|
Gunderic
Gunderic (; 379–428), King of Hasding Vandals (407-418), then King of Vandals and Alans (418–428), led the Hasding Vandals, a Germanic tribe originally residing near the Oder River, to take part in the barbarian invasions of the Western Roman Empire in the fifth century. History He was a son of King Godigisel, the Hasdingi's Vandal king when his people breached the Rhine river frontier of the Empire on the last day of 406. During that year, the Vandals had become heavily involved in a war with the Franks, who were already settled as allies of the Romans, and who attempted to keep the Vandals out. Godigisel was killed in the fighting and Gunderic succeeded him. Gunderic and his people ultimately crossed the Pyrenees into the Iberian Peninsula in October 409. With the Hasdingi portion of the Vandals he established the Kingdom in the Roman province of Gallaecia (north-western Iberia). They were driven out by the Visigoths in 418 on the orders of the Romans (the Visigoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vandal kingdoms first within the Iberian Peninsula, and then in the western Mediterranean islands, and North Africa. Archaeologists associate the early Vandals with the Przeworsk culture, which has led to some authors equating them to the Lugii, who were another group of Germanic peoples associated with that same archaeological culture and region. Expanding into Dacia during the Marcomannic Wars and to Pannonia during the Crisis of the Third Century, the Vandals were confined to Pannonia by the Goths around 330 AD, where they received permission to settle from Constantine the Great. Around 400, raids by the Huns from the east forced many Germanic tribes to migrate west into the territory of the Roman Empire and, fearing that they might be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandal Warriors
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vandal kingdoms first within the Iberian Peninsula, and then in the western Mediterranean islands, and North Africa. Archaeologists associate the early Vandals with the Przeworsk culture, which has led to some authors equating them to the Lugii, who were another group of Germanic peoples associated with that same archaeological culture and region. Expanding into Dacia during the Marcomannic Wars and to Pannonia during the Crisis of the Third Century, the Vandals were confined to Pannonia by the Goths around 330 AD, where they received permission to settle from Constantine the Great. Around 400, raids by the Huns from the east forced many Germanic tribes to migrate west into the territory of the Roman Empire and, fearing that they might be targe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandal Conquest Of Roman Africa
The Vandal conquest of Roman Africa, also known as the Vandal conquest of North Africa, was the conquest of Mauretania Tingitana, Mauretania Caesariensis, and Africa Proconsolaris by the migrating Vandals and Alans. The conflict lasted 13 years with a period of four years of peace, and led to the establishment of the Vandal Kingdom in 435. Primary sources Saint Augustine of Hippo, Bishop Capreolus, Honoratus Antoninus, Prosper of Aquitaine, Theodoret, and Possidius wrote contemporary accounts of the Vandal invasion. Hydatius documented the Vandals' activities in the Iberian peninsula before crossing into Africa. ''Life of Augustine'' by Possidius was written before the Vandalic seizure of Carthage in 439. Victor Vitensis's ''A History of the African Province Persecution, in the Times of Genseric and Huneric, the Kings of the Vandals'' covered the Vandalic conquest and Roman counterattacks. Background The Roman Empire had been in a state of decline by the beginning of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godigisel
Godigisel ( 359– 406) was King of the Hasdingi Vandals until his death in 406. It is unclear when or how he became king; however, in 405 he formed and led a coalition of Germanic peoples, including the Hasdingi Vandals, Silingi Vandals, Suebi, and others from Pannonia with the intention of invading Roman Gaul. Before crossing the Rhine River into Gaul, he was killed in the Vandal–Frankish war, possibly in late 406. Shortly after his death (traditionally dated to 31 December 406), this group of Vandals and their allies crossed the Rhine, possibly while it was frozen, into the territory of the Roman Empire The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of .... Godigisel was succeeded by his eldest surviving son, Gunderic. Godigisel was also the father of Genseric, who succeeded G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genseric
Gaiseric ( – 25 January 477), also known as Geiseric or Genseric (; reconstructed Vandalic: ) was king of the Vandals and Alans from 428 to 477. He ruled over a kingdom and played a key role in the decline of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century. The murder of Roman Emperor Valentinian III, who had betrothed his daughter to Gaiseric's son Huneric, led the Vandal king to invade Italy. The invasion culminated in his most famous exploit, the capture and plundering of Rome in June 455. Gaiseric repulsed two major attempts by both halves of the Roman Empire to reclaim North Africa, inflicting devastating defeats on the forces of Majorian in 460 and Basiliscus in 468. As a result, the Romans abandoned their campaign against the Vandals and concluded peace with Gaiseric. Gaiseric died in Carthage in 477 and was succeeded by his son, Huneric. Through his nearly fifty years of rule, Gaiseric raised a relatively inconsequential Germanic tribe to the status of a major Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silingi
The Silings or Silingi (; – ) were a Germanic tribe, part of the larger Vandal group. The Silingi at one point lived in Silesia, and the names ''Silesia'' and ''Silingi'' may be related.Jerzy Strzelczyk, "Wandalowie i ich afrykańskie państwo" p. 29, Warszawa 1992. History The Silingi are first mentioned by Claudius Ptolemaeus in the 2nd century, who wrote that they had lived south of the Suevic Semnones, and like them they lived on both sides of the Elbe river. To their east, across the river Suevus (probably the Oder river) were a Lugian people called the Omani, and south of them were the Calucones. The tribe of Nahanarvali is speculated by modern scholars to be the same people as the Silingi. Tacitus Germania, 43 mentions the Naharvali as the keepers of sanctuary of the Lugian federation (the grove to twin gods Alcis). Tacitus does not mention the Silingi; however, he places the Naharvali in about the same geographical area in which Ptolemaeus placed the Silingi. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasdingi
The Hasdingi were one of the Vandal peoples of the Roman era. The Vandals were Germanic peoples, who are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language, and were first reported during the first centuries of the Roman empire in the area which is now Poland, eastern Germany, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia. Famously, the Hasdingi led a successful invasion of Roman North Africa, creating a kingdom with its capital at Carthage in what is now Tunisia. During the Marcomannic wars, the Hasdingi helped the Romans and were able to settle in the Carpathian and Pannonian areas which are now in Hungary and Romania. At the end of 406, they participated together with Silingi Vandals and Sarmatian Alans in the crossing of the Rhine. Their king Godigisel lost his life in battle against the Franks during the crossing. After some years in Gaul, these peoples moved into the Iberian peninsula. The Hasdingi settled in Gallaecia (today Galicia, Asturias and the north of Portugal) along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attaces
Addac or Attaces (died 418) was king of the western Alans in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula, modern Spain and Portugal). In 409, the Alans settled in the provinces of Lusitania and Carthaginiensis: ''Alani Lusitaniam et Carthaginiensem provincias, et Wandali cognomine Silingi Baeticam sortiuntur''. Some doubt whether the Alans held all or just parts of Carthaginiensis.Bury, 203 and n2. He was the successor of Respendial, who led the Alans, together with the Vandals and Suevi, on an invasion of the Western Roman Empire beginning in 406. In 418 Attaces was defeated and killed in battle during the Gothic war in Spain with the Visigothic king Wallia, who had attacked the invading tribes on behalf of the emperor Honorius, in " Tartessian" lands, probably near Gibraltar Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
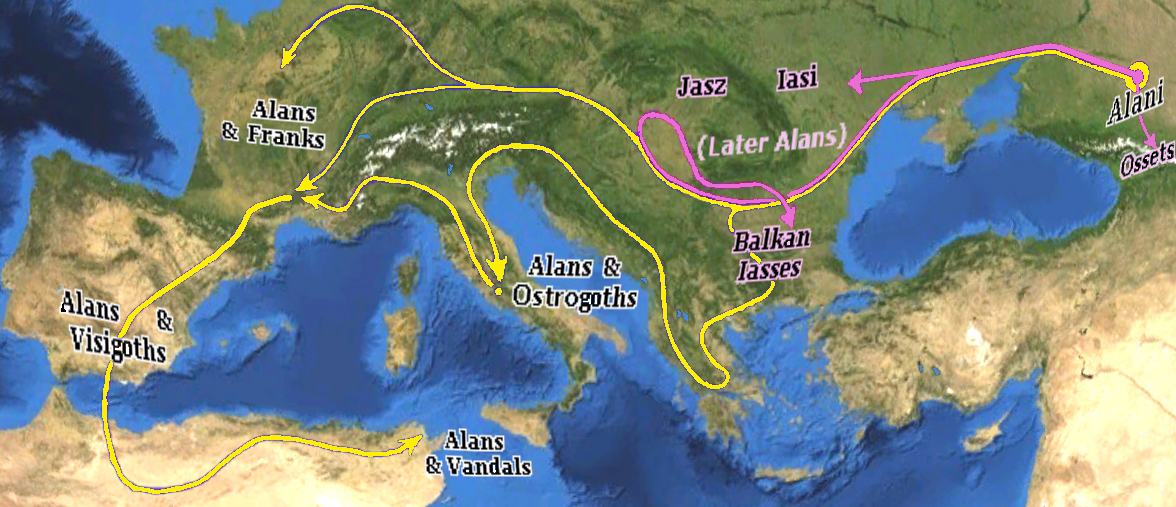
Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of China, Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Ancient Rome, Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the South Caucasus provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe, thereby assimilating a sizeable portion of the associated Alans. Upon the Huns, Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossing Of The Rhine
The crossing of the Rhine River by a mixed group of barbarians which included Vandals, Alans and Suebi is traditionally considered to have occurred on the last day of the year 406 (December 31, 406). The crossing transgressed one of the Roman Empire, Late Roman Empire's most secure ''Limes (Roman Empire), limites'' or boundaries; as such, it has been considered a climactic moment in the decline of the Roman Empire, decline of the Empire. It initiated a wave of destruction of Roman cities and the collapse of Roman civic order in northern Gaul. That, in turn, occasioned the rise of three usurpers in succession in the province of Roman Britain, Britannia. Therefore, the crossing of the Rhine is a marker date in the Migration Period during which various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes moved westward and southward from southern Scandinavia and northern Germania. Ancient sources Several written accounts document the crossing, supplemented by the time line of Prosper of Aquitaine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces created in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula) in 27 BC. Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basic divisions of Hispania under the Visigoths. Its territory approximately corresponds to modern Andalusia. Name In Latin, ' is an adjectival form of ', the Roman name for the Guadalquivir River, whose fertile valley formed one of the most important parts of the province. History Before Romanization, the mountainous area that was to become Baetica was occupied by several settled Iberian tribal groups. Celtic influence was not as strong as it was in the Celtiberian north. According to the geographer Claudius Ptolemy, the indigenes were the powerful Turdetani, in the valley of the Guadalquivir in the west, bordering on Lusitania, and the partly Hellenized Turduli with their city Baelo, in the hinterland behind the coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |