211) was a Byzantine Empress by marriage to the Byzantine Emperor Alexios III Angelos. Euphrosyne was the daughter of Andronikos Doukas Kamateros, a high-ranking official who held the titles of '' megas droungarios'' and '' pansebastos'' and his wife, an unknown Kantakouzene. She was related to the Emperor Constantine X and Irene Doukaina, empress of Alexios I Komnenos. Both of her brothers had rebelled against Andronikos I Komnenos; one was imprisoned and the other was blinded. Life Euphrosyne married Alexios Angelos, the older brother of the future Emperor Isaac II Angelos in c. 1169 CE. Although Isaac II bestowed many titles and honors upon his brother, Alexios seized the throne on April 8, 1195, deposing Isaac and proclaiming himself emperor. In this he was assisted by Euphrosyne, who had organized a party of aristocratic supporters. Euphrosyne took control of the palace and quelled the opposition herself, securin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
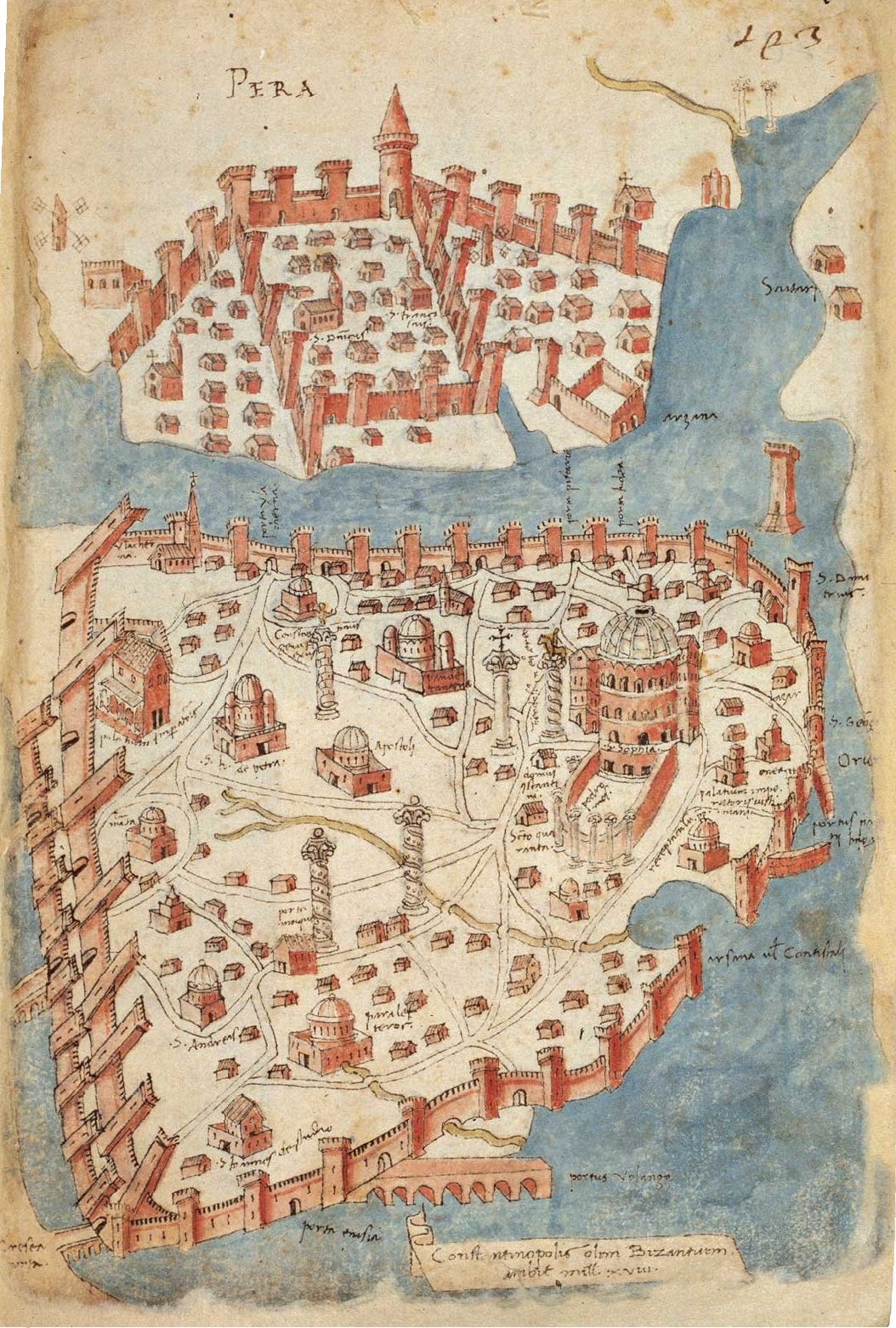
Sack Of Constantinople
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusaders sacked and destroyed most of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the city, the Latin Empire (known to the Byzantines as the '' Frankokratia'', or the Latin occupation) was established and Baldwin of Flanders crowned as Emperor Baldwin I of Constantinople in Hagia Sophia. After the city's sacking, most of the Byzantine Empire's territories were divided up among the Crusaders. Byzantine aristocrats also established a number of small independent splinter states—one of them being the Empire of Nicaea, which would eventually recapture Constantinople in 1261 and proclaim the reinstatement of the Empire. However, the restored Empire never managed to reclaim all its former territory or attain its earlier economic strength, and it gradually succumbed to the rising Ottoman Empire over the following two centuries. The Byzantine Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |