|
Göksu River
The Göksu River (), known in classical antiquity, antiquity as the Calycadnus and in the Middle Ages as the Saleph, is a river on the Taşeli, Taşeli Plateau in southern Turkey. Its two sources arise in the Taurus Mountains—the northern in the Geyik Mountains and the southern in the Haydar Mountains—and meet south of Mut (District), Mersin, Mut. The combined stream then flows south to the Göksu Delta in the Mediterranean Sea near Silifke. Names is Turkish language, Turkish for "Sky Water". It is also known as the Geuk Su. It was known to the ancient Greeks as the ''Kalýkadnos'' (), latinization of names, latinized as the . It was known in the Middle Ages as the . Course The river is 260 km long and empties into the Mediterranean Sea 16 km southeast of Silifke (in Mersin province). The Göksu Delta, including Akgöl Lake and Paradeniz, Paradeniz Lagoon, is one of the most important breeding areas in the Near East; over 300 bird species have been observed. Amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silifke Castle
Silifke Castle () is a medieval castle in Turkey. Geography The castle is in Silifke district of Mersin Province. It is situated to the west of Silifke city center, to the south of Göksu River (''Calydanus'' of the antiquity) and to the north of the Turkish state highway D.715. Although its altitude is only with respect to sea level, it is dominant over Silifke plains and the southern section of Göksu valley. History Silifke (Roman: ''Seleucia''; Byzantine: ''kastron Seleukeias''; Arab: ''Salûqiya''; Armenian: ''Selefkia'' or ''Selewkia''; Frankish: ''Le Selef'') was an important city in antiquity. Founded by and named after Seleucus I Nicator (359 BC-281 BC), one of the Diadochi who served as an infantry general under Alexander the Great. Few traces of the 3rd-century-B.C. settlement survive. There are fragments of a late Roman theater, necropolis, bath, 2nd-century temple, as well as a 5th-century Byzantines cistern. The 1st-century-A.D. stone bridge built during the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
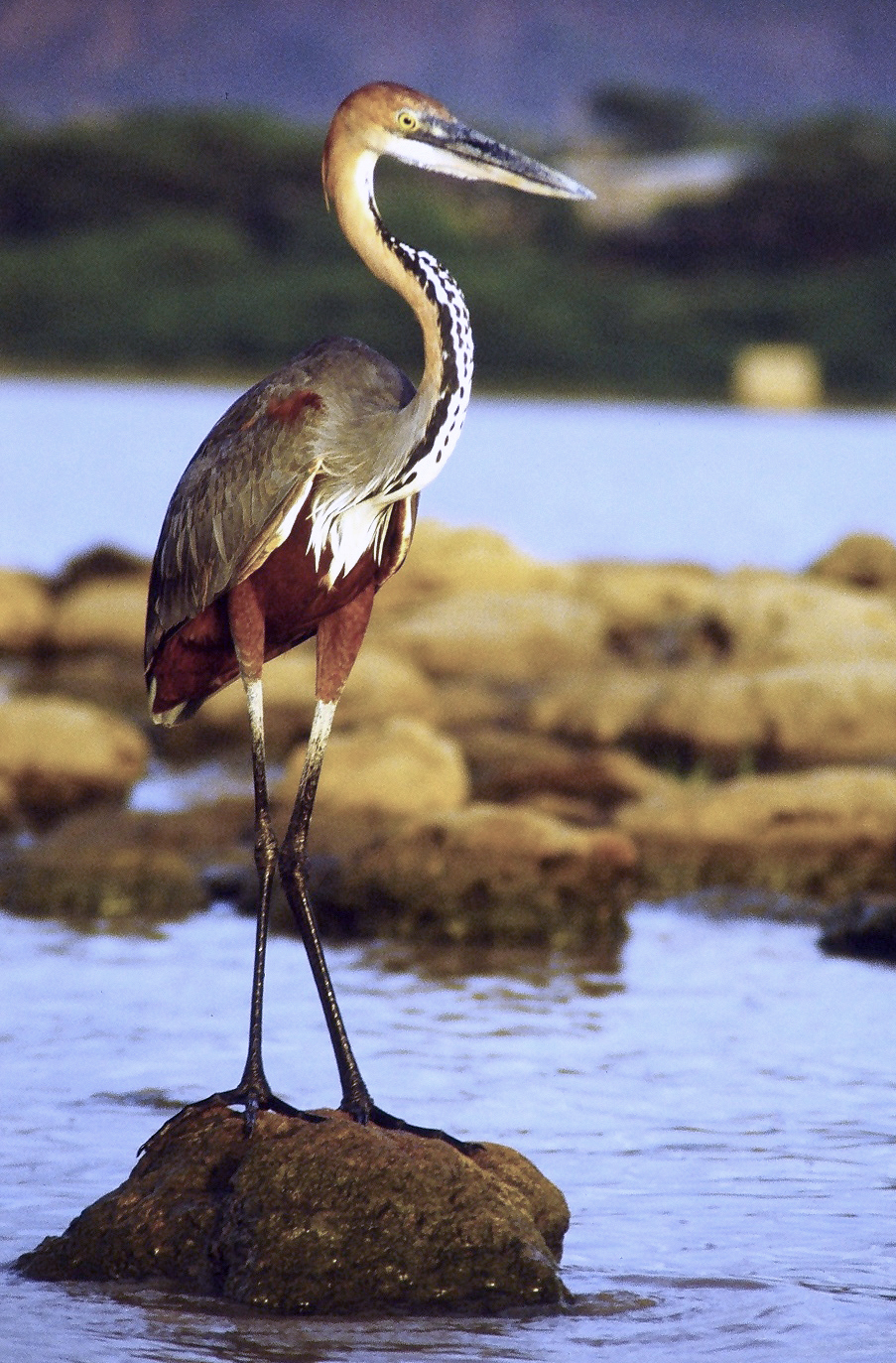
Heron
Herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 75 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genus ''Botaurus'' are referred to as bitterns, and, together with the zigzag heron, or zigzag bittern, in the monotypic genus ''Zebrilus'', form a monophyletic group within the Ardeidae. Egrets do not form a biologically distinct group from herons, and tend to be named differently because they are mainly white or have decorative plumes in breeding plumage. Herons, by evolutionary adaptation, have long beaks. The classification of the individual heron/egret species is fraught with difficulty, and no clear consensus exists about the correct placement of many species into either of the two major genera, ''Ardea (genus), Ardea'' and ''Egretta''. Similarly, the relationships of the genus, genera in the family are not completely resolved. However, one species formerly considered to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Christianity
Early Christianity, otherwise called the Early Church or Paleo-Christianity, describes the History of Christianity, historical era of the Christianity, Christian religion up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325. Spread of Christianity, Christianity spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish diaspora throughout the Eastern Mediterranean. The first followers of Christianity were Jews who had Proselyte, converted to the faith, i.e. Jewish Christians, as well as Phoenicia, Phoenicians, i.e. Christianity in Lebanon, Lebanese Christians. Early Christianity contains the Apostolic Age and is followed by, and substantially overlaps with, the Patristic era. The Apostolic sees claim to have been founded by one or more of the Apostles in the New Testament, apostles of Jesus, who are said to have Dispersion of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
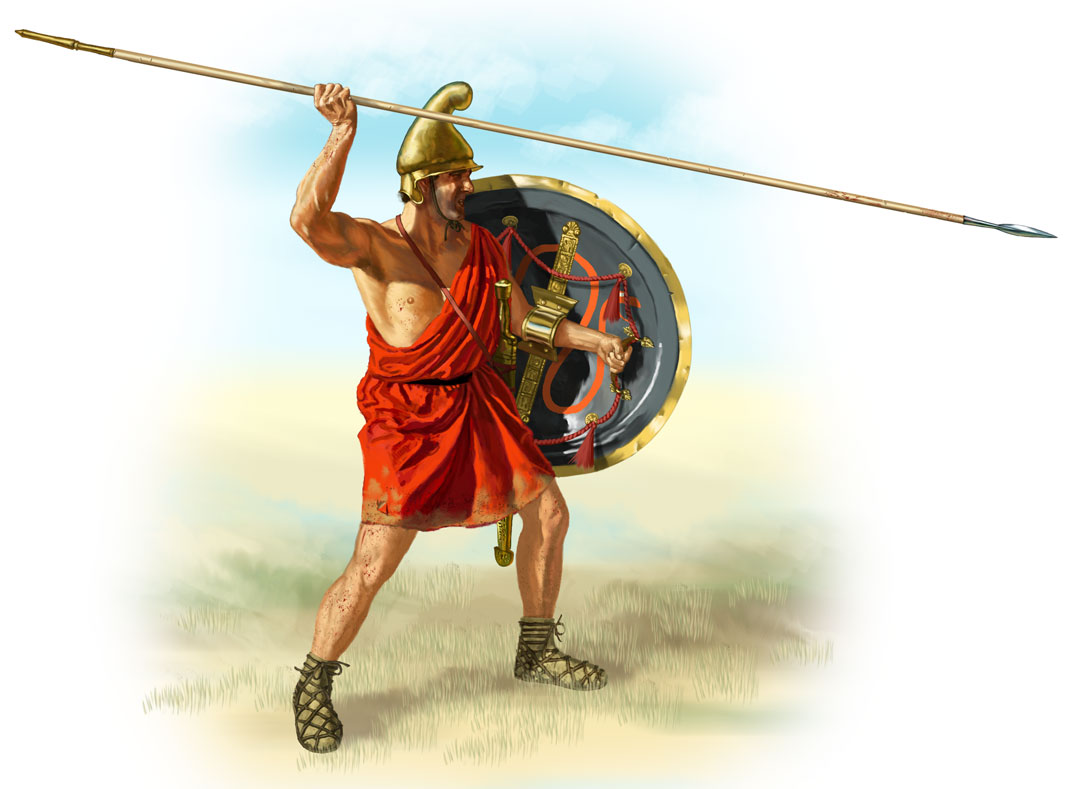
Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the eponymous Seleucid Empire, led by the Seleucid dynasty. Initially a secondary player in the power struggles following Alexander's death, Seleucus rose to become the total ruler of Asia Minor, Syria (region), Syria, Mesopotamia, and the Iranian plateau, assuming the title of ''basileus'' (king). The Seleucid Empire was one of the major powers of the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic world, until it was overcome by the Roman Republic and Parthian Empire in the late second and early first centuries BC. While serving under Alexander, Seleucus was commander of the ''Hypaspists, Hypaspistai,'' an elite Macedonian infantry unit. After the death of Alexander in June 323 BC, Seleucus initially supported Perdiccas, the regent of Alexander's em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucia Ad Calycadnum
Silifke is a municipality and district of Mersin Province, Turkey. Its area is 2,692 km2, and its population is 132,665 (2022). It is west of the city of Mersin, on the west end of the Çukurova plain. Silifke lies on the Göksu River, the ancient Calycadnus, near its outlet into the Mediterranean. The river flows from the nearby Taurus Mountains and the city is surrounded by attractive countryside along its banks. Names Turkish () derives from Greek ''Seléfkeia'' (, ), the late medieval and modern form of ancient Greek ''Seleúkeia'' (; ), named for its founder Seleucus I Nicator, king of the Seleucid Empire. It was distinguished from the many other places of that name as Seleucia on the Calycadnus (), Seleucia in Cilicia, Seleucia in Isauria, Seleucia Trachea, and Seleucia Tracheotis. The site of the ancient city of Olba () is also within the boundaries of modern-day Silifke. History Antiquity Located a few miles from the mouth of the Göksu River, Seleucia wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilician Pirates
Cilician pirates dominated the Mediterranean Sea from the 2nd century BC until their suppression by Pompey in 67–66 BC. Because there were notorious pirate strongholds in Cilicia, on the southern coast of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), the term "Cilician" was long used to generically refer to any pirates in the Mediterranean. Rise of piracy With the destruction of Carthage, the demise of the Seleucid Empire, and Ptolemaic Egypt on the wane, there was no strong naval power left in the Mediterranean. Rome was the only major Mediterranean power left, but, being land-based, it had a reduced navy at that time and relied on hiring ships as needed. Rome protected the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic seas, on account of their proximity, with expeditions sent against the pirate bases on the Ligurian and Illyrian coast. As a result, the pirates became consolidated and organized. The smaller communities of the Greek and African waters were left to make their own arrangements. Communities unable t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holmi
Holmi or Holmoi (), or Holmia, also possibly called Hermia, was a Greek town of Cilicia Tracheia with a harbor, a little to the south-west of Seleucia ad Calycadnum. When Seleucia ad Calycadnum was founded, the inhabitants of Holmi migrated there. Its site is located near Taşucu Taşucu is a neighbourhood in the municipality and district of Silifke, Mersin Province, Turkey. Its population is 15,184 (2022). Before the 2013 reorganisation, it was a town (''belde''). It had obtained the status of ''belde'' after the local el ... in Asiatic Turkey. References Populated places in ancient Cilicia Former populated places in Turkey History of Mersin Province Greek colonies in Anatolia {{Mersin-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Colonization
Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of Archaic Greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries BC, across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea. The Archaic expansion differed from the Iron Age migrations of the Greek Dark Ages, in that it consisted of organised direction (see ) away from the originating ''metropolis'' rather than the simplistic movement of tribes, which characterised the aforementioned earlier migrations. Many colonies, or (, ), that were founded during this period eventually evolved into strong Greek city-states, functioning independently of their ''metropolis''. Motives Greek colonisation was typically motivated by a combination of factors, depending on the context. Many Greek city-states experienced strong economic growth with consequent overpopulation of the motherland, such that the existing territory of these Greek city-states could no longer support a growing polity. The areas where the Greeks would try to colonise were hospitable a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionian Greeks
The Ionians (; , ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the traditional four major tribes of Ancient Greece, alongside the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaeans. The Ionian dialect was one of the three major linguistic divisions of the Hellenic world, together with the Dorian and Aeolian dialects. When referring to populations, "''Ionian''" defines several groups in Classical Greece. In its narrowest sense, the term referred to the region of Ionia in Asia Minor. In a broader sense, it could be used to describe all speakers of the Ionic dialect, which in addition to those in Ionia proper also included the Greek populations of Euboea, the Cyclades, and many cities founded by Ionian colonists. Finally, in the broadest sense it could be used to describe all those who spoke languages of the East Greek group, which included Attic. The foundation myth which was current in the Classical period suggested that the Ionians were named after Ion, son of Xuthus, who lived in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
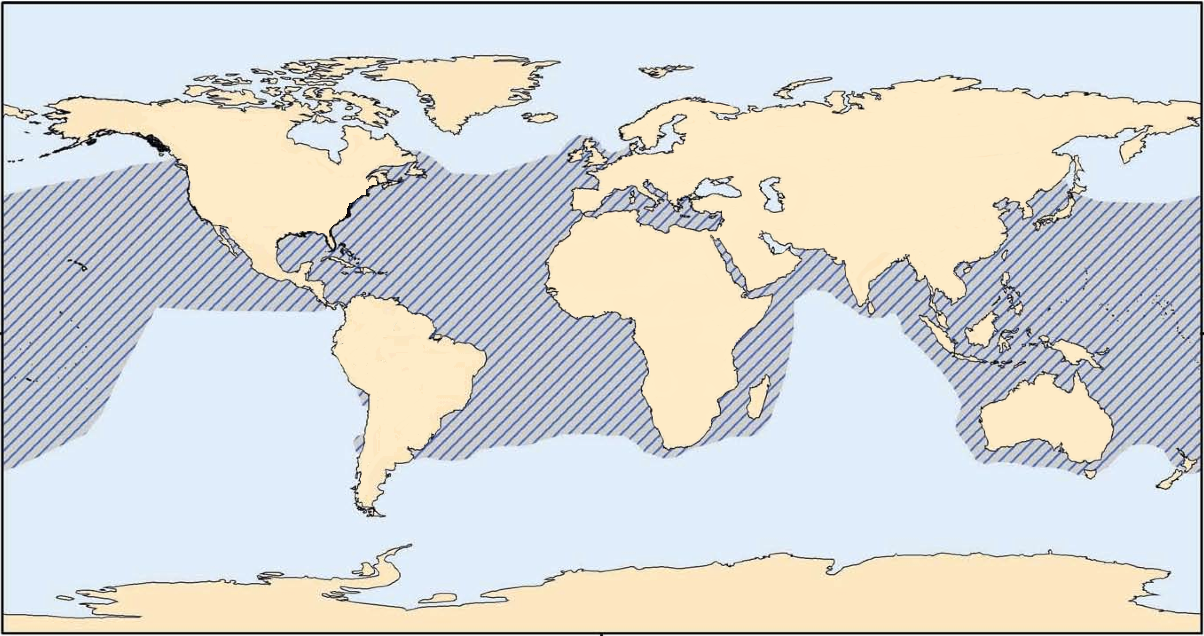
Loggerhead Sea Turtle
The loggerhead sea turtle (''Caretta caretta'') is a species of sea turtle, oceanic turtle distributed throughout the world. It is a marine reptile, belonging to the Family (biology), family Cheloniidae. The average loggerhead measures around in carapace length when fully grown. The adult loggerhead sea turtle weighs approximately , with the largest specimens weighing in at more than . The skin ranges from yellow to brown in color, and the shell is typically reddish brown. No external differences in sex are seen until the turtle becomes an adult, the most obvious difference being the adult males have thicker tails and shorter plastrons (lower shells) than the females. The loggerhead sea turtle is found in the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, as well as the Mediterranean Sea. It spends most of its life in saltwater and estuarine habitats, with females briefly coming ashore to lay eggs. The loggerhead sea turtle has a low reproductive rate; fem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World Warbler
The Old World warblers are a large group of birds formerly grouped together in the bird family Sylviidae. They are not closely related to the New World warblers. The family held over 400 species in over 70 genera, and were the source of much taxonomic confusion. Two families were split out initially, the cisticolas into Cisticolidae and the kinglets into Regulidae. In the past 20–30 years they have been the subject of much research and many species are now placed into other families, including the Acrocephalidae, Cettiidae, Phylloscopidae, and Megaluridae. In addition some species have been moved into existing families or have not yet had their placement fully resolved. Only a small number of warblers, in just two genera, are now retained in the family Sylviidae. Characteristics Most Old World warblers are of generally undistinguished appearance, though some species are boldly marked. The sexes are often identical, but may be clearly distinct, notably in the genera '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nightingale
The common nightingale, rufous nightingale or simply nightingale (''Luscinia megarhynchos''), is a small passerine bird which is best known for its powerful and beautiful song. It was formerly classed as a member of the thrush family Turdidae, but is now more generally considered to be an Old World flycatcher, Muscicapidae. It belongs to a group of more terrestrial species, often called chats. Etymology "Nightingale" is derived from "night" and the Old English ''galan'', "to sing". The genus name ''Luscinia'' is Latin for "nightingale" and ''megarhynchos'' is from Ancient Greek ''megas'', "great" and ''rhunkhos'' "bill". Subspecies *Western nightingale (''L. m. megarhynchos'') – western Europe, North Africa and Asia Minor, wintering in tropical Africa *Caucasian nightingale (''L. m. africana'') – the Caucasus and eastern Turkey to southwestern Iran and Iraq, wintering in East Africa *Eastern nightingale (''L. m. golzii'') – the Aral Sea to Mongolia, wintering in co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |