|
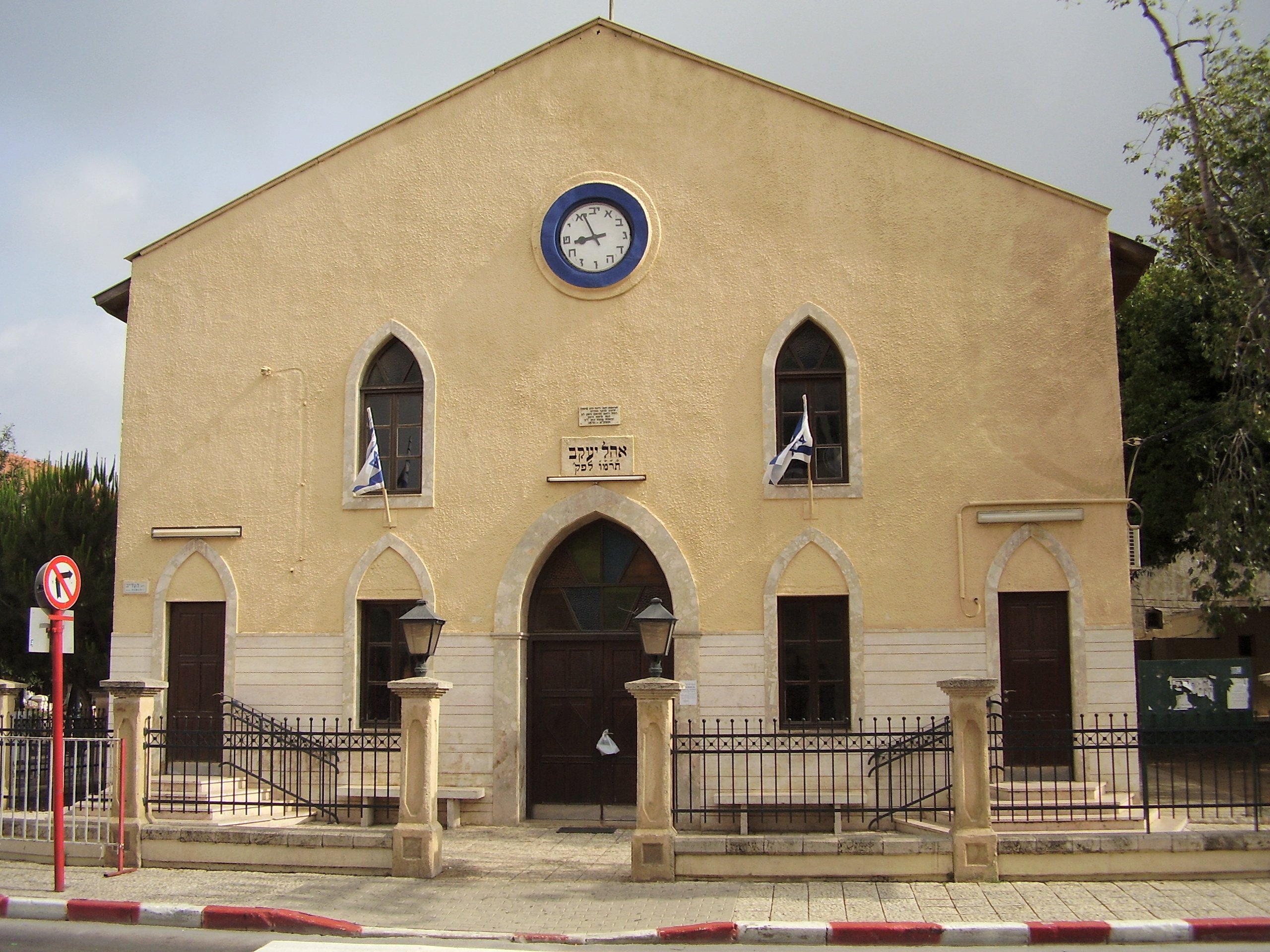
Great Synagogue (Petah Tikva)
The Great Synagogue of Petah Tikva, ( he, בית הכנסת הגדול בפתח תקוה), is the city's central synagogue and located on Hovevei Zion Street, in the centre of Petah Tikva, Israel. The building was designed by Daniel HaCohen Lifshitz, one of the pioneering residents of the city and is named after James Mayer de Rothschild, the father of the Baron Edmond James de Rothschild. History Construction of the Great Synagogue of Petah Tikva began in 1885 with a contribution from the Hovevei Zion movement. Edmond James de Rothschild donated the money needed to complete the building, which was named Beit Yaacov in honor of his father.Religious Renewal, Haaretz, November 22, 2019 The building includes a main sanctuary with overlooking women's section, as well as two smaller adjoining prayer rooms, and another room used for studying and praying. In the 1930s, a copper dome was added on the eastern facade. Six medallion images were painted between the arches of the central ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petah Tikva
Petah Tikva ( he, פֶּתַח תִּקְוָה, , ), also known as ''Em HaMoshavot'' (), is a city in the Central District of Israel, east of Tel Aviv. It was founded in 1878, mainly by Haredi Jews of the Old Yishuv, and became a permanent settlement in 1883 with the financial help of Baron Edmond de Rothschild. In , the city had a population of . Its population density is approximately . Its jurisdiction covers 35,868 dunams (~35.9 km2 or 15 sq mi). Petah Tikva is part of the Tel Aviv Metropolitan Area. Etymology Petah Tikva takes its name (meaning "Door of Hope") from the biblical allusion in Hosea 2:15: "... and make the valley of Achor a door of hope." The Achor Valley, near Jericho, was the original proposed location for the town. The city and its inhabitants are sometimes known by the nickname "Mlabes" after the Arab village preceding the town. (See "Ottoman era" under "History" below.) History Tell Mulabbis, an archaeological mound in modern Petah Tikva, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazzan
A ''hazzan'' (; , lit. Hazan) or ''chazzan'' ( he, חַזָּן , plural ; Yiddish ''khazn''; Ladino ''Hasan'') is a Jewish musician or precentor trained in the vocal arts who helps lead the congregation in songful prayer. In English, this prayer leader is often referred to as a cantor, a term also used in Christianity. ''Sh'liaḥ tzibbur'' and the evolution of the hazzan The person leading the congregation in public prayers is called the '' sh'liaḥ tzibbur'' (Hebrew for " emissary of the congregation"). Jewish law restricts this role to adult Jews; among Orthodox Jews, it is restricted to males. In theory, any lay person can be a ''sh'liaḥ tzibbur''; many synagogue-attending Jews will serve in this role from time to time, especially on weekdays or when having a Yartzeit. Someone with good Hebrew pronunciation is preferred. In practice, in synagogues without an official Hazzan, those with the best voice and the most knowledge of the prayers serve most often. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Central District (Israel)
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Petah Tikva
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory A factory, manufacturing plant or a production plant is an industrial facility, often a complex consisting of several buildings filled with machinery, where workers manufacture items or operate machines which process each item into another. ... (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, monument, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodox Synagogues In Israel
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to: Religion * Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-paganism or Hinduism Christian Traditional Christian denominations * Eastern Orthodox Church, the world's second largest Christian church, that accepts seven Ecumenical Councils *Oriental Orthodox Churches, a Christian communion that accepts three Ecumenical Councils Modern denominations * True Orthodox Churches, also called Old Calendarists, a movement that separated from the mainstream Eastern Orthodox Church in the 1920s over issues of ecumenism and calendar reform * Reformed Orthodoxy (16th–18th century), a systematized, institutionalized and codified Reformed theology * Neo-orthodoxy, a theological position also known as ''dialectical theology'' * Paleo-orthodoxy, (20th–21st century), a movement in the United States focusing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashkenazi Synagogues
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singular: , Modern Hebrew: are a Jewish diaspora population who coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. Their traditional diaspora language is Yiddish (a West Germanic language with Jewish linguistic elements, including the Hebrew alphabet), which developed during the Middle Ages after they had moved from Germany and France into Northern Europe and Eastern Europe. For centuries, Ashkenazim in Europe used Hebrew only as a sacred language until the revival of Hebrew as a common language in 20th-century Israel. Throughout their numerous centuries living in Europe, Ashkenazim have made many important contributions to its philosophy, scholarship, literature, art, music, and science. The rabbinical term '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashkenazi Jewish Culture In Israel
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singular: , Modern Hebrew: are a Jewish diaspora population who coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. Their traditional diaspora language is Yiddish (a West Germanic language with Jewish linguistic elements, including the Hebrew alphabet), which developed during the Middle Ages after they had moved from Germany and France into Northern Europe and Eastern Europe. For centuries, Ashkenazim in Europe used Hebrew only as a sacred language until the revival of Hebrew as a common language in 20th-century Israel. Throughout their numerous centuries living in Europe, Ashkenazim have made many important contributions to its philosophy, scholarship, literature, art, music, and science. The rabbinical term '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Of Israel
The architecture of Israel has been influenced by the different architectural styles of those who have inhabited the country over time, sometimes modified to suit the local climate and landscape. Byzantine churches, Crusader castles, Islamic madrasas, Templer houses, Arab arches and minarets, Russian Orthodox onion domes, International Style modernist buildings, sculptural concrete Brutalist architecture, and glass-sided skyscrapers all are part of the architecture of Israel. History Early period Ancient regional architecture can be divided into two phases based on building materials — stone and sundried mud brick. Most of the stones used were limestone. After the Hellenistic period, hard limestone was used for columns, capitals, bases or also the Herodian enclosure walls of the Temple Mount. In the north of the country, basalt was used for building stone, door sockets, door pivots but also for drainage. Fieldstone were placed randomly or laid in courses as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Synagogue (other)
Great Synagogue or Grand Synagogue may refer to; * Belz Great Synagogue, in Jerusalem, the second-largest synagogue in the world * Dohány Street Synagogue the Great Synagogue (''Nagy Zsinagóga'') of Budapest, Europe's largest and the world's fourth largest synagogue. * Great City Synagogue (Lviv), Ukraine * Great Synagogue of Europe, built Brussels in 1878, dedicated as the Synagogue of Europe in 2008 * Great Synagogue (Białystok), destroyed in 1941 * Great Synagogue (Bila Tserkva) * Great Synagogue (Constanța) * Great Synagogue (Copenhagen) * Great Synagogue (Danzig), destroyed in 1939 * Great Synagogue (Deventer) * Great Synagogue (Florence) * Great Synagogue (Gibraltar), oldest synagogue on the Iberian Peninsula * Great Synagogue (Grodno) * Great Synagogue (Iaşi) * Great Synagogue (Jasło), destroyed during World War lI * Great Synagogue (Jerusalem) * Great Synagogue (Katowice), destroyed in 1939 * Great Choral Synagogue (Kyiv) * Great Synagogue (Łódź), destroy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Israel
Religion in Israel is manifested primarily in Judaism, the ethnic religion of the Jewish people. The State of Israel declares itself as a " Jewish and democratic state" and is the only country in the world with a Jewish-majority population (see Jewish state). Other faiths in the country include Islam (predominantly Sunni), Christianity (mostly Melkite and Orthodox) and the religion of the Druze people. Religion plays a central role in national and civil life, and almost all Israeli citizens are automatically registered as members of the state's 14 official religious communities, which exercise control over several matters of personal status, especially marriage. These recognized communities are Orthodox Judaism (administered by the Chief Rabbinate), Islam, the Druze faith, the Roman, Armenian Catholic, Maronite, Greek Catholic, Syriac Catholic, Chaldean, Greek Orthodox, Syriac Orthodox, Armenian Apostolic and Anglican churches, and the Baháʼí Faith. The religious a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Synagogues In Israel
This is a list of notable synagogues in Israel. Only those that have Wikipedia entries are included here. Center District * Great Synagogue (Petah Tikva), Great Synagogue (Petah Tikva) * Yeshurun Central Synagogue (Gedera) Haifa District *Congregation Emet v'Shalom (Nahariya) *Ohel Ya'akov Synagogue (Zikhron Ya'akov) Jerusalem District North District *Abuhav synagogue (Safed) *Ari Ashkenazi Synagogue (Safed) *Old synagogues of Tiberias (Tiberias) *Or Torah Synagogue (Acre, Israel, Acre) *Peki'in Synagogue (Peki'in) *Al-Muallaq Mosque, Ramchal Synagogue (Akko, Acre) *Shfaram Ancient Synagogue (Shfaram) Tel Aviv District *Brit Olam Ono, (Kiryat Ono, on Ono Academic College campus) *Cymbalista Synagogue and Jewish Heritage Center, (Tel Aviv) *Great Synagogue (Tel Aviv), Great Synagogue (Tel Aviv) *Hechal Yehuda Synagogue (Tel Aviv) South District References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Synagogues In Israel Synagogues in Israel, Lists of religious buildings and structures i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Jerusalem Post
''The Jerusalem Post'' is a broadsheet newspaper based in Jerusalem, founded in 1932 during the British Mandate of Palestine by Gershon Agron as ''The Palestine Post''. In 1950, it changed its name to ''The Jerusalem Post''. In 2004, the paper was bought by Mirkaei Tikshoret, a diversified Israeli media firm controlled by investor Eli Azur. In April 2014, Azur acquired the newspaper ''Maariv''. The newspaper is published in English and previously also printed a French edition. Originally a left-wing newspaper, it underwent a noticeable shift to the political right in the late 1980s. From 2004 editor David Horovitz moved the paper to the center, and his successor in 2011, Steve Linde, pledged to provide balanced coverage of the news along with views from across the political spectrum. In April 2016, Linde stepped down as editor-in-chief and was replaced by Yaakov Katz, a former military reporter for the paper who previously served as an adviser to former Prime Minister Naftal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |