|
Geoglossaceae
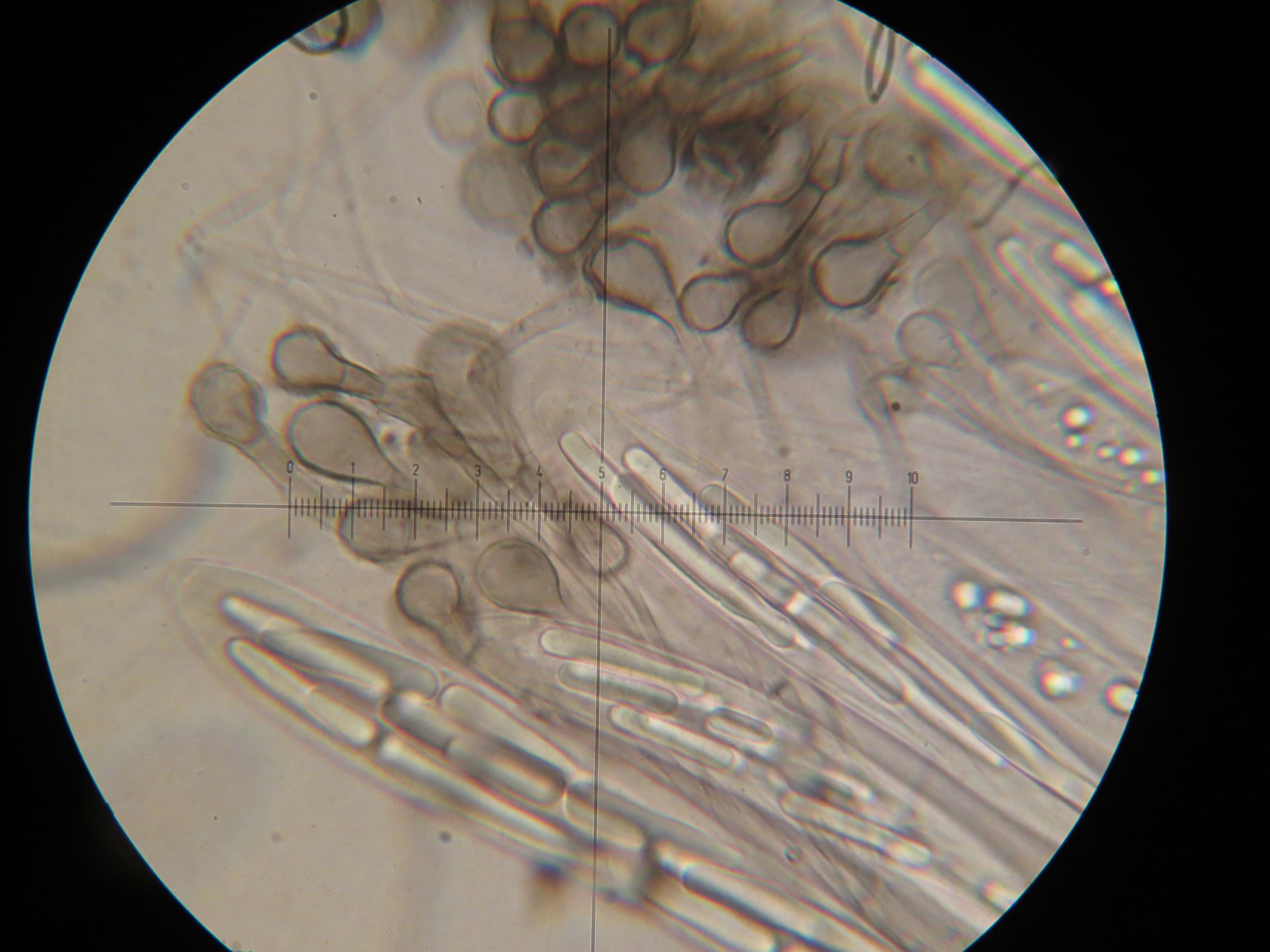
Geoglossaceae is a family of fungi in the order Geoglossales, class Geoglossomycetes. These fungi are broadly known as earth tongues. The ascocarps of most species in the family Geoglossaceae are terrestrial and are generally small, dark in color, and club-shaped with a height of 2–8 cm. The ascospores are typically light-brown to dark-brown and are often multiseptate. Other species of fungi have been known to parasitize ascocarps. The use of a compound microscope is needed for accurate identification."Family: Geoglossaceae." The Hidden Forest. 26 Aug. 2009 . Systematics The fungi that are now included in the fungal class Geoglossomycetes were previously considered by mycologists to be a family (Geoglossaceae) within the class Leotiomycetes. The family Geoglossaceae ''sensu lato'' was previously defined with 6 genera and 48 species. Early molecular evidence using ribosomal DNA suggested that Geoglossaceae ''sensu lato'' was not a monophyletic group, and that the hyalin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoglossum Umbratile
''Geoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called earth tongues. The type species is ''Geoglossum glabrum''. ''Geoglossum'' species are distinguished from the related genus '' Trichoglossum'' by the lack of setae on the spore bearing surface. ''Geoglossum'' species are characterized by dark, club-shaped, terrestrial ascocarps with a fertile hymenium continuing downward from the apex of the ascocarp along the stipe, eventually intergrading with a sterile stipe. The ascospores of ''Geoglossum'' range from translucent to dark brown, and are fusiform, and multiseptate. Identification of species is based on the gross morphology of the ascocarp, color and septation of the ascospores, and shape and ornamentation of the paraphyses. Taxonomy ''Geoglossum'' was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1794, who created the genus to accommodate ''Clavaria ophioglossoides'' L. and three other species: ''Geoglossum hirsutum'' (now ''Trichoglos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoglossum Sphagnophilum
''Geoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called earth tongues. The type species is '' Geoglossum glabrum''. ''Geoglossum'' species are distinguished from the related genus '' Trichoglossum'' by the lack of setae on the spore bearing surface. ''Geoglossum'' species are characterized by dark, club-shaped, terrestrial ascocarps with a fertile hymenium continuing downward from the apex of the ascocarp along the stipe, eventually intergrading with a sterile stipe. The ascospores of ''Geoglossum'' range from translucent to dark brown, and are fusiform, and multiseptate. Identification of species is based on the gross morphology of the ascocarp, color and septation of the ascospores, and shape and ornamentation of the paraphyses. Taxonomy ''Geoglossum'' was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1794, who created the genus to accommodate ''Clavaria ophioglossoides'' L. and three other species: ''Geoglossum hirsutum'' (now ''Trichoglo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoglossum
''Geoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called earth tongues. The type species is ''Geoglossum glabrum''. ''Geoglossum'' species are distinguished from the related genus ''Trichoglossum'' by the lack of setae on the spore bearing surface. ''Geoglossum'' species are characterized by dark, club-shaped, terrestrial ascocarps with a fertile hymenium continuing downward from the apex of the ascocarp along the stipe, eventually intergrading with a sterile stipe. The ascospores of ''Geoglossum'' range from translucent to dark brown, and are fusiform, and multiseptate. Identification of species is based on the gross morphology of the ascocarp, color and septation of the ascospores, and shape and ornamentation of the paraphyses. Taxonomy ''Geoglossum'' was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1794, who created the genus to accommodate ''Clavaria ophioglossoides'' L. and three other species: ''Geoglossum hirsutum'' (now ''Trichogloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoglossum Barlae
''Geoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called earth tongues. The type species is ''Geoglossum glabrum''. ''Geoglossum'' species are distinguished from the related genus ''Trichoglossum'' by the lack of setae on the spore bearing surface. ''Geoglossum'' species are characterized by dark, club-shaped, terrestrial ascocarps with a fertile hymenium continuing downward from the apex of the ascocarp along the stipe, eventually intergrading with a sterile stipe. The ascospores of ''Geoglossum'' range from translucent to dark brown, and are fusiform, and multiseptate. Identification of species is based on the gross morphology of the ascocarp, color and septation of the ascospores, and shape and ornamentation of the paraphyses. Taxonomy ''Geoglossum'' was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1794, who created the genus to accommodate ''Clavaria ophioglossoides'' L. and three other species: ''Geoglossum hirsutum'' (now ''Trichogloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoglossum Simile
''Geoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called earth tongues. The type species is '' Geoglossum glabrum''. ''Geoglossum'' species are distinguished from the related genus '' Trichoglossum'' by the lack of setae on the spore bearing surface. ''Geoglossum'' species are characterized by dark, club-shaped, terrestrial ascocarps with a fertile hymenium continuing downward from the apex of the ascocarp along the stipe, eventually intergrading with a sterile stipe. The ascospores of ''Geoglossum'' range from translucent to dark brown, and are fusiform, and multiseptate. Identification of species is based on the gross morphology of the ascocarp, color and septation of the ascospores, and shape and ornamentation of the paraphyses. Taxonomy ''Geoglossum'' was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1794, who created the genus to accommodate ''Clavaria ophioglossoides'' L. and three other species: ''Geoglossum hirsutum'' (now ''Trichoglo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoglossum Glabrum
''Geoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called earth tongues. The type species is '' Geoglossum glabrum''. ''Geoglossum'' species are distinguished from the related genus '' Trichoglossum'' by the lack of setae on the spore bearing surface. ''Geoglossum'' species are characterized by dark, club-shaped, terrestrial ascocarps with a fertile hymenium continuing downward from the apex of the ascocarp along the stipe, eventually intergrading with a sterile stipe. The ascospores of ''Geoglossum'' range from translucent to dark brown, and are fusiform, and multiseptate. Identification of species is based on the gross morphology of the ascocarp, color and septation of the ascospores, and shape and ornamentation of the paraphyses. Taxonomy ''Geoglossum'' was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1794, who created the genus to accommodate ''Clavaria ophioglossoides'' L. and three other species: ''Geoglossum hirsutum'' (now ''Trichoglo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoglossum Nigritum
''Geoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called earth tongues. The type species is ''Geoglossum glabrum''. ''Geoglossum'' species are distinguished from the related genus ''Trichoglossum'' by the lack of setae on the spore bearing surface. ''Geoglossum'' species are characterized by dark, club-shaped, terrestrial ascocarps with a fertile hymenium continuing downward from the apex of the ascocarp along the stipe, eventually intergrading with a sterile stipe. The ascospores of ''Geoglossum'' range from translucent to dark brown, and are fusiform, and multiseptate. Identification of species is based on the gross morphology of the ascocarp, color and septation of the ascospores, and shape and ornamentation of the paraphyses. Taxonomy ''Geoglossum'' was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1794, who created the genus to accommodate ''Clavaria ophioglossoides'' L. and three other species: ''Geoglossum hirsutum'' (now ''Trichogloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichoglossum Octopartitum
''Trichoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called hairy earth tongues. The type species is ''Trichoglossum hirsutum''. Members of the genus ''Trichoglossum'' have tiny hairs known as setae on the spore bearing surface. The related genus ''Geoglossum'' lacks hairs on the spore bearing surface. History The genus ''Trichoglossum'' was created by Émile Boudier, who constructed the new genus to include species of ''Geoglossum'' bearing prominent setae. Numerous authors have examined this genus since its creation, with many new species and varieties described. Index Fungorum ''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names (scientific names) in the fungus kingdom. the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and the Institute of M ... currently lists 47 names, including forms and varieties, while Kirk et al. (2008) acknowledge 19 species. Publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichoglossum
''Trichoglossum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Geoglossaceae. They are commonly called hairy earth tongues. The type species is ''Trichoglossum hirsutum''. Members of the genus ''Trichoglossum'' have tiny hairs known as setae on the spore bearing surface. The related genus '' Geoglossum'' lacks hairs on the spore bearing surface. History The genus ''Trichoglossum'' was created by Émile Boudier, who constructed the new genus to include species of ''Geoglossum'' bearing prominent setae. Numerous authors have examined this genus since its creation, with many new species and varieties described. Index Fungorum ''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names (scientific names) in the fungus kingdom. the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and the Institute of M ... currently lists 47 names, including forms and varieties, while Kirk et al. (2008) acknowledge 19 species. Publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutinoglossum Glutinosum
''Glutinoglossum glutinosum'', commonly known as the viscid black earth tongue or the glutinous earthtongue, is a species of fungus in the family Geoglossaceae (the earth tongues). Widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere, it has been found in northern Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Although previously thought to exist in Australasia, collections made from these locations have since been referred to new species. ''G. glutinosum'' is a saprophytic species that grows on soil in moss or in grassy areas. The smooth, nearly black, club-shaped fruitbodies grow to heights ranging from . The head is up to long, and the stipes are sticky. Several other black earth tongue species are quite similar in external appearance, and many can be reliably distinguished only by examining differences in microscopic characteristics, such as spores, asci, and paraphyses. First described in 1796 as a species of '' Geoglossum'', the fungus has gone through several changes of gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoleotia
''Sarcoleotia'' is a genus of fungi in the earth tongue family Geoglossaceae. There is no known common name. History The genus was first described by Japanese mycologists Seiya Ito and Sanshi Imai in 1934, who separated ''Sarcoleotia'' from ''Leotia'' Pers. based on the fleshy, non-gelatinous ascocarps and subcylindrical ascospores. ''Sarcoleotia nigra'' was described as the type species in the same publication from collections made in Hokkaido, Japan. Maas Geesteranus created ''S. platypus'' by transferring ''Helvella platypus'' DC. into the genus. Korf transferred ''Mitrula globosa'' to the genus in 1971, creating ''S. globosa''. Dennis transferred ''Coryne turficola'' to the genus in 1971. Lastly, Rahm reported "Sarcoleotia clandestina" from Switzerland in 1975, but this name is regarded as '' nomen nudum'' as no valid description of the species exists. Some debate exists over the accepted number of species in ''Sarcoleotia''. Maas Geesteranus considered ''S. nigra'' a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothomitra
''Nothomitra'' is a genus of fungi in the earth tongue family Geoglossaceae. There is no known common name. ''Nothomitra'' is morphologically distinguished from ''Microglossum'' in that the fertile hymenium in ''Nothomitra'' is not flattened as in ''Microglossum''. Furthermore, the hymenium in ''Nothomitra'' is distinctly free at the junction of the stipe, unlike in ''Microglossum'' in which the hymenium is flattened and gradually intergrades with the stipe. History The genus was first circumscribed by Dutch mycologist Rudolph Arnold Maas Geesteranus from specimens collected in Upper Austria in autumn 1964. Two additional species were later described: '' Nothomitra kovalii'' was described by Ain Raitviir in 1971Raitviir A. 1971. The Geoglossaceae of the Far East, 52–83. In: Plants and Animals of the Far East (ed. E Parmasto). Valgus, Tallinn. from Kunashir in the Kuril Islands, and '' Nothomitra sinensis'' was described by Zhuang and Wang in 1997 from China. The placement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |