|
Grevilleoideae
The Grevilleoideae are a subfamily of the plant family Proteaceae. Mainly restricted to the Southern Hemisphere, it contains around 46 genera and about 950 species. Genera include ''Banksia'', ''Grevillea'', and ''Macadamia''. Description The Grevilleoideae grow as trees, shrubs, or subshrubs. They are highly variable, making a simple, diagnostic identification key for the subfamily essentially impossible to provide. One common and fairly diagnostic characteristic is the occurrence of flowers in pairs that share a common bract. However, a few Grevilleoideae taxa do not have this property, having solitary flowers or inflorescences of unpaired flowers. In most taxa, the flowers occur in densely packed heads or spikes, and the fruit is a follicle. Distribution and habitat Grevilleoideae are mainly a Southern Hemisphere family. The main centre of diversity is Australia, with around 700 of 950 species occurring there, and South America also contains taxa. However, the Grevilleoidea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteoideae
Proteoideae is one of the five subfamilies of the plant family Proteaceae. The greatest diversity is in Africa, but there are also many species in Australia; a few species occur in South America, New Caledonia, and elsewhere. Taxonomy Proteoideae was essentially defined by Robert Brown in his 1810 ''On the natural order of plants called Proteaceae''. Brown divided Proteaceae into two "sections" based on whether or not the fruits were dehiscent or indehiscence. He also noted that Brown's two "sections" corresponded closely with what are now recognised as the two largest Proteaceae subfamilies, Proteoideae and Grevilleoideae, and both the indehiscence of Proteoideae and the paired flowers of Grevilleoideae are still recognised as key diagnostic characters. Brown did not publish names for his two sections, and it would not be until 1836 that the name Proteoideae would be published by Amos Eaton. The modern framework for classification of the genera within Proteaceae was laid by L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
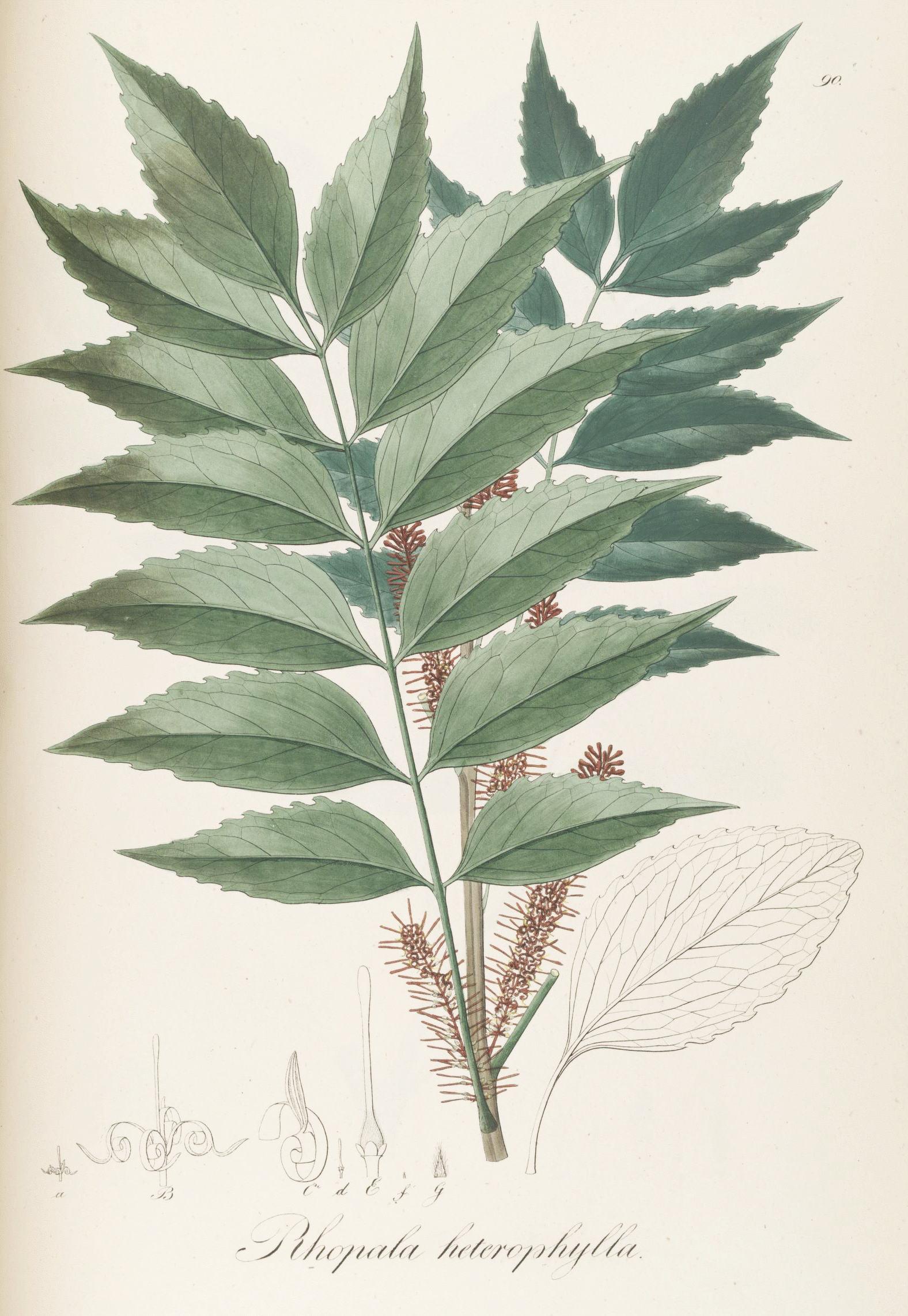
Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Proteales. Well-known genera include ''Protea'', ''Banksia'', ''Embothrium'', ''Grevillea'', ''Hakea'' and ''Macadamia''. Species such as the New South Wales waratah (''Telopea speciosissima''), king protea (''Protea cynaroides''), and various species of ''Banksia'', ''soman'', and ''Leucadendron'' are popular cut flowers. The nuts of ''Macadamia integrifolia'' are widely grown commercially and consumed, as are those of Gevuina avellana on a smaller scale. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentrations of diversity. Etymology The name Proteaceae was adapted by Robert Brown from the name Proteae coined in 1789 for the family by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, based on the genus ''Protea'', which in 1767 Carl Linnaeus derived from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia
''Banksia'' is a genus of around 170 species in the plant family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and fruiting "cones" and heads. ''Banksias'' range in size from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up to 30 metres (100 ft) tall. They are found in a wide variety of landscapes: sclerophyll forest, (occasionally) rainforest, shrubland, and some more arid landscapes, though not in Australia's deserts. Heavy producers of nectar, ''banksias'' are a vital part of the food chain in the Australian bush. They are an important food source for nectarivorous animals, including birds, bats, rats, possums, stingless bees and a host of invertebrates. Further, they are of economic importance to Australia's nursery and cut flower industries. However, these plants are threatened by a number of processes including land clearing, frequent burning and disease, and a number of species are rare and endangered. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brabejum Stellatifolium
''Brabejum'' is a genus of a single species of large evergreen tree, ''Brabejum stellatifolium'' in the family Proteaceae, commonly called wild almond, bitter almond or ghoeboontjie. It is restricted in the wild to South Africa's Western Cape province, where it grows in thickets along the banks of streams. The plant is of botanical interest as being Africa's only member of the large grevilleoid subfamily. It is a bushy small tree with branches widely at ground level and numerous erect vigorous stems. Leaves grow up to 6 in (15 cm) long, narrow and bluntly toothed, appear at intervals along the branches, mostly in whorls of 6. In summer, the plant bears white flowers densely crowded on spikes arising from rusty buds at the leaf axils. The fruits to 2 in (5 cm) long, magenta to reddish brown, similar to an almond, appear in autumn. The nut is too bitter to eat; however, in earlier times it was boiled, roasted, and ground to make a "coffee" drink. This tree has special sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed on the axis of a plant. The modifications can involve the length and the nature of the internodes and the phyllotaxis, as well as variations in the proportions, compressions, swellings, adnations, connations and reduction of main and secondary axes. One can also define an inflorescence as the reproductive portion of a plant that bears a cluster of flowers in a specific pattern. The stem holding the whole inflorescence is called a peduncle. The major axis (incorrectly referred to as the main stem) above the peduncle bearing the flowers or secondary branches is called the rachis. The stalk of each flower in the inflorescence is called a pedicel. A flower that is not part of an inflorescence is called a solitary flower and its stalk is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follicle (fruit)
In botany, a follicle is a dry unilocular fruit formed from one carpel, containing two or more seeds. It is usually defined as dehiscing by a suture in order to release seeds, for example in ''Consolida'' (some of the larkspurs), peony and milkweed (''Asclepias''). Some difficult cases exist however, so that the term indehiscent follicle is sometimes used, for example with the genus ''Filipendula'', which has indehiscent fruits that could be considered intermediate between a (dehiscent) follicle and an (indehiscent) achene. An aggregate fruit that consists of follicles may be called a follicetum. Examples include hellebore, aconite, ''Delphinium'', ''Aquilegia'' or the family Crassulaceae, where several follicles occur in a whorl on a shortened receptacle, or ''Magnolia'', which has many follicles arranged in a spiral on an elongated receptacle. The follicles of some species dehisce by the ventral suture (as in ''Banksia''), or by the dorsal suture (as in ''Magnolia'').Kapil, R. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Alexander Sidney Johnson
Lawrence Alexander Sidney Johnson FAA, (26 June 1925 – 1 August 1997) known as Lawrie Johnson, was an Australian taxonomic botanist. He worked at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Sydney, for the whole of his professional career, as a botanist (1948–1972), Director (1972–1985) and Honorary Research Associate (1986–1997). - originally published in ''Historical Records of Australian Science'', vol.13, no.4, 2001. Alone or in collaboration with colleagues, he distinguished and described four new families of vascular plants, 33 new genera, 286 new species (including posthumous publications), and reclassified another 395 species. Of the families he described, Rhynchocalycaceae (with B. G. Briggs, 1985) is accepted by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG). Hopkinsiaceae and Lyginiaceae, (which he and B. G. Briggs proposed in 2000 be carved out of Anarthriaceae), have not been accepted by the APG. Lawrie Johnson died of cancer in 1997. He received many honours and awards, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryandra Sessilis 2 Cape Naturaliste Email
''Banksia'' ser. ''Dryandra'' is a series of 94 species of shrub to small tree in the plant genus ''Banksia''. It was considered a separate genus named ''Dryandra'' until early 2007, when it was merged into ''Banksia'' on the basis of extensive molecular and morphological evidence that ''Banksia'' was paraphyletic with respect to ''Dryandra''. Taxonomy The dryandras were named in honour of Swedish botanist Jonas C. Dryander. The first specimens of a ''Dryandra'' were collected by Archibald Menzies, surgeon and naturalist to the Vancouver Expedition. At the request of Joseph Banks, Menzies collected natural history specimens wherever possible during the voyage. During September and October 1791, while the expedition were anchored at King George Sound, he collected numerous plant specimens, including the first specimens of '' B. sessilis'' (Parrotbush) and '' B. pellaeifolia''. Upon Menzies' return to England, he turned his specimens over to Banks; as with most other spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grevillia Banksii0
''Grevillea'', commonly known as spider flowers, is a genus of about 360 species of evergreen flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. Plants in the genus ''Grevillea'' are shrubs, rarely trees, with the leaves arranged alternately along the branches, the flowers zygomorphic, arranged in racemes at the ends of branchlets, and the fruit a follicle that splits down one side only, releasing one or two seeds. Description Plants in the genus ''Grevillea'' are shrubs, rarely small trees with simple or compound leaves arranged alternately along the branchlets. The flowers are zygomorphic and typically arranged in pairs along a sometimes branched raceme at the ends of branchlets. The flowers are bisexual, usually with four tepals in a single whorl. There are four stamens and the gynoecium has a single carpel. The fruit is a thin-walled follicle that splits down only one side, releasing one or two seeds before the next growing season. Taxonomy The genus ''Grevillea'' was first formall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomatia Silaifolia Email
''Lomatia'' is a genus of 12 species of evergreen flowering plants in the protea family Proteaceae. Within the family, they have been placed, alone, in their own subtribe, Lomatiinae according to Johnson & Briggs 1975 classification of the family and subsequently in ''Flora of Australia'' (1995). The genus has a Pacific Rim distribution, with members native to eastern Australia and southern South America, forming a part of the Antarctic flora. The species range from prostrate shrubs less than tall to small trees up to tall. Genetic analysis using microsatellite markers showed that species found close together geographically are most closely related to each other. ''Lomatia dentata'', then ''L. hirsuta'' and ''L. ferruginea'' all diverged successively from the lineage that gave rise to Australian species. The three Tasmanian species (with ''L. tasmanica'' sister to the other two species) are sister to the mainland Australian group. ''L. tasmanica'' of the three tasmania specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sten Sinuatus
The STEN (or Sten gun) is a family of British submachine guns chambered in 9×19mm which were used extensively by British and Commonwealth forces throughout World War II and the Korean War. They had a simple design and very low production cost, making them effective insurgency weapons for resistance groups, and they continue to see usage to this day by irregular military forces. The Sten served as the basis for the Sterling submachine gun, which replaced the Sten in British service until the 1990s, when it, and all other submachine guns, were replaced by the SA80. The Sten is a select fire, blowback-operated weapon which mounts its magazine on the left. Sten is an acronym, from the names of the weapon's chief designers, Major Reginald V. Shepherd and Harold J. Turpin, and "En" for the Enfield factory. Over four million Stens in various versions were made in the 1940s, making it the second most produced submachine gun of the Second World War, after the Soviet PPSh-41. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |