|
Goethe (crater)
Goethe Basin is an impact basin at 81.4° N, 54.3° W on Mercury approximately 317 kilometers in diameter. It is named after German poet Johann Wolfgang von Goethe. Description Goethe was not listed as an impact basin by Wood and Head because they considered the '' Mariner 10'' photography too poor to confirm basin structures. However, most workers, beginning with Murray and others, have identified it as a basin. Goethe is bounded on its north and east sides by a gently sloping wall and discontinuous, low, hummocky rim material that may consist of ejecta deposits. These materials are similar to those occurring around the Caloris Basin in the Tolstoj quadrangle. On its west side, Goethe is bounded by at least three subparallel ridges or tilted blocks, which are separated by narrow troughs partly filled with smooth plains material. If an inner concentric ring ever existed, it is buried under the smooth plains material that now extends across the basin. A narrow, concentric s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Wolfgang Von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as treatises on botany, anatomy, and colour. He is widely regarded as the greatest and most influential writer in the German language, his work having a profound and wide-ranging influence on Western literary, political, and philosophical thought from the late 18th century to the present day.. Goethe took up residence in Weimar in November 1775 following the success of his first novel, ''The Sorrows of Young Werther'' (1774). He was ennobled by the Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Karl August, in 1782. Goethe was an early participant in the ''Sturm und Drang'' literary movement. During his first ten years in Weimar, Goethe became a member of the Duke's privy council (1776–1785), sat on the war and highway commissions, oversaw the reopening of silver min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facies
In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or condition of formation), and the changes that may occur in those attributes over a geographic area. A facies encompasses all of the characteristics of a rock including its chemical, physical, and biological features that distinguish it from adjacent rock. The term facies was introduced by the Swiss geologist Amanz Gressly in 1838 and was part of his significant contribution to the foundations of modern stratigraphy, which replaced the earlier notions of Neptunism. Types of facies Sedimentary facies Ideally, a Sedimentary structures, sedimentary facies is a distinctive rock unit that forms under certain conditions of sedimentation, reflecting a particular process or environment. Sedimentary facies are either descriptive or interpretative. Sedimentary facies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
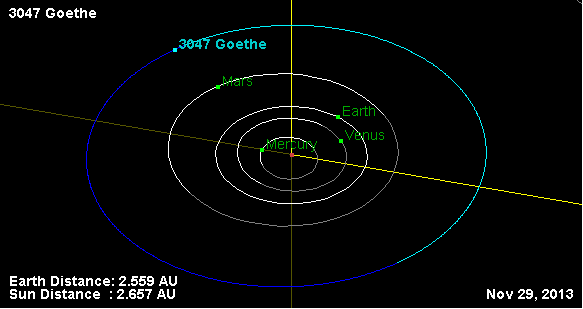
3047 Goethe
3047 Goethe, provisional designation , is a bright background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 24 September 1960, by Dutch astronomer couple Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten on photographic plates taken by Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The asteroid was named after German poet Johann Wolfgang von Goethe. Orbit and classification ''Goethe'' is a non-family asteroid of the main belt's background population. It orbits the Sun in the central asteroid belt at a distance of 2.6–2.7 AU once every 4 years and 3 months (1,569 days; semi-major axis of 2.64 AU). Its orbit has a low eccentricity of 0.03 and a low inclination of 2 ° with respect to the ecliptic. The body's observation arc begins with its official discovery observation at Palomar in September 1960. In May 2156, it will pass at from the asteroid 29 Amphitrite at a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laxness (crater)
Laxness is a crater on Mercury, located near the north pole. It was named by the IAU in 2013, after Iceland Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...ic writer Halldór Laxness. S band radar data from the Arecibo Observatory collected between 1999 and 2005 indicates a radar-bright area along the southern interior of Laxness, which is probably indicative of a water ice deposit, and lies within the permanently shadowed part of the crater.Chabot, N. L., D. J. Lawrence, G. A. Neumann, W. C. Feldman, and D. A. Paige, 2018. Mercury's Polar Deposits. In ''Mercury: The View After MESSENGER'' edited by Sean C. Solomon, Larry R. Nittler, and Brian J. Anderson. Cambridge Planetary Science. Chapter 13, Figure 13.2. Fuller crater is southeast of Laxness. Both lie in the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuller (crater)
Fuller is a crater on Mercury, located near the north pole. It was named by the IAU in 2013, after American engineer and architect Richard Buckminster Fuller Richard Buckminster Fuller (; July 12, 1895 – July 1, 1983) was an American people, American architect, systems theorist, writer, designer, inventor, philosopher, and futurist. He styled his name as R. Buckminster Fuller in his writings, .... S band radar data from the Arecibo Observatory collected between 1999 and 2005 indicates a radar-bright area along the southern interior of Fuller, which is probably indicative of a water ice deposit, and lies within the permanently shadowed part of the crater.Chabot, N. L., D. J. Lawrence, G. A. Neumann, W. C. Feldman, and D. A. Paige, 2018. Mercury's Polar Deposits. In ''Mercury: The View After MESSENGER'' edited by Sean C. Solomon, Larry R. Nittler, and Brian J. Anderson. Cambridge Planetary Science. Chapter 13, Figure 13.2. Laxness crater is northwest of Full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angelou (crater)
Angelou is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 18 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on September 11, 2019. Angelou is named for the American poet and author Maya Angelou. Angelou lies on the west side of the much larger Goethe Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as tr ... crater. References Impact craters on Mercury Maya Angelou {{Mercury-planet-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghost Crater
A palimpsest , in planetary astronomy, is an ancient crater that has been degraded over time. They may also be referred to as "ghost craters", "degraded craters", "buried craters", or "pathological craters". Palimpsests have been identified on Mercury, the Earth, the Moon, Mars, Ganymede, Callisto, and possibly even Titan. On Mars, these features are morphologically described as craters that are "flat-floored, rimless, extremely shallow, without central peaks, and would probably represent what remains after erosion." On an icy moon of the outer Solar System, a palimpsest is a crater whose relief has disappeared due to creep of the icy surface ("viscous relaxation") or subsequent cryovolcanic outpourings, leaving a circular albedo feature, perhaps with a "ghost" of a rim. Icy surfaces of natural satellites like Callisto Callisto most commonly refers to: *Callisto (mythology), a nymph *Callisto (moon), a moon of Jupiter Callisto may also refer to: Art and entertainment *''Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Despréz (crater)
Despréz is a crater on Mercury with a diameter of 47.05 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ... (IAU) in 1979. Despréz is named for the French composer Josquin des Prez, who lived from 1440 to 1521. Despréz has a region of permanent shadow along its southern rim, which has a bright radar signature. This is interpreted to represent a deposit of water ice.John K. Harmon, Martin A. Slade, Melissa S. Rice, 2011. Radar imagery of Mercury’s putative polar ice: 1999–2005 Arecibo results. ''Icarus'', 211, p37-50doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2010.08.007/ref> References Impact craters on Mercury Crater {{Mercury-planet-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Mosaic
In the field of photographic imaging, a photographic mosaic, also known under the term Photomosaic, is a picture (usually a photograph) that has been divided into (usually equal sized) tiled sections, each of which is replaced with another photograph that matches the target photo.Cartwright (2007) p.102 quote: Photographic mosaic, also known as Photomosaic, a portmanteau of photo and mosaic, is a picture that is divided into small sections. When viewed as a whole, it appears to be one image, when in fact the image is made up of hundreds or even thousands of smaller images. When viewed at low magnifications, the individual pixels appear as the primary image, while close examination reveals that the image is in fact made up of many hundreds or thousands of smaller images. Most of the time they are a computer-created type of montage. There are two kinds of mosaic, depending on how the matching is done. In the simpler kind, each part of the target image is averaged down to a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massif
In geology, a massif ( or ) is a section of a planet's crust that is demarcated by faults or flexures. In the movement of the crust, a massif tends to retain its internal structure while being displaced as a whole. The term also refers to a group of mountains formed by such a structure. In mountaineering and climbing literature, a massif is frequently used to denote the main mass of an individual mountain. The massif is a smaller structural unit of the crust than a tectonic plate, and is considered the fourth-largest driving force in geomorphology. The word is taken from French (in which the word also means "massive"), where it is used to refer a large mountain mass or compact group of connected mountains forming an independent portion of a range. One of the most notable European examples of a massif is the Massif Central of the Auvergne region of France. The Face on Mars is an example of an extraterrestrial massif. Massifs may also form underwater, as with the Atlanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goethe Basin Topography PIA15536
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as treatises on botany, anatomy, and colour. He is widely regarded as the greatest and most influential writer in the German language, his work having a profound and wide-ranging influence on Western literary, political, and philosophical thought from the late 18th century to the present day.. Goethe took up residence in Weimar in November 1775 following the success of his first novel, ''The Sorrows of Young Werther'' (1774). He was ennobled by the Duke of Saxe-Weimar, Karl August, in 1782. Goethe was an early participant in the ''Sturm und Drang'' literary movement. During his first ten years in Weimar, Goethe became a member of the Duke's privy council (1776–1785), sat on the war and highway commissions, oversaw the reopening of silver min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolstoj Quadrangle
The Tolstoj quadrangle in the equatorial region of Mercury runs from 144 to 216° longitude and -25 to 25° latitude. It was provisionally called "Tir", but renamed after Leo Tolstoy by the International Astronomical Union in 1976. Also called Phaethontias. It contains the southern part of Caloris Planitia, which is the largest and best preserved basin seen by ''Mariner 10''. This basin, about 1550 km in diameter, is surrounded by a discontinuous annulus of ejecta deposits of the Caloris Group that are embayed and covered by broad expanses of smooth plains. The southeast half of the quadrangle is dominated by ancient crater deposits, by nondescript rolling to hummocky plains materials between individual craters, and by isolated patches of nondescript plains. The ancient and degraded Tolstoj multiring basin, about 350 km in diameter, is in the south-central part of the quadrangle. The large, well-preserved crater Mozart (285 km diameter) is a prominent feature in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |