|
GPHS-RTG
GPHS-RTG or general-purpose heat source — radioisotope thermoelectric generator, is a specific design of the radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) used on US space missions. The GPHS-RTG was used on ''Ulysses'' (1), ''Galileo'' (2), '' Cassini-Huygens'' (3), and '' New Horizons'' (1). The GPHS-RTG has an overall diameter of 0.422 m and a length of 1.14 m. Each GPHS-RTG has a mass of about 57 kg and generates about 300 watts of electrical power at the start of mission (5.2 We/kg), using about 7.8 kg of Pu-238 which produces about 4,400 watts of thermal power.G. L. BennettSpace Nuclear Power: Opening the Final Frontier AIAA 2006-4191, 4th International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference and Exhibit (IECEC), 26–29 June 2006, San Diego, California The plutonium oxide fuel is in 18 GPHSs. Note that the GPHS are cuboid although they contain cylindrical plutonium based pellets. The GPHS-RTG units used on spacecraft were not created by NASA. They were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator
A radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG, RITEG), sometimes referred to as a radioisotope power system (RPS), is a type of nuclear battery that uses an array of thermocouples to convert the heat released by the decay of a suitable radioactive material into electricity by the Seebeck effect. This type of generator has no moving parts. RTGs have been used as power sources in satellites, space probes, and uncrewed remote facilities such as a series of lighthouses built by the Soviet Union inside the Arctic Circle. RTGs are usually the most desirable power source for unmaintained situations that need a few hundred watts (or less) of power for durations too long for fuel cells, batteries, or generators to provide economically, and in places where solar cells are not practical. Safe use of RTGs requires containment of the radioisotopes long after the productive life of the unit. The expense of RTGs tends to limit their use to niche applications in rare or special situations. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Power In Space
Nuclear power in space is the use of nuclear power in outer space, typically either small fission systems or radioactive decay for electricity or heat. Another use is for scientific observation, as in a Mössbauer spectrometer. The most common type is a radioisotope thermoelectric generator, which has been used on many space probes and on crewed lunar missions. Small fission reactors for Earth observation satellites, such as the TOPAZ nuclear reactor, have also been flown. A radioisotope heater unit is powered by radioactive decay and can keep components from becoming too cold to function, potentially over a span of decades. The United States tested the SNAP-10A nuclear reactor in space for 43 days in 1965, with the next test of a nuclear reactor power system intended for space use occurring on 13 September 2012 with the Demonstration Using Flattop Fission (DUFF) test of the Kilopower reactor. After a ground-based test of the experimental 1965 Romashka reactor, which used u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Probe
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by , during STS-34. ''Galileo'' arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory built the ''Galileo'' spacecraft and managed the ''Galileo'' program for NASA. West Germany Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm supplied the propulsion module. NASA's Ames Research Center managed the atmospheric probe, which was built by Hughes Aircraft Company. At launch, the orbiter and probe together had a mass of and stood tall. Spacecraft are normally stabilized either by spinning around a fixed axis or by maintaining a fixed orientation with reference to the Sun and a star. ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator
The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for NASA space missions such as the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Energy's Office of Space and Defense Power Systems within the Office of Nuclear Energy. The MMRTG was developed by an industry team of Aerojet Rocketdyne and Teledyne Energy Systems. Background Space exploration missions require safe, reliable, long-lived power systems to provide electricity and heat to spacecraft and their science instruments. A uniquely capable source of power is the radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – essentially a nuclear battery that reliably converts heat into electricity. Radioisotope power has been used on eight Earth orbiting missions, eight missions to the outer planets, and the Apollo missions after Apollo 11 to the Moon. The outer Solar System missions are the ''Pioneer 10'' and ''11'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectric Materials
Thermoelectric materials show the thermoelectric effect in a strong or convenient form. The ''thermoelectric effect'' refers to phenomena by which either a temperature difference creates an electric potential or an electric current creates a temperature difference. These phenomena are known more specifically as the Seebeck effect (creating a voltage from temperature difference), Peltier effect (driving heat flow with an electric current), and Thomson effect (reversible heating or cooling within a conductor when there is both an electric current and a temperature gradient). While all materials have a nonzero thermoelectric effect, in most materials it is too small to be useful. However, low-cost materials that have a sufficiently strong thermoelectric effect (and other required properties) are also considered for applications including power generation and refrigeration. The most commonly used thermoelectric material is based on bismuth telluride (). Thermoelectric materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), with a team led by Alan Stern, the spacecraft was launched in 2006 with the primary mission to perform a flyby study of the Pluto system in 2015, and a secondary mission to fly by and study one or more other Kuiper belt objects (KBOs) in the decade to follow, which became a mission to 486958 Arrokoth. It is the fifth space probe to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System. On January 19, 2006, ''New Horizons'' was launched from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station by an Atlas V rocket directly into an Earth-and-solar escape trajectory with a speed of about . It was the fastest (average speed with respect to Earth) man-made object ever launched from Earth. It is not the fastest speed recorded for a spacecraft, which as of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
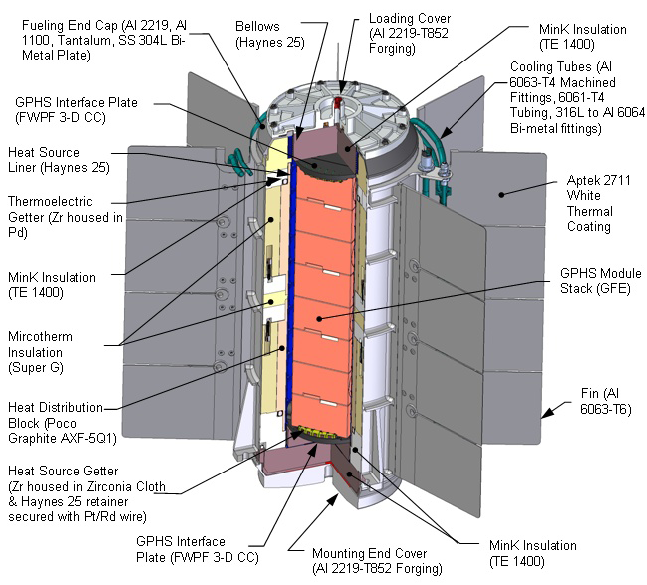
General Purpose Heat Source
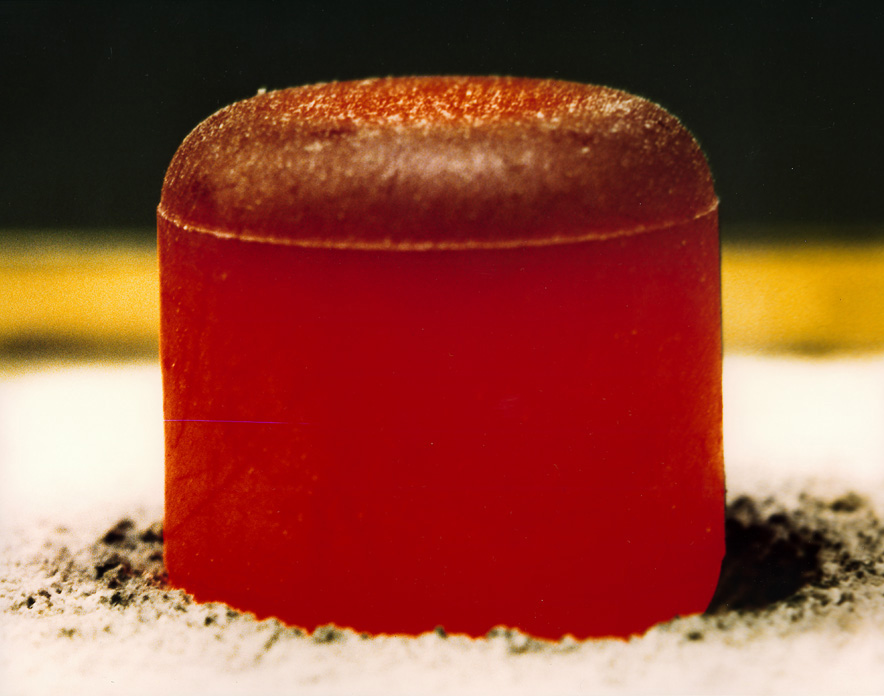
The general-purpose heat source is a U.S. DOE-designed radioactive heat source for radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTG) or Stirling radioisotope generators (SRG). It is meant for space applications and is packaged as a stackable module. Characteristics GPHSs are fueled with plutonium-238 dioxide. Each module has a temperature of over 600 degrees Celsius and delivers 250 watts at the time of manufacture. They measure 9.948 cm wide x 9.32 cm deep x 5.82 cm high and weigh no more than 1.44 kg each. Safety GPHSs are designed with safety in mind and employ iridium-clad plutonium-238 dioxide pellets. The generated alpha particles are blocked by the cladding, thus no further radiation shielding is necessary. The pellets are encased within nested layers of carbon-based material and placed within an aeroshell housing to comprise the complete module. The modules can withstand extreme conditions including a launch-pad explosion or a high-speed reentry. Overheati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General-purpose Heat Source
The general-purpose heat source is a U.S. DOE-designed radioactive heat source for radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTG) or Stirling radioisotope generators (SRG). It is meant for space applications and is packaged as a stackable module. Characteristics GPHSs are fueled with plutonium-238 dioxide. Each module has a temperature of over 600 degrees Celsius and delivers 250 watts at the time of manufacture. They measure 9.948 cm wide x 9.32 cm deep x 5.82 cm high and weigh no more than 1.44 kg each. Safety GPHSs are designed with safety in mind and employ iridium-clad plutonium-238 dioxide pellets. The generated alpha particles are blocked by the cladding, thus no further radiation shielding is necessary. The pellets are encased within nested layers of carbon-based material and placed within an aeroshell housing to comprise the complete module. The modules can withstand extreme conditions including a launch-pad explosion or a high-speed reentry. Overheati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulysses Probe
''Ulysses'' ( , ) was a robotic space probe whose primary mission was to orbit the Sun and study it at all latitudes. It was launched in 1990 and made three "fast latitude scans" of the Sun in 1994/1995, 2000/2001, and 2007/2008. In addition, the probe studied several comets. ''Ulysses'' was a joint venture of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), under leadership of ESA with participation from Canada's National Research Council. The last day for mission operations on ''Ulysses'' was 30 June 2009. To study the Sun at all latitudes, the probe needed to change its orbital inclination and leave the plane of the Solar System. To change the orbital inclination of a spacecraft to about 80° requires a large change in heliocentric velocity, the energy to achieve which far exceeded the capabilities of any launch vehicle. To reach the desired orbit around the Sun, the mission's planners chose a gravity assist ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium-238
Plutonium-238 (238Pu or Pu-238) is a fissile, radioactive isotope of plutonium that has a half-life of 87.7 years. Plutonium-238 is a very powerful alpha emitter; as alpha particles are easily blocked, this makes the plutonium-238 isotope suitable for usage in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) and radioisotope heater units. The density of plutonium-238 at room temperature is about 19.8 g/cc. The material will generate about 0.57 watts/gram of 238Pu. The bare sphere critical mass of metallic plutonium-238 is not precisely known, but its calculated range is between 9.04 and 10.07 kilograms. History Initial production Plutonium-238 was the first isotope of plutonium to be discovered. It was synthesized by Glenn Seaborg and associates in December 1940 by bombarding uranium-238 with deuterons, creating neptunium-238. The subsequent decay via β− decay creates Plutonium-238. + → + 2 The neptunium isotope then undergoes β− decay to plutoniu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |