|
Grant County, Washington
Grant County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, the population was 99,123. The county seat is Ephrata, and the largest city is Moses Lake. The county was formed out of Douglas County in February 1909 and is named for U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant. Grant County comprises the Moses Lake, WA Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also part of the Moses Lake-Othello, WA Combined Statistical Area. History Native American cultures in the area included the Interior Salish, Wenatchi, and Okanagan. The first white settlers began to arrive in the mid-to-late-19th century, primarily with the goal of raising livestock. One government official described the area in 1879 as, "…a desolation where even the most hopeful can find nothing in its future prospects to cheer." When railroads arrived they also brought new settlers, and the economy began a shift from ranching to dryland farming. This transition required the people to have ready a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grant County Courthouse (Washington)
The Grant County Courthouse building is located in Ephrata, Washington and is the Administrative Center of Government for Grant County. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1975. with Construction The original courthouse was a two-story, wood-framed building, built shortly after Grant County was created in 1909. The wood building was constructed in 1909 (and the first courthouse of Grant County) by J. O. Cunningham of Wilson Creek for a bid of $4,975. The original courthouse, however, was of modest construction and quickly became outdated as Grant County grew, and due to the growth of the Grant County government, inadequate space for county personnel, the lack of archival storage, and safety concerns, a new courthouse building was necessary. The former courthouse was later transformed into a community Methodist church. Construction of a new Grant County Courthouse began late July 1917 with the purchase of two city blocks in downtown Ephrata. With plans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranch
A ranch (from es, rancho/Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of a farm. These terms are most often applied to livestock-raising operations in Mexico, the Western United States and Western Canada, though there are ranches in other areas.For terminologies in Australia and New Zealand, see Station (Australian agriculture) and Station (New Zealand agriculture). People who own or operate a ranch are called ranchers, cattlemen, or stockgrowers. Ranching is also a method used to raise less common livestock such as horses, elk, American bison, ostrich, emu, and alpaca.Holechek, J.L., Geli, H.M., Cibils, A.F. and Sawalhah, M.N., 2020. Climate Change, Rangelands, and Sustainability of Ranching in the Western United States. ''Sustainability'', ''12''(12), p.4942. Ranches generally consist of large areas, but may be of nearly any size. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Coulee Dam
Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerhouses. The third powerhouse ("Nat"), completed in 1974 to increase energy production, makes Grand Coulee the largest power station in the United States by nameplate-capacity at 6,809 MW. The proposal to build the dam was the focus of a bitter debate during the 1920s between two groups. One group wanted to irrigate the ancient Grand Coulee with a gravity canal while the other pursued a high dam and pumping scheme. The dam supporters won in 1933, but, although they fully intended otherwise, the initial proposal by the Bureau of Reclamation was for a "low dam" tall which would generate electricity without supporting irrigation. That year, the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation and a consortium of three companies called MWAK (Mason-Walsh-Atkinson K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia Basin Project
The Columbia Basin Project (or CBP) in Central Washington, United States, is the irrigation network that the Grand Coulee Dam makes possible. It is the largest water reclamation project in the United States, supplying irrigation water to over of the large project area, all of which was originally intended to be supplied and is still classified irrigable and open for the possible enlargement of the system. Water pumped from the Columbia River is carried over of main canals, stored in a number of reservoirs, then fed into of lateral irrigation canals, and out into of drains and wasteways. The Grand Coulee Dam, powerplant, and various other parts of the CBP are operated by the Bureau of Reclamation. There are three irrigation districts (the Quincy-Columbia Basin Irrigation District, the East Columbia Basin Irrigation District, and the South Columbia Basin Irrigation District) in the project area, which operate additional local facilities. History The U.S. Bureau of Reclama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington State Legislature
The Washington State Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a bicameral body, composed of the lower Washington House of Representatives, composed of 98 Representatives, and the upper Washington State Senate, with 49 Senators plus the Lieutenant Governor acting as president. The state is divided into 49 legislative districts, each of which elect one senator and two representatives. The State Legislature meets in the Legislative Building at the Washington State Capitol in Olympia. As of January 2021, Democrats control both houses of the Washington State Legislature. Democrats hold a 57-41 majority in the House of Representatives and a 28-21 majority in the Senate (with one Democratic senator caucusing with the 20 Republicans). History The Washington State Legislature traces its ancestry to the creation of the Washington Territory in 1853, following successful arguments from settlers north of the Columbia River to the U.S. federal govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quincy, Washington
Quincy is a city in Grant County, Washington, United States. The population was 7,543 at the 2020 census. History Geologic history Quincy lies atop a part of the Columbia River Basalt Group which is overlain by Pleistocene outburst flood deposits. The Missoula Floods had one of their outlets at Trinidad, close to Quincy and another near Ancient Lakes, which includes the Ancient Lakes of the Columbia Valley AVA. Glacial erratics carried from as far away as Montana can be found nearby. The area also has an abundance of rimrock. Great Northern Railway Quincy was founded as a railroad camp during construction of the Great Northern Railway in 1892, and was incorporated on March 27, 1907. It was named after Quincy, Illinois. Grand Coulee Dam The arrival of the water from the Grand Coulee Dam in 1952 changed the town. Geography Quincy is located at (47.233691, −119.852296). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which, is land and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson Creek, Washington
Wilson Creek is a town in Grant County, Washington, United States. The population was 204 at the 2020 census. History The area around Crab and Wilson creeks were inhabited by Native American peoples until the arrival of settlers in the late 19th century. John Marlin and the Urquhart Brothers established their homes in the area in 1870s and were followed by a military road connecting Fort Walla Walla to Camp Chelan that passed near the area. A railroad was built through the area in 1892. Wilson Creek was platted in 1903 and officially incorporated on May 8, 1903. When Grant County was created in 1909, Wilson Creek was its largest town with around 600 people. The town grew little, however, and by the mid-20th century had been surpassed by Ephrata and Quincy. Despite the slowing of growth, Wilson Creek established a port district in March 1960. The Port of Wilson Creek is home to an airport, which was renovated in 1984 and again in the 2000s when updates were made to the runw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigability
A body of water, such as a river, canal or lake, is navigable if it is deep, wide and calm enough for a water vessel (e.g. boats) to pass safely. Such a navigable water is called a ''waterway'', and is preferably with few obstructions against direct traverse that needed avoiding, such as rocks, reefs or trees. Bridges built over waterways must have sufficient clearance. High flow speed may make a channel unnavigable due to risk of ship collisions. Waters may be unnavigable because of ice, particularly in winter or high-latitude regions. Navigability also depends on context: a small river may be navigable by smaller craft such as a motorboat or a kayak, but unnavigable by a larger freighter or cruise ship. Shallow rivers may be made navigable by the installation of locks that regulate flow and increase upstream water level, or by dredging that deepens parts of the stream bed. Inland water transport systems Inland Water Transport (IWT) Systems have been used for centurie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. It flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state of Oregon before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The river is long, and its largest tributary is the Snake River. Its drainage basin is roughly the size of France and extends into seven US states and a Canadian province. The fourth-largest river in the United States by volume, the Columbia has the greatest flow of any North American river entering the Pacific. The Columbia has the 36th greatest discharge of any river in the world. The Columbia and its tributaries have been central to the region's culture and economy for thousands of years. They have been used for transportation sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
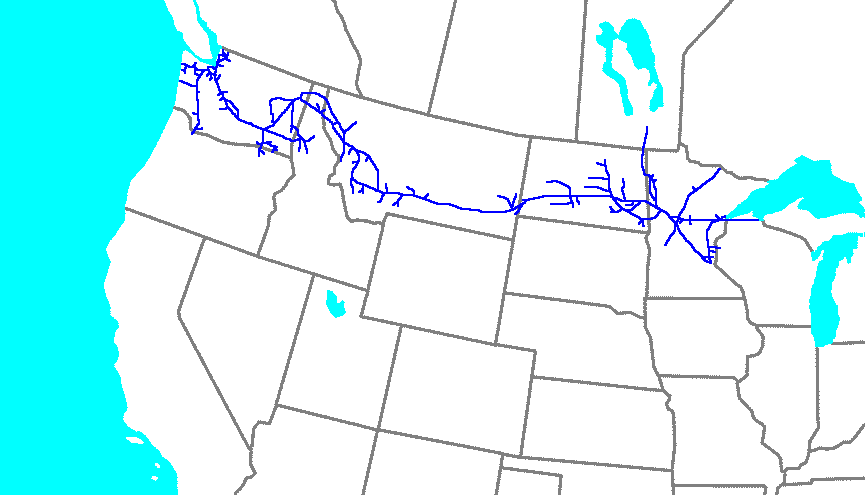
Northern Pacific Railroad
The Northern Pacific Railway was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest. It was approved by Congress in 1864 and given nearly of land grants, which it used to raise money in Europe for construction. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former President Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in western Montana on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about of track and served a large area, including extensive trackage in the states of Idaho, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin. In addition, the NP had an international branch to Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The main activities were shipping wheat and other farm products, cattle, timber, and minerals; bringing in consumer goods, transporting passengers; and selling land. The Northern Pacific was headquartered in Minnesota, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)