|
Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota (often referred to as glomeromycetes, as they include only one class, Glomeromycetes) are one of eight currently recognized divisions within the kingdom Fungi, with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromycota form arbuscular mycorrhizas (AMs) with the thalli of bryophytes and the roots of vascular land plants. Not all species have been shown to form AMs, and one, ''Geosiphon pyriformis'', is known not to do so. Instead, it forms an endocytobiotic association with ''Nostoc'' cyanobacteria. The majority of evidence shows that the Glomeromycota are dependent on land plants (''Nostoc'' in the case of ''Geosiphon'') for carbon and energy, but there is recent circumstantial evidence that some species may be able to lead an independent existence. The arbuscular mycorrhizal species are terrestrial and widely distributed in soils worldwide where they form symbioses with the roots of the majority of plant species (>80%). They can also be found in wetla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
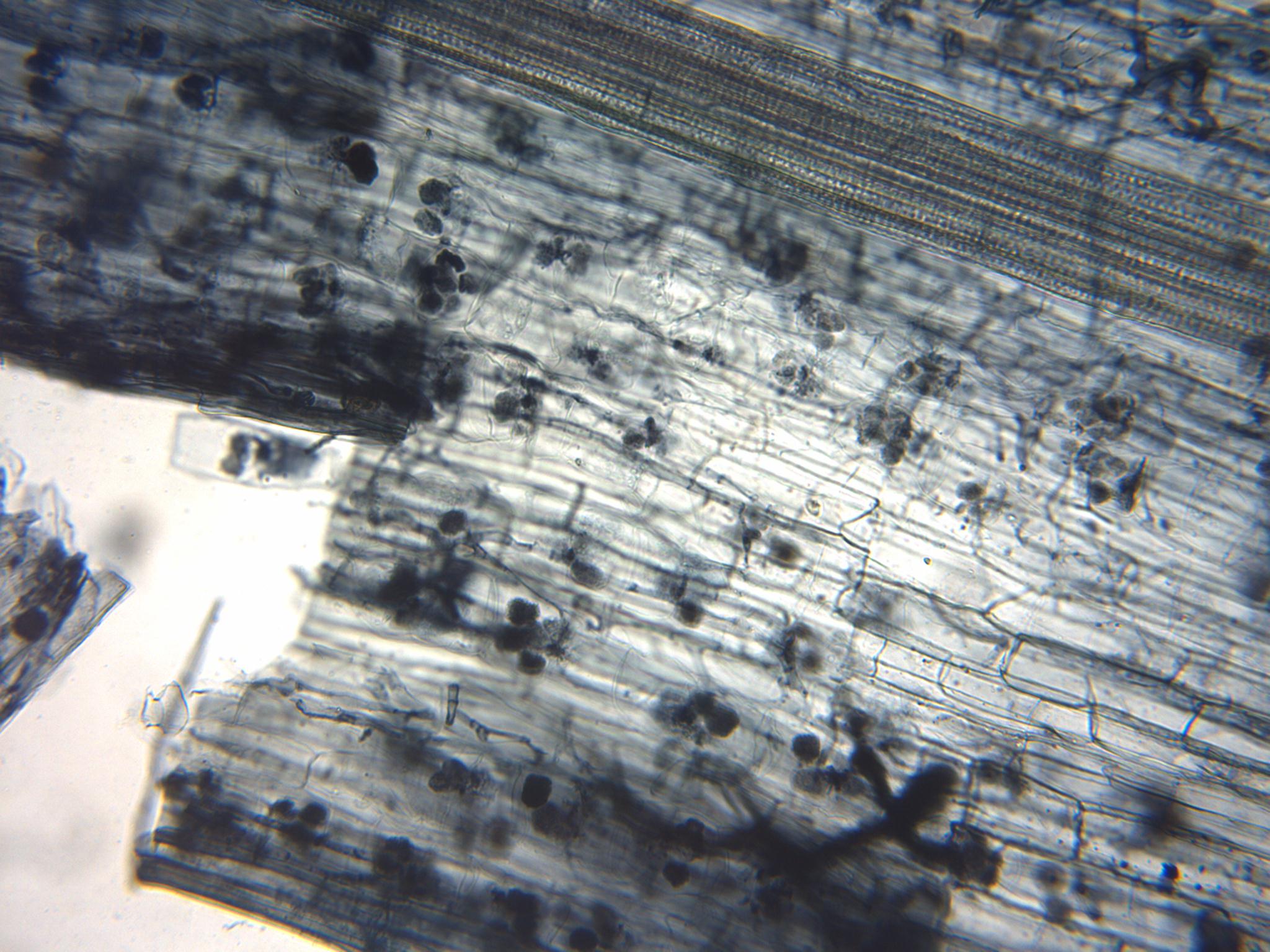
Arbuscular Mycorrhiza
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'', a.k.a. ''endomycorrhiza'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''AM fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (Not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza or ericoid mycorrhiza.) Arbuscular mycorrhizae are characterized by the formation of unique structures, arbuscules and vesicles, by Glomeromycota and Mucoromycota, sister clades of the more well-known and diverse dikaryan fungi (all three are together called "symbiomycota"). AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis played a crucial role in the initial colonisation of land by plants and in the evolution of the vascular plants. It has been said that it is quicker to list the plants that do not form endomycorrhizae than those that do. This symbiosis is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosiphon
''Geosiphon'' is a genus of fungus in the family Geosiphonaceae. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species ''Geosiphon pyriformis'', first described by Kützing in 1849 as ''Botrydium pyriforme''. In 1915, Von Wettstein characterized ''Geosiphon pyriforme'' as a multinucleate alga containing endosymbiotic cyanobacteria, although he also noted the presence of chitin, a component of fungal cell walls. In 1933, Knapp was the first to suggest the fungal origin of the species and described it as a lichen with endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. It is the only member of the Glomeromycota known to not form a symbiosis with terrestrial plants in the form of arbuscular mycorrhiza. Life cycle ''Geosiphon pyriformis'' is known for being the symbiont of ''Nostoc''. The ''Geosiphon''-''Nostoc'' symbiosis, as by modern definitions, is not a lichen, since it is an intracellular association. Also, by functional and evolutionary implications it is more comparable to the arbuscular mycorrhiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeosporales
Archaeosporales is an order of fungi best known as arbuscular mycorrhiza to vascular land plants (Tracheophyta). But also form free living endocyte symbioses with cyanobacteria. The free living forms have a Precambrian fossil record back 2.2 Ga, well before evolution of Tracheophyta Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They a .... References Glomeromycota Fungus orders {{fungus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diversisporales
The ''Diversisporales'' are an order of generally hypogeous (underground) arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi within the division Glomeromycota. Many have vesicles for energy storage, or auxiliary cells. Species In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ... produce a wide range of spore types, hence the name. References Fungus orders {{glomeromycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomerales
Glomerales is an order of symbiotic fungi within the phylum Glomeromycota. Biology These fungi are all biotrophic mutualists. Most employ the arbuscular mycorrhizal method of nutrient exchange with plants. They produce large (.1-.5mm) spores (azygospores and chlamydospores) with thousands of nuclei. Phylogeny All members of their phylum were once thought to be related to the Endogonaceae, but have been found through molecular sequencing data, to be a closer relation to the Dikarya. Their fossil record extends back to the Ordovician period (460 million years ago). Orthography The family name Glomeraceae upon which this order level name is based, was incorrectly spelled 'Glomaceae', hence the order name was incorrectly spelled 'Glomales'. Both are correctable errors, to Glomeraceae and Glomerales, as governed by the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature. The incorrect spellings are commonplace in the literature, unfortunately. See also * Glomalin Glomalin is a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraglomerales
The Paraglomerales are a group of exclusively hypogeous (underground) arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ... that rarely produce vesicles and reproduce through unpigmented spores. It includes the species '' Paraglomus brasilianum'', '' Paraglomus laccatum'', and '' Paraglomus occultum''. References Glomeromycota[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomus (fungus)
''Glomus'' is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, and all species form symbiotic relationships (mycorrhizae) with plant roots. ''Glomus'' is the largest genus of AM fungi, with ''ca.'' 85 species described, but is currently defined as non-monophyletic. Classification ''Glomus'' is one of the genera in the family Glomeraceae, in the division Glomeromycota. Some members of the genus were originally described as ''Sclerocystis'' species, but this genus has been entirely transferred to ''Glomus''. However, further taxonomic changes are likely as the phylogeny of AM fungi becomes better understood. ''Glomus'' is likely related to the fossil fungus '' Glomites'', discovered in the Rhynie chert deposits from the Early Devonian (400 million years ago). Ecology As with other AM fungi, all ''Glomus'' species are thought to be obligate symbionts, dependent on their mycorrhizal association with plant roots to complete their life cycle. They cannot be cultured in the laboratory i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division (mycology)
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about 8 phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships between phyla, which are contained in larger clades, like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguished them as a group ("a self-contained unity") ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucoromycota
Mucoromycota is a division within the kingdom fungi. They include a diverse group of various molds, including the common bread molds ''Mucor'' and ''Rhizopus''. It is a sister phylum to Dikarya. It consists of mainly mycorrhizal fungi, root endophytes, and plant decomposers; Glomeromycotina, Mortierellomycotina, and Mucoromycotina. Informally known as zygomycetes I, Mucoromycota includes Mucoromycotina, Mortierellomycotina, and Glomeromycotina. Mucoromycotina and Glomeromycotina can form mycorrhiza-like relationships with nonvascular plants. Mucoromycota contain multiple mycorrhizal lineages, root endophytes, and decomposers of plant-based carbon sources. Mucoromycotina species known as mycoparasites, or putative parasites of arthropods are like saprobes. When Mucoromycota infect animals, they are seen as opportunistic pathogens. Mucoromycotina are fast growing fungi and early colonizers of carbon rich substrates. Mortierellomycotina are common soil fungi that occur as root ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenocyte
A coenocyte () is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without their accompanying cytokinesis, in contrast to a syncytium, which results from cellular aggregation followed by dissolution of the cell membranes inside the mass. The word syncytium in animal embryology is used to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm of invertebrates. A coenocytic colony is referred to as a coenobium (plural coenobia), and most coenobia are composed of a distinct number of cells, often as a multiple of two (4, 8, etc.). Research suggests that coenobium formation may be a defense against grazing in some species. Physiological examples Protists Diplomonads, like '' Giardia'', have two nuclei. Ciliates have cells that contain two nuclei: a macronucleus and a micronucleus. The schizont of apicomplexan parasites is a form of a coenocyte (i.e. a plasmodium in the general sense) as well as the plasmodia of microsporidian (Fungi) and myxosporidian (Metazoa) parasites. The tro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |