|
Gustav Albrecht, 5th Prince Of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg
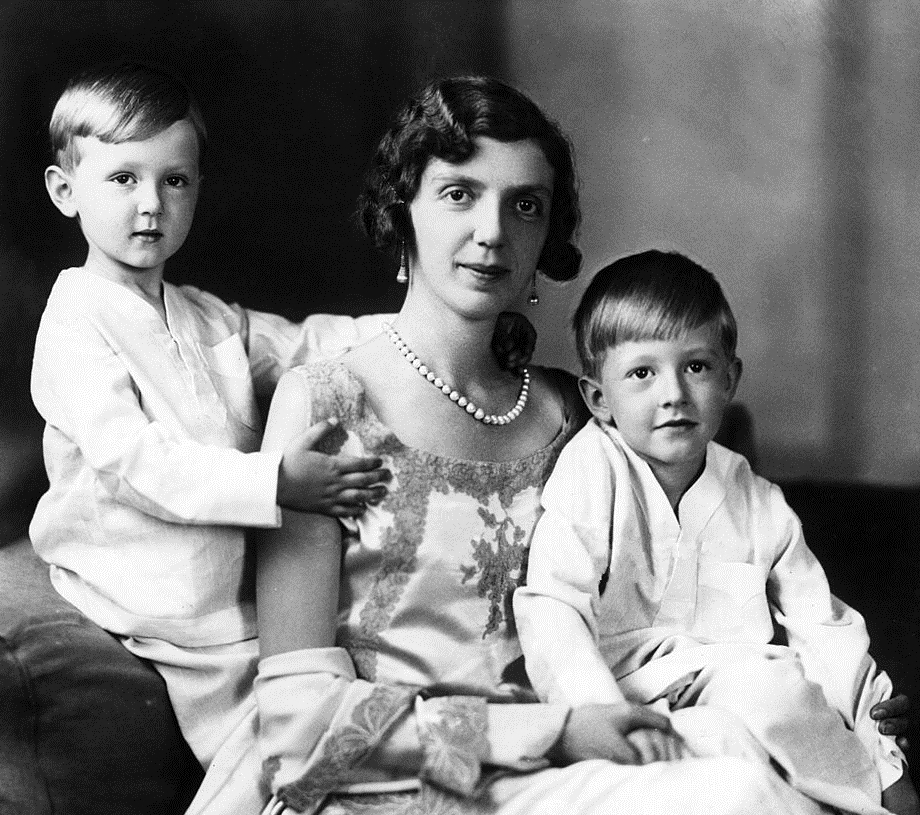
Gustav Albrecht, 5th Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (Gustav Albrecht Alfred Franz Friedrich Otto Emil Ernst; 28 February 1907 – 1944) was prince and head of the House of Sayn-Wittgenstein. He was the son of Richard, 4th Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg. Personal life Prince Gustav Albrecht Alfred Franz Friedrich Otto Emil Ernst was born on 28 February 1907 at Berleburg, Germany. Montgomery-Massingberd, Hugh (editor). Burke's Guide to the Royal Family, Burke's Peerage, London, 1973, pp. 269-270,302. He married Margareta Fouché d'Otrante (28 March 1909 – 25 August 2005), daughter of Charles Fouché, 6th Duc d'Otrante, on 26 January 1934 at Björnlunda, Södermanland Län, Sweden. In June 1944, he was serving as an officer in the German Army during the campaign against the Soviet Union. After disappearing during a mission near the Belarusian city of Orsha, Gustav Albrecht was declared missing in action. His family did not seek to have him declared dead until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg
Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg was one of several imperial counties and later principalities ruled by the House of Sayn-Wittgenstein. Most of the former county is located in the present district of Siegen-Wittgenstein (in the modern state of North Rhine-Westphalia), Germany. The residence was the town and palace in Berleburg (now Bad Berleburg). History Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg was a partition of Sayn-Wittgenstein in the 16th century; the southern and more-developed portion was the County of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Wittgenstein with its seat Laaspe (now Bad Laasphe) and its residence Wittgenstein Castle, whereas Berleburg is tucked away in a very rural landscape in the midst of vast forests. Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg was raised from a county with Imperial immediacy to an immediate principality (''Reichsfürstentum'') in 1792, and was German Mediatisation, mediatised to the Grand Duchy of Hesse in 1806 before being annexed to Prussia in 1816. Counts and reigning princes Counts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front, also known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union and its successor states, and the German–Soviet War in modern Germany and Ukraine, was a Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II fought between the European Axis powers and Allies of World War II, Allies, including the Soviet Union (USSR) and Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland. It encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans), and lasted from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. Of the estimated World War II casualties, 70–85 million deaths attributed to World War II, around 30 million occurred on the Eastern Front, including 9 million children. The Eastern Front was decisive in determining the outcome in the European theatre of World War II, European theatre of operations in World War II, eventually serving as the main reason for the defeat of Nazi Germany and the Axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1910–1990
Year 191 ( CXCI) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Apronianus and Bradua (or, less frequently, year 944 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 191 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Parthia * King Vologases IV of Parthia dies after a 44-year reign, and is succeeded by his son Vologases V. China * A coalition of Chinese warlords from the east of Hangu Pass launches a punitive campaign against the warlord Dong Zhuo, who seized control of the central government in 189, and held the figurehead Emperor Xian hostage. After suffering some defeats against the coalition forces, Dong Zhuo forcefully relocates the imperial capital from Luoyang to Chang'an. Before leaving, Dong Zhuo orders his troops to loot the tombs of the Han emperors, and then destroy Luoyang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz, Landgrave Of Hesse
Moritz, Landgrave of Hesse (legally ''Moritz Friedrich Karl Emanuel Humbert Prinz und Landgraf von Hessen''; 6 August 1926 – 23 May 2013) was the son of Prince Philip, Landgrave of Hesse, and the head of the House of Brabant and the German House of Hesse. Life Landgrave Moritz was born at Racconigi Castle, in Italy. During the Second World War, Moritz's mother, Princess Mafalda of Savoy, was arrested by the Nazis for alleged subversive activities and died in the Buchenwald concentration camp in 1944 as a result of a U.S. bombing raid on the camp. Moritz and his siblings (Moritz, Otto and Elisabeth) were given sanctuary in the Vatican under the care of their Aunt and Uncle Louis, Prince of Hesse and by Rhine and Margaret Campbell Geddes who adopted them. After the War they were reunited with their father in Germany. Together with his younger brothers, he took part in the ship tour organized by Queen Frederica and her husband King Paul of Greece in 1954, which became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solms-Laubach
Solms-Laubach was a County of southern Hesse and eastern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The House of Solms had its origins in Solms, Hesse. History Solms-Laubach was originally created as a partition of Solms-Lich. In 1537 Philip, Count of Solms-Lich, ruling count at Lich, purchased the ''Herrschaft'' Sonnewalde in Lower Lusatia which he left to his younger son Otto of Solms-Laubach (1496–1522), together with the county of Laubach. While Lich and Laubach were counties with imperial immediacy, Sonnewalde remained a semi-independent state country within the March of Lusatia (the latter being an immediate state of the Holy Roman Empire). A later Count Otto (1550–1612) moved to Sonnewalde and built the castle in 1582. In 1596 he also purchased the nearby Herrschaft of Baruth which was also elevated to a state country within the March of Lusatia. The branch then was divided into the twigs of Solms-Laubach, Solms-Sonnewalde and Solms-Baruth. Solms-Laubach partitioned betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Benedikte Of Denmark
Princess Benedikte of Denmark, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (Benedikte Astrid Ingeborg Ingrid, born 29 April 1944) is a member of the Danish royal family. She is the second daughter and child of King Frederik IX and Queen Ingrid of Denmark. She is the younger sister of Queen Margrethe II of Denmark, and therefore the aunt of Margrethe's son, the current King of Denmark, Frederik X. She is also an older sister of Queen Anne-Marie of Greece. Princess Benedikte often represents the Danish monarch at official or semi-official events. She and her late husband, Richard, 6th Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg, had three children. Princess Benedikte is currently tenth and last in the line of succession to the Danish throne. Early life Birth and family Princess Benedikte was born on 29 April 1944 at Frederik VIII's Palace, her parents' residence at the Amalienborg palace complex, the principal residence of the Danish royal family in the district of Frederiksstaden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Merit Cross
The War Merit Cross () was a state decoration of Nazi Germany during World War II. By the end of the conflict it was issued in four degrees and had an equivalent civil award. A " de-Nazified" version of the War Merit Cross was reissued in 1957 by the ''Bundeswehr'' for its veterans. History This award was created by Adolf Hitler in October 1939 as a successor to the non-combatant Iron Cross which was used in earlier wars (similar medal but with a different ribbon). The award would recognize bravery or service in the furtherance of the war effort that fell short of the award of the Iron Cross. The award was graded in the same manner as the Iron Cross: ''War Merit Cross Second Class'', ''War Merit Cross First Class'', and ''Knights Cross of the War Merit Cross''. The award was authorized for both military personnel and for civilians. The award had two variants: ''with swords'' and ''without swords''. Those with swords recognized bravery not directly connected to front-line activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
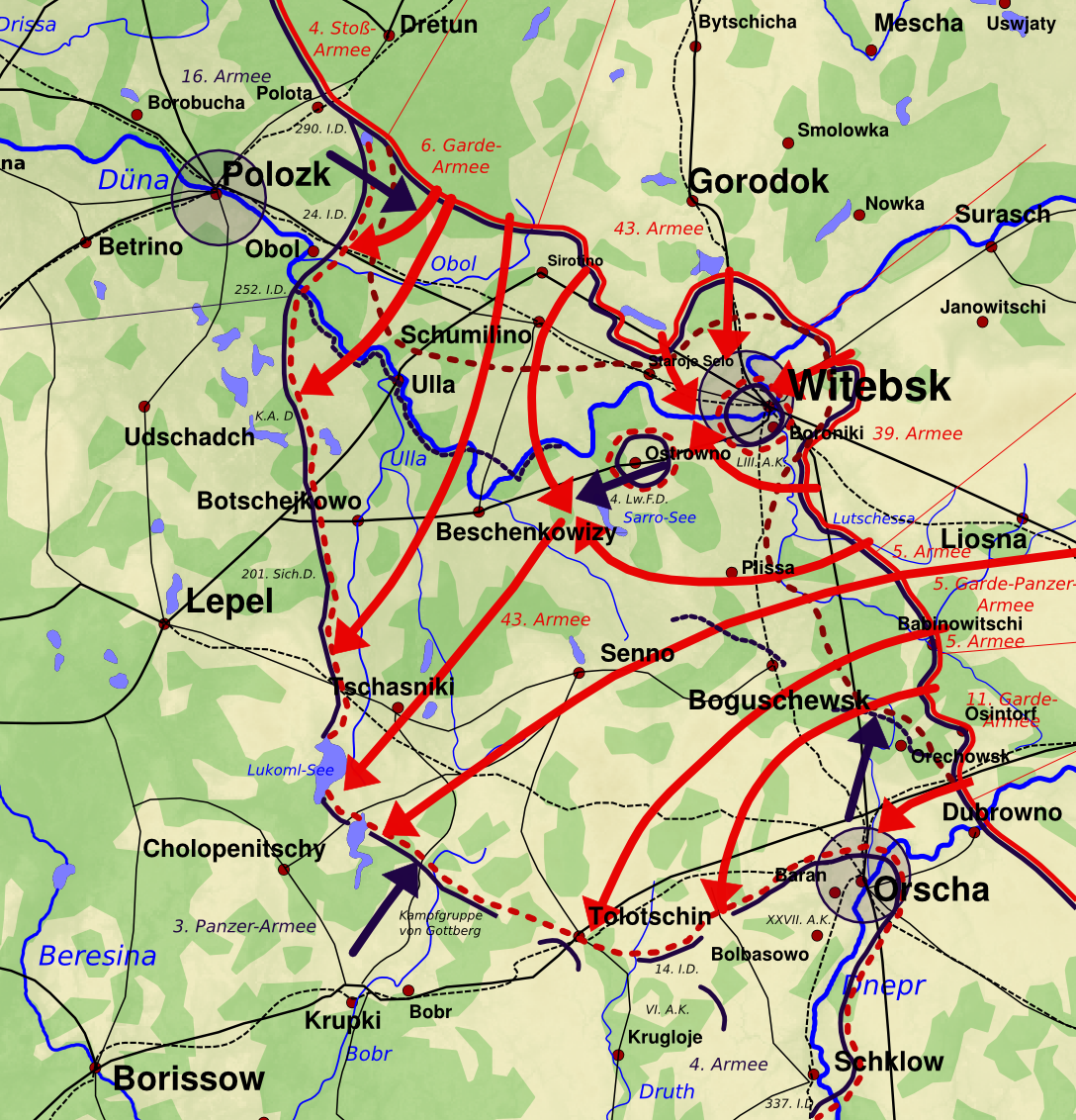
Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration () was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (), a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, just over two weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west. It was during this operation that Nazi Germany was forced to fight simultaneously on two major fronts for the first time since the war began. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of the divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. The overall engagement is the largest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while setting the stage for the subsequent isolation of 300,000 German soldiers in the Courland Pocket. On 22 June 1944, the Red Army attacked Army Group Centre in Byelorussia, with the objective of encircling and destroying its main component armies. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
23rd Panzer Division (Wehrmacht)
The 23rd Panzer Division () was an armoured division in the German Army during World War II. Formed in France in late 1941, the division spent its entire combat history on the Eastern Front. History The 23rd Panzer Division was established on the 21st of September 1941 in France. It was built around the 101st Panzer Brigade and two infantry regiments and initially equipped with "booty tanks" which were soon after exchanged for German tanks. In March 1942, the division went to the Eastern Front near Kharkov as a subdivision of the German Sixth Army. It was to remain within the Army Group South for the major part of its service. The division took part in the German advance to the Caucasus, but was subsequently sent north to Stalingrad. It escaped encirclement when the 6th Army was trapped there, and took part in the subsequent failed relief attempt. At the end of its first year on the Eastern Front the 23rd Panzer Division had lost 90 percent of its tanks.Mitcham, p. 169 On 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rittmeister
Rittmaster () is usually a commissioned officer military rank used in a few armies, usually equivalent to Captain. Historically it has been used in Germany, Austria-Hungary, Scandinavia, and some other countries. A is typically in charge of a squadron (a company-sized unit called a "troop" in the United States, as opposed to the U.S. cavalry squadron of larger battalion size), and is the equivalent of a ''Hauptmann'' rank (or captain in most army branches). Spelling * * * (until 1951) * (bokmål; the spelling ''ritmester'' was used until 1907) or ''rittmeister'' (nynorsk) * The armies of many Central and Eastern European countries adopted a localised term for the similar rank. * * * * * Czechia The rank of is an 'ensign' rank, used by both branches in the Czech Army. It is ranked OR-5 within the NATO rank structure. The immediate senior rank is called () and is ranked OR-6. The Netherlands The Dutch rank ''Ritmeester'', is the rank of squadron leading officers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranks And Insignia Of The German Army (1935–1945)
The as the German Army (Wehrmacht), German army and part of the inherited its uniforms and rank structure from the of the Weimar Republic (1921–1935). There were few alterations and adjustments made as the army grew from a limited peacetime defense force of 100,000 men to a war-fighting force of several million men. These ranks and insignia were specific to the Heer and in special cases to senior Wehrmacht officers in the independent services; the uniforms and rank systems of the other branches of the , the (Air Force) and (Navy), were different, as were those of the uniforms and insignia of the Schutzstaffel, SS which was a Party organization outside the . The Nazi Party also had its own series of Nazi Germany paramilitary ranks, paramilitary uniforms and insignia. Insignia National Emblem: or The visual acknowledgement of the new Nazi Party, National Socialist reality came on 17 February 1934, when the Commander-in-Chief, Werner von Blomberg, ordered the Nazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Officer
A senior officer is an officer of a more senior grade in military or other uniformed services. In military organisations, the term may refer to any officer above junior officer rank, but usually specifically refers to the middle-ranking group of commissioned officers above junior officer ranks but below flag, general or air rank. In most countries, this includes the ranks of lieutenant commander/major/ squadron leader, commander/ lieutenant colonel/ wing commander and naval captain/colonel/group captain, or their equivalents. In some countries, it also includes brigadiers and commodores. Sometimes, particularly in the army, this grade is referred to as field-grade officers, field officers or officers of field rank. Historically, a regiment or battalion's field officers made up its command element. Canada In the Canadian Armed Forces, the term "senior officer" () is used in all three services. It includes the army and air force ranks of major, lieutenant-colonel, and colone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |