|
Halasana
Halasana (; ) or Plough pose is an inverted asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. Its variations include Karnapidasana with the knees by the ears, and Supta Konasana with the feet wide apart. Etymology and origins The name Halasana comes from Sanskrit , "plough" and , "posture" or "seat". The pose is described and illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' as ''Lāṇgalāsana'', which also means plough pose in Sanskrit. Karnapidasana is not found in the medieval hatha yoga texts. It is described independently in Swami Vishnudevananda's 1960 ''Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga'' in the Sivananda Yoga tradition, and by B. K. S. Iyengar in his 1966 ''Light on Yoga'', implying that it may have older origins. The name comes from the Sanskrit words () meaning "ears", () meaning "to squeeze", and () meaning "posture" or "seat". File:Arair champige a reil.png, The completed pose resembles a traditional plough. File:Sritattvanidhi Lalangasana.jpg, ''Lāṇgal� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Asanas
An asana (Sanskrit: आसन, IAST: āsana) is a body posture, used in both medieval hatha yoga and modern yoga. The term is derived from the Sanskrit word for 'seat'. While many of the oldest mentioned asanas are indeed seated postures for meditation, asanas may be standing, seated, arm-balances, twists, inversions, forward bends, backbends, or reclining in prone or supine positions. The asanas have been given a variety of English names by competing schools of yoga. The traditional number of asanas is the symbolic 84, but different texts identify different selections, sometimes listing their names without describing them. Some names have been given to different asanas over the centuries, and some asanas have been known by a variety of names, making tracing and the assignment of dates difficult. For example, the name Muktasana is now given to a variant of Siddhasana with one foot in front of the other, but has also been used for Siddhasana and other cross-legged meditation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marguerite Agniel
Marguerite Agniel (1891 – c. 1971) was a Broadway actress and dancer, who then became a health and beauty guru in New York in the early 20th century. She is known for her 1931 book ''The Art of the Body: Rhythmic Exercise for Health and Beauty'', one of the first to combine yoga and nudism. After appearing in '' Vogue'' in 1926, she wrote for '' Physical Culture'' and other magazines. In the 1930s, she published a series of books, including ''Body Sculpture'' and ''Your Figure'', advocating health and beauty practices, illustrated mainly with photographs of herself. Agniel stated that her dance technique derived from Ruth St. Denis (who had followed François Delsarte), while her "aesthetic athletics" came mainly from the physical culture advocate, Bernarr Macfadden. She described the sexologist Havelock Ellis and the musicologist Sigmund Spaeth as major influences. Life Marguerite Agniel was born on January 21, 1891, one of the six children of George Agniel and Ada L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
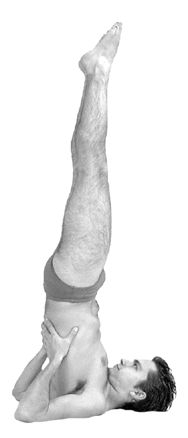
Sarvangasana
Sarvangasana (), Shoulder stand, or more fully Salamba Sarvangasana (Supported Shoulder stand), is an inverted asana in modern yoga as exercise; similar poses were used in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra. Many named variations exist, including with legs in lotus position and Supta Konasana with legs wide apart, toes on the ground. ''Sarvāṅgāsana'' has been nicknamed the "queen" or "mother" of all the asanas. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit , "supported", , "all limbs", i.e. "the whole body", and , "posture"," position", or "seat". The name Sarvangasana is modern, but similar inverted poses were in use in medieval hatha yoga as a mudra, Viparita Karani, which is documented in the 14th century '' Śiva Saṃhitā'' 4.45-47, the 15th century '' Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' 3.78-81, the 17th century '' Gheraṇḍa Saṃhitā'' 3.33-35, and other early texts such as the '' Dattātreyayogaśāstra''. The purpose of Viparita Karani had been to reverse the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverted Asanas
Inverse or invert may refer to: Science and mathematics * Inverse (logic), a type of conditional sentence which is an immediate inference made from another conditional sentence * Additive inverse, the inverse of a number that, when added to the original number, yields zero * Compositional inverse, a function that "reverses" another function * Inverse element * Inverse function, a function that "reverses" another function **Generalized inverse, a matrix that has some properties of the inverse matrix but not necessarily all of them * Multiplicative inverse (reciprocal), a number which when multiplied by a given number yields the multiplicative identity, 1 ** Inverse matrix of an Invertible matrix Other uses * Invert level, the base interior level of a pipe, trench or tunnel * ''Inverse'' (website), an online magazine * An outdated term for an LGBT person; see Sexual inversion (sexology) See also * Inversion (other) * Inverter (other) * Opposite (disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Iyengar Way
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Dipika
Yoga (UK: , US: ; 'yoga' ; ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated with its own philosophy in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as practiced in the Hindu, Jain, and Buddhist traditions. Yoga may have pre-Vedic origins, but is first attested in the early first millennium BCE. It developed as various traditions in the eastern Ganges basin drew from a common body of practices, including Vedic elements. Yoga-like practices are mentioned in the ''Rigveda'' and a number of early Upanishads, but systematic yoga concepts emerge during the fifth and sixth centuries BCE in ancient India's ascetic and Śramaṇa movements, including Jainism and Buddhism. The ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'', the classical text on Hindu yoga, samkhya-based but influenced by Buddhism, dates to the early centuries of the Common Era. Hatha yoga texts began to emerge between the ninth and 11th centuries, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |