|
Gábor Téglás
Gábor Téglás (March 23, 1848–February 4, 1916) was a Hungarian archaeologist. Born in Brassó (Brașov), in the Principality of Transylvania, he attended primary and secondary school in his native city. Téglás then studied law at the Royal University of Pest. Returning to Transylvania in 1871, he became a teacher at the state high school in Déva.Gáll, pp. 146-47 After settling in Déva, Téglás began to undertake archaeological research in the surrounding Hunyad County. Meanwhile, he set up the high school's annual journal, where his first research appeared. In 1888, he was elected a corresponding member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. The same year, he became director of the high school, serving until 1904. At that point, he left for Budapest, leading a withdrawn existence in his house while continuing to publish. His research focused on prehistory and Roman Dacia Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brașov
Brașov (, , ; , also ''Brasau''; ; ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the county seat (i.e. administrative centre) of Brașov County. According to the 2021 Romanian census, 2021 census, with 237,589 inhabitants, Brașov is the Cities in Romania, 6th most populous city in Romania. The Brașov metropolitan area, metropolitan area was home to 371,802 residents. Brașov is located in the central part of the country, about north of Bucharest and from the Black Sea. It is surrounded by the Southern Carpathians and is part of the historical region of Transylvania. Historically, the city was the centre of the Burzenland (), once dominated by the Transylvanian Saxons (), and a significant commercial hub on the trade roads between Austria (then Archduchy of Austria, within the Habsburg monarchy, and subsequently Austrian Empire) and Turkey (then Ottoman Empire). It is also where the Deșteaptă-te, române!, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Transylvania (1711–1867)
The Principality of Transylvania, from 1765 the Grand Principality of Transylvania, was a Lands of the Hungarian Crown, realm of the Hungarian Crown ruled by the Habsburg and Habsburg-Lorraine monarchs of the Habsburg monarchy (later Austrian Empire) and governed by mostly Hungarians. After the Ottomans were ousted from most of the territories of medieval Kingdom of Hungary, and after the failure of Rákóczi's War of Independence (1703–1711), the Habsburg dynasty claimed the former territories of the Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Principality of Transylvania under the capacity of their title of "King of Hungary". During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the April Laws of 1848 (after the Transylvanian Diet's confirmation on 30 May and the Ferdinand I of Austria, king's approval on 10 June for Transylvania to become once again an integral part of Hungary). After the failure of the revolution, the March ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eötvös Loránd University
Eötvös Loránd University (, ELTE, also known as ''University of Budapest'') is a Hungarian public research university based in Budapest. Founded in 1635, ELTE is one of the largest and most prestigious public higher education institutions in Hungary. The 28,000 students at ELTE are organized into nine faculties, and into research institutes located throughout Budapest and on the scenic banks of the Danube. ELTE is affiliated with 5 Nobel laureates, as well as winners of the Wolf Prize, Fulkerson Prize and Abel Prize, the latest of which was Abel Prize winner László Lovász in 2021. The predecessor of Eötvös Loránd University was founded in 1635 by Cardinal Péter Pázmány in Nagyszombat, Kingdom of Hungary (today Trnava, Slovakia) as a Catholic university for teaching theology and philosophy. In 1770, the university was transferred to Buda. It was named Royal University of Pest until 1873, then University of Budapest until 1921, when it was renamed Royal Hungarian Pá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deva, Romania
Deva (; Hungarian: ''Déva'', Hungarian pronunciation: ; German: ''Diemrich'', ''Schlossberg'', ''Denburg''; Latin: ''Sargetia''; is a city in Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania, on the left bank of the river Mureș. It is the capital of Hunedoara County. Name Its name was first recorded in 1269 as castrum ''Dewa''. The origin of the name gave rise to controversy. It is considered that the name comes from the ancient Dacian word ''dava'', meaning "fortress" (as in ''Pelendava'', ''Piroboridava'', or ''Zargidava''). Other theories trace the name to a Roman Legion, the Legio II Augusta, transferred to Deva from Castrum Deva, now Chester ('' Deva Victrix'') in Britain. János András Vistai assume the name is of old Turkic origin from the name Gyeücsa. Others assert that the name is probably of Slavic origin where ''Deva'' or ''Devín'' means "girl" or "maiden" (a similar case exists in Slovakian for the Devín Castle, located at the confluence of the Danu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
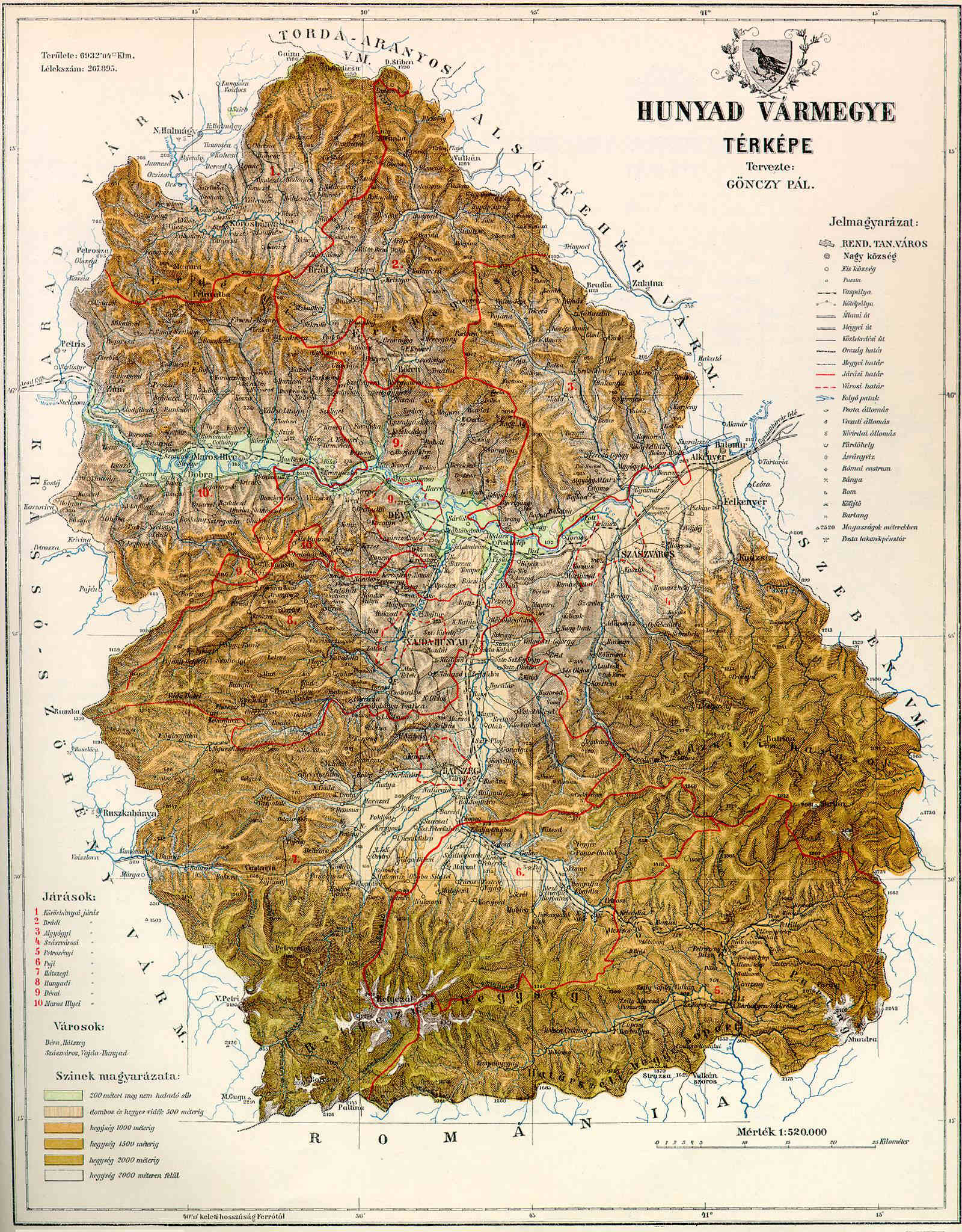
Hunyad County
Hunyad (today mainly Hunedoara (county), Hunedoara) was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary, of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and of the Principality of Transylvania (other), Principality of Transylvania. Its territory is now in Romania in Transylvania. The capital of the county was Déva (present-day Deva, Romania, Deva). Geography After 1876, Hunyad county shared borders with Romania and the Hungarian counties Krassó-Szörény, Arad (Hungarian county), Arad, Torda-Aranyos, Alsó-Fehér and Szeben. Its area was 7,809 km2 around 1910. Etymology The toponym Hunyad most likely comes from the Hungarian language, Hungarian verb, meaning 'to close' or 'to die'. According to linguist Géza Kuun, the name may keep the memory of the Huns. History The first known civilization living on the territory were the Scythian culture, Scythian Agathyrsi and Sigynnae. Later the Dacians under their leader Burebista esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Academy Of Sciences
The Hungarian Academy of Sciences ( , MTA) is Hungary’s foremost and most prestigious learned society. Its headquarters are located along the banks of the Danube in Budapest, between Széchenyi rakpart and Akadémia utca. The Academy's primary functions include the advancement of scientific knowledge, the dissemination of research findings, the support of research and development, and the representation of science in Hungary both domestically and around the world. History The origins of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences date back to 1825, when Count István Széchenyi offered one year's income from his estate to establish a ''Learned Society''. He made this offer during a session of the Diet in Pressburg (Pozsony, now Bratislava), then the seat of the Hungarian Parliament. Inspired by his gesture, other delegates soon followed suit. The Society’s mission was defined as the development of the Hungarian language and the promotion of sciences and the arts in the Hungarian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last region which is split among Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119 under Hadrian, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and around 158, Dacia Sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1848 Births
1848 is historically famous for the wave of revolutions, a series of widespread struggles for more liberal governments, which broke out from Brazil to Hungary; although most failed in their immediate aims, they significantly altered the political and philosophical landscape and had major ramifications throughout the rest of the century. Ereignisblatt aus den revolutionären Märztagen 18.-19. März 1848 mit einer Barrikadenszene aus der Breiten Strasse, Berlin 01.jpg, Cheering revolutionaries in Berlin, on March 19, 1848, with the new flag of Germany Lar9 philippo 001z.jpg, French Revolution of 1848: Republican riots force King Louis-Philippe to abdicate Zeitgenössige Lithografie der Nationalversammlung in der Paulskirche.jpg, German National Assembly's meeting in St. Paul's Church Pákozdi csata.jpg, Battle of Pákozd in the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 Events January–March * January 3 – Joseph Jenkins Roberts is sworn in as the first president of the inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1916 Deaths
Events Below, the events of the First World War have the "WWI" prefix. January * January 1 – The British Empire, British Royal Army Medical Corps carries out the first successful blood transfusion, using blood that has been stored and cooled. * January 9 – WWI: Gallipoli Campaign – The last British troops are evacuated from Gallipoli, as the Ottoman Empire prevails over a joint British and French operation to capture Constantinople. * January 10 – WWI: Erzurum Offensive – Russia defeats the Ottoman Empire. * January 12 – The Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony, part of the British Empire, is established in modern-day Tuvalu and Kiribati. * January 13 – WWI: Battle of Wadi (1916), Battle of Wadi – Ottoman Empire forces defeat the British, during the Mesopotamian campaign in modern-day Iraq. * January 29 – WWI: Paris is bombed by German Empire, German zeppelins. * January 31 – WWI: An attack is planned on Verdun, France. Febru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Brașov
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eötvös Loránd University Alumni
Eötvös is an old spelling of the Hungarian word ötvös, meaning " gold- and silversmith". __NOTOC__ Family name Eötvös can refer to one of several Hungarian people: * Ignác Eötvös (1763–1838), Hungarian politician * József Eötvös (1813–1871), Hungarian statesman and author * Loránd Eötvös (1848–1919), Hungarian physicist * Zoltán Eötvös (1891–1936), Hungarian speed skater * Péter Eötvös (1944–2024), Hungarian composer and conductor * József Eötvös (musician) (born 1962) Hungarian guitar player Ötvös * Fülöp Ö. Beck (; 1873–1945), Hungarian sculptor, medal maker Otvos * A. Dorian Otvos (1893–1945), American writer and composer * Jim Otvos, academician Other Eötvös can also refers to several concepts and a place, all named for Loránd Eötvös: * an eotvos (unit), a unit of gravitational gradient * the Eötvös effect, a concept in geodesy * the Eötvös experiment The Eötvös experiment was a physics experiment that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The Hungarian Academy Of Sciences
Member may refer to: * Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon * Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set * In object-oriented programming, a member of a class ** Field (computer science), entries in a database ** Member variable, a variable that is associated with a specific object * Limb (anatomy), an appendage of the human or animal body ** Euphemism for penis * Structural component of a truss, connected by nodes * User (computing), a person making use of a computing service, especially on the Internet * Member (geology), a component of a geological formation * Member of parliament * The Members, a British punk rock band * Meronymy, a semantic relationship in linguistics * Church membership, belonging to a local Christian congregation, a Christian denomination and the universal Church * Member, a participant in a club or learned society A learned society ( ; also scholarly, intellectual, or academic society) is an organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |