|
Górnośląskie Zagłębie Węglowe
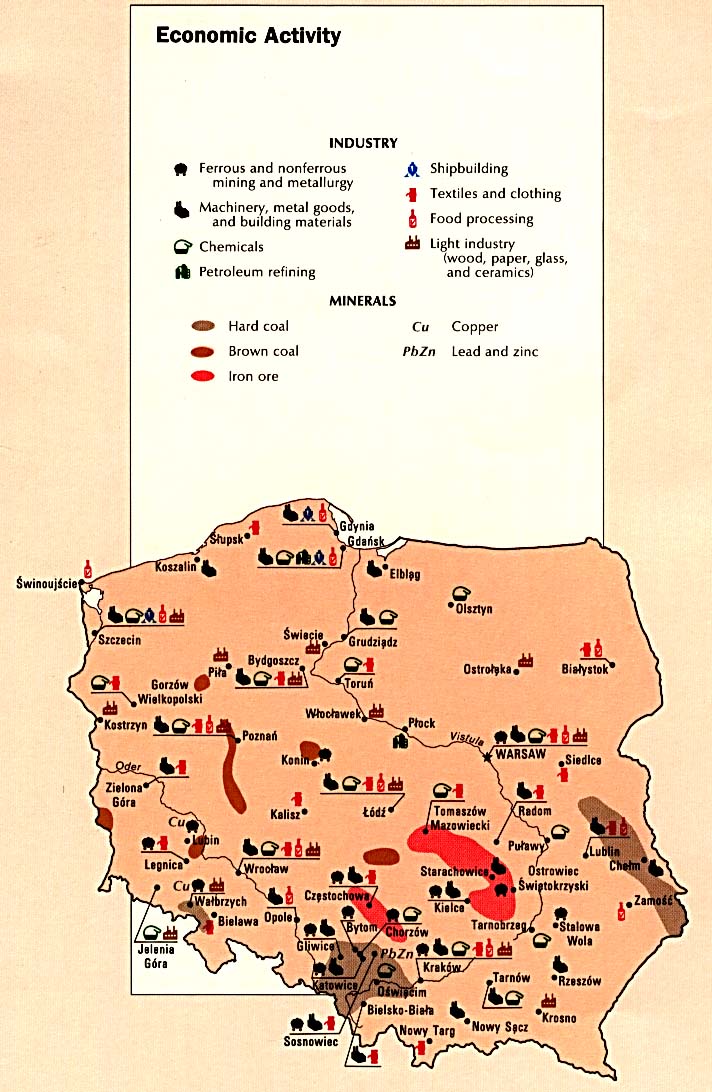
The Upper Silesian Coal Basin (''USCB''; , ) is a coal basin in Silesia, in Poland and the Czech Republic."''Górnośląskie Zagłębie Węglowe''" - Encyclopedia The Basin also contains a number of other minable resources, such as methane, cadmium, lead, silver and zinc. Coal depth is approximately 1,000 meters, and contains about 70 billion tons, with good extraction potential. Industrial areas within the Upper Silesian Coal Basin include the following: * |
Silesian Voivodeship
Silesian Voivodeship ( ) is an administrative province in southern Poland. With over 4.2 million residents and an area of 12,300 square kilometers, it is the second-most populous, and the most-densely populated and most-urbanized region of Poland. It generates 11.9% of Polish GDP and is characterized by a high life satisfaction, low income inequalities, and high wages. The region has a diversified geography. The Beskid Mountains cover most of the southern part of the voivodeship, with the highest peak of Pilsko on the Polish-Slovakian border reaching above sea level. Silesian Upland dominates the central part of the region, while the hilly, limestone Kraków-Częstochowa Upland, Polish Jura closes it from the northeast. Katowice urban area, located in the central part of the region, is the second most-populous urban area in Poland after Warsaw, with 2.2 million people, and one of Poland's seven supra-regional metropolises, while Rybnik, Bielsko-Biała and Częstochowa and their r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy Of Poland
The economy of Poland is an emerging and developing, high-income, industrialized mixed economy that serves as the sixth-largest in the European Union by nominal GDP and fifth-largest by GDP (PPP). Poland boasts the extensive public services characteristic of most developed economies and is one of few countries in Europe to provide no tuition fees for undergraduate and postgraduate education and with universal public healthcare that is free at a point of use. Since 1988, Poland has pursued a policy of economic liberalisation but retained an advanced public welfare system. It ranks 19th worldwide in terms of GDP (PPP), 20th in terms of GDP (nominal), and 21st in the 2023 Economic Complexity Index. Among OECD nations, Poland has a highly efficient and strong social security system; social expenditure stood at roughly 22.7% of GDP. The largest component of Poland's economy is the service sector (62.3%), followed by industry (34.2%) and agriculture (3.5%). Following the economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesian University Of Technology
The Silesian University of Technology (Polish language, Polish name: Politechnika Śląska; ) is a university located in the Polish province of Silesia, with most of its facilities in the city of Gliwice. It was founded in 1945 by Polish professors of the Lviv University of Technology, Lwow Polytechnic, who were Polish population transfers (1944–1946), forced to leave their native city and move to the Recovered Territories (see also Kresy). In 2023, the prestigious Perspektywy Foundation ranked it as the 6th best university of technology and the 12th overall in Poland. Organization Silesian University of Technology is organized into 13 faculties and 1 research institute: *Faculty of Architecture, *Faculty of Automatic control, Automatic Control, Electronics and Computer Science, *Faculty of Civil Engineering, *Faculty of Chemistry, *Faculty of Electrical Engineering, *Faculty of Mining, Safety Engineering and Industrial Automation, *Faculty of Biomedical Engineering *Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katowice
Katowice (, ) is the capital city of the Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland and the central city of the Katowice urban area. As of 2021, Katowice has an official population of 286,960, and a resident population estimate of around 315,000. Katowice is a central part of the Metropolis GZM, with a population of 2.3 million, and a part of a larger Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan area that extends into the Czech Republic and has a population of around 5 million people, making it List of metropolitan areas in Europe#Polycentric metropolitan areas in the European Union, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the European Union."''Study on Urban Functions (Project 1.4.3)''" – European Observation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Silesia
The University of Silesia in Katowice () is an autonomous state-run university in Katowice, Silesia Province, Poland. The university offers higher education and research facilities. It offers undergraduate, masters, and PhD degree programs, as well as postgraduate, postdoctoral research, habilitation, and continuous education and training programs. History The history of the University of Silesia in Katowice dates back to 1928, when the Instytut Pedagogiczny w Katowicach (''Pedagogical Institute in Katowice'') was established in Katowice which existed till 1939. In 1950, the Higher Pedagogical School in Katowice was established, however, first preparations to formation of what would later become the University of Silesia in Katowice were taken just after the end of Second World War. In June 1962, a branch of Jagiellonian University was settled in Katowice, which concentrated, apart from humanities, on mathematics, physics and law. Together with the Higher Pedagogical Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Mining In Poland
__NOTOC__ Coal in Poland is partly mined and partly imported. 144 million metric tons of coal was mined in 2012, providing 55 percent of that country's primary energy consumption. Poland is the second-largest coal-mining country in Europe, after Germany, and the ninth-largest coal producer in the world. The country consumes nearly all the coal it mines, and is no longer a major coal exporter. Coal mines are concentrated mainly in Upper Silesia. The most profitable mines were Marcel Coal Mine and Zofiówka Coal Mine. In communist times (1945–1989) one of the most important and largest mines was 1 Maja Coal Mine. In 2020, coal played a significant role in Poland's energy mix, making up to 69.5% of the nation's energy production and 68.5% of its electricity generation. It accounted for 40.2% of the Total Energy Supply (TES). The largest portion of coal consumption was in electricity and heat generation, representing 75.6% of the total demand. The industrial sector followed, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europa
Europa may refer to: Places * Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace * Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro * Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development * Europa Cliffs, Alexander Island, Antarctica * Europa Island, a small island in the Mozambique Channel which is a possession of France * Europa Point, Gibraltar; the southernmost point of Gibraltar * Europa Road, Gibraltar * Plaça d'Europa, Barcelona, Spain; a square * Europa, Missouri, US; a community * Europe, known as Europa in many European languages Celestial bodies * Europa (moon), a moon of Jupiter * 52 Europa, an asteroid Buildings and structures * Europa building, the seat of the European Council and Council of the European Union in Brussels, Belgium * Europa Hotel (other) * Europa Hut, a Swiss mountain hut * Europa Tower, Vilnius, Lithuania * Europa-Park, A theme park in Rust, Germany People * Europa of Macedon, the daughter of Phili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Spatial Planning Observation Network
The European Observation Network for Territorial Development and Cohesion, often shortened as ESPON, is a European funded programme under the objective of "European Territorial Cooperation" of the Cohesion Policy of the European Union. It is co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund - Interreg. The mission of the programme is to support policy development in relation to the aim of territorial cohesion and a harmonious development of the European territory. Firstly it provides comparable information, evidence, analyses and scenarios on territorial dynamics and secondly it reveals territorial capital and potentials for the development of regions and larger territories thus contributing to European competitiveness, territorial cooperation and a sustainable and balanced development. The current ESPON 2020 Programme is carried through by 28 European Union Member States as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland and the European Commission The European Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katowice-Ostrava Metropolitan Area
The Katowice-Ostrava metropolitan areaBrookings Institutionbr>Redefining global cities: The seven types of global metro economies(2016), p. 16. European Spatial Planning Observation Network (ESPON"''Metroborder: Cross-border Polycentric Metropolitan Regions''"– Final report, 31 December 2010, (also known as Upper Silesian-Moravian metropolitan area or Upper Silesian urban-industrial agglomeration) is a polycentric metropolitan area in southern Poland and northeastern Czech Republic, centered on the cities of Katowice and Ostrava, and has around 5 million inhabitants. Geographically, it is located mainly in Upper Silesia, with small parts of the area also in the historical regions of Moravia and Lesser Poland. Administratively, it is located in the three administrative units ( NUTS-2 class): mainly Silesian Voivodeship and a small western part of Lesser Poland Voivodeship in Poland, and also a small eastern part of Moravian-Silesian Region in the Czech Republic. The metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravian-Silesian Region
The Moravian-Silesian Region () is one of the 14 administrative regions of the Czech Republic. Before May 2001, it was called the Ostrava Region (). The region is located in the north-eastern part of its historical region of Moravia and in most of the Czech Silesia, Czech part of the historical region of Silesia. The region borders the Olomouc Region to the west and the Zlín Region to the south. It also borders two other countries – Poland (Opole Voivodeship, Opole and Silesian Voivodeships) to the north and Slovakia (Žilina Region) to the east. It is a highly Industrialisation, industrialized region, its capital Ostrava was actually called the "Steel Heart of the Republic". In addition, it has several mountainous areas where the landscape is relatively preserved. Nowadays, the economy of the region benefits from its location in the Czech/Polish/Slovak borderlands. Administrative division Traditionally, the region has been divided into six districts () which still exist a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
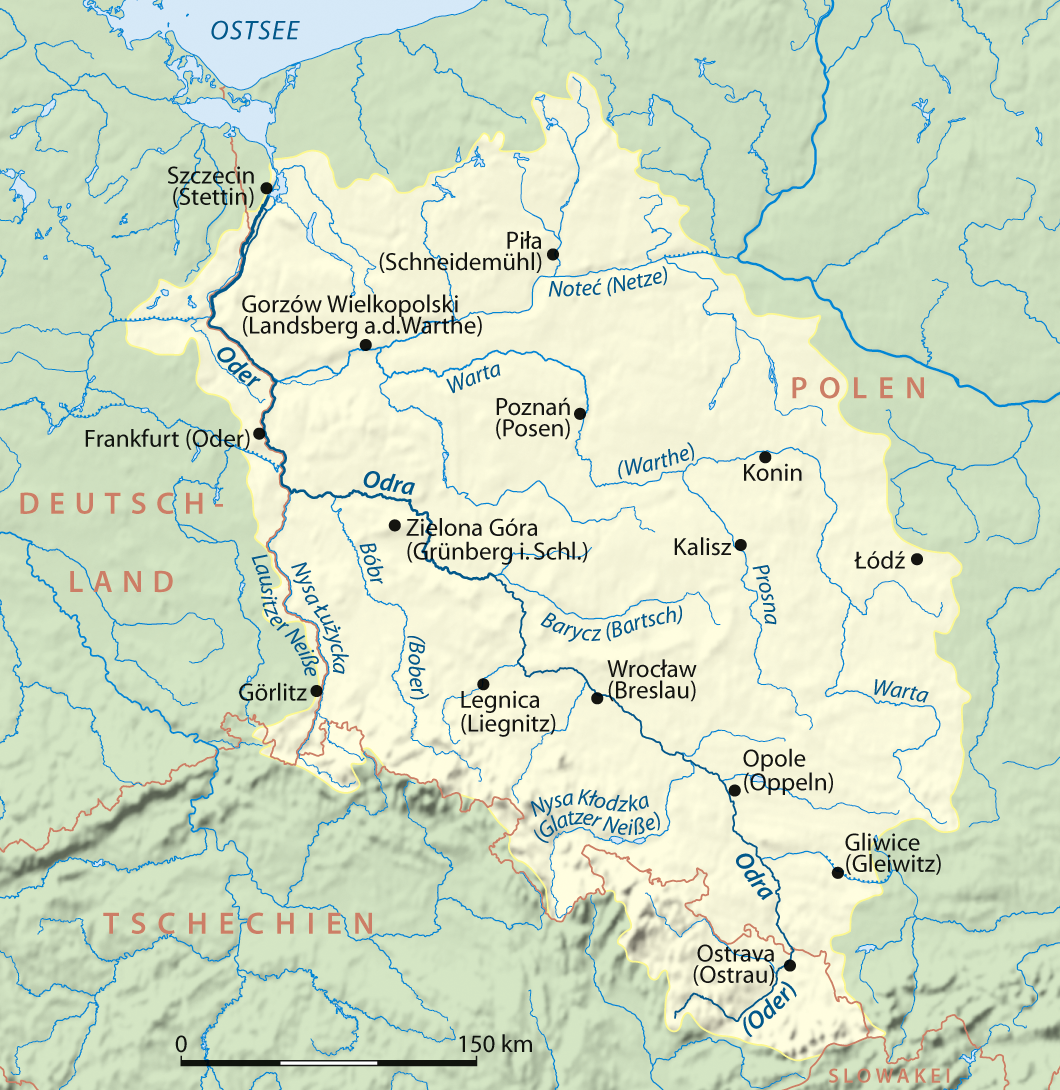
Oder River
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany as part of the Oder–Neisse line. The river ultimately flows into the Szczecin Lagoon north of Szczecin and then into three branches (the Dziwna, Świna and Peene) that empty into the Bay of Pomerania of the Baltic Sea. Names The Oder is known by several names in different languages, but the modern ones are very similar: English and ; Czech, Polish, and , ; (); ; Medieval Latin: ''Od(d)era''; Renaissance Latin: ''Viadrus'' (invented in 1534). The origin of this name is said by onomastician Jürgen Udolph to come from the Illyrian word ''*Adra'' (“water vein”). Ptolemy knew the modern Oder as the Συήβος (''Suebos''; Latin ''Suevus''), a name apparentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |