|
Grobiņa Stadium
Grobiņa (; ) is a town in South Kurzeme Municipality in the Courland region of Latvia, eleven kilometers east of Liepāja. It was founded by the Teutonic Order, Teutonic Knights in the 13th century. Some ruins of their Grobina castle are still visible. The town was given its charter in 1695. During the Early Middle Ages, Grobiņa (or Grobin) was the most important political centre on the territory of Latvia. There was a centre of Scandinavian settlement on the Baltic Sea, comparable in many ways to Hedeby and Birka but probably predating them both. About 3,000 surviving burial mounds contain the most impressive remains of the Vendel Age in Northern Europe. Scandinavian settlement The settlement at Grobin was excavated by Birger Nerman in 1929 and 1930. Nerman found remains of an earthwork stronghold, which had been protected on three sides by the Ālande River. Three Vendel Age cemeteries may be dated to the period between 650 and 800 AD. One of them was military in character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombina
The fire-bellied toads are a group of six species of small frogs (most species typically no longer than ) belonging to the genus ''Bombina''. The name "fire-bellied" is derived from the brightly colored red- or yellow-and-black patterns on the toads' ventral regions, which act as aposematic coloration, a warning to predators of the toads' reputedly foul taste. The other parts of the toads' skins are green or dark brown. When confronted with a potential predator, these toads commonly engage in an unkenreflex, ''Unken-'' being the combining form of ''Unke'', German for fire-bellied toad. In the unkenreflex, the toad arches its back, raising its front and back legs to display the aposematic coloration of its ventral side. Species The currently recognized species are: Biology The female of the species typically lays 80–300 eggs that can be found hanging off plant stems. The offspring develop in pools or puddles. Their metamorphosis is complete within a few weeks, peaking in J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the world's largest brackish water basin. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. It is a Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea and marginal sea of the Atlantic with limited water exchange between the two, making it an inland sea. The Baltic Sea drains through the Danish straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia (divided into the Bothnian Bay and the Bothnian Sea), the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olof (I) Of Sweden
Olof (Old Norse: ''Óláfr'') was a Swedish monarch or local ruler who ruled over Birka, an important port town, and possibly Uppsala, an important early Swedish political center, in about 852, when the Catholic missionary Saint Ansgar made his second voyage from Germany to Birka in about the year 851 or 852 A.D. He had an ambivalent attitude to Christianity, and was known as a successful warrior king in the Baltic region. Olof is not mentioned in the Icelandic sagas of the 12th and 13th century, which give a different line of succession of supposed Viking Age Swedish rulers, but the '' Vita Ansgari'', the near-contemporary writings of Ansgar's companion Rimbert, and the 11th-century account of Adam of Bremen both mention him and are generally seen as more reliable than the sagas. Religious dispositions Ansgar had undertaken missionary work among the Swedes in 829-831, and laid the foundations to a fragile congregation based in the important merchant town Birka. By the early 85 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curonians
:''The Kursenieki are also sometimes known as Curonians.'' The Curonians or Kurs (; ) were a medieval Balts, Baltic tribe living on the shores of the Baltic Sea in the 5th–16th centuries, in what are now western parts of Latvia and Lithuania. They eventually merged with other Baltic tribes contributing to the ethnogenesis of present-day Latvians and Lithuanians. Curonians gave their name to the region of Courland (''Kurzeme''), Kuršėnai town, Curonian spit and many other localities. They spoke the Curonian language. Origin The ethnic origin of the Curonians has been disputed in the past. Some researchers place the Curonians in the eastern Baltic group.Östen Dahl (ed.) 2001, ''The Circum-Baltic Languages: Typology and Contact,'' vol. 1 Others hold that the Curonians were related to Old Prussians who belonged in the western Baltic group. History The historical Curonians were described in contemporary sources as warriors, sailors and pirates. They are on the record havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vita Ansgari
The ''Vita Ansgarii'', also known as the ''Vita Anskarii'', is the hagiography of saint Ansgar, written by Rimbert, his successor as archbishop in the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen. The ''Vita'' is an important source not only in detailing Ansgar's Scandinavian missionary work, but also in its descriptions of the everyday lives of people during the Viking Age. Date The ''Vita Anskarii'' was written sometime between the years 869 and 876. Author Not much is known about Rimbert's life, the main source being the '' Vita Rimberrti'', written 865–909. Rimbert was likely brought up at the monastery at Torhout in Flanders. His training as a monk was focused on missionary work. Rimbert's early years residing in Flanders may explain why he shared such a strong passion for missionary work in the North. Like his predecessor, he may also have had Scandinavian origins, compelling him to save his people. Rimbert died in 888 which meant the missions to Scandinavia collapsed. Rimbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimbert
Saint Rimbert (or Rembert) (''c.'' 830 - 11 June 888 in Bremen) was archbishop of Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen, Hamburg-Bremen, in the northern part of the East Francia, Kingdom of East Frankia from 865 until his death in 888. He most famously wrote the life of Saint Ansgar, the ''Vita Ansgari,'' one of the most popular Hagiography, hagiographies of the middle ages. Biography Little is directly known about Rimbert, much of the information available regarding his life comes from the ''Vita Rimberti'', a hagiography written by an unknown author, likely produced some time in the 10th century. While his place of birth is uncertain it is widely accepted by historians that Rimbert was Danish. As a monk he trained in Turholt (Torhout), after which he shared a missionary trip to Scandinavia with his mentor Ansgar, Bishop of Hamburg. Upon Ansgar's death in 865, Rimbert was unanimously elected Archbishop of Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen, Hamburg-Bremen. Upon his election, Rimbert travelle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotland
Gotland (; ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a Provinces of Sweden, province/Counties of Sweden, county (Swedish län), Municipalities of Sweden, municipality, and List of dioceses, deaneries and parishes of the Church of Sweden, diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the north, as well as the Karlsö Islands (Lilla Karlsö, Lilla and Stora Karlsö, Stora) to the west. The population is 61,023 (2024) of which about 23,600 live in Visby, the main town. Outside Visby, there are minor settlements and a mainly rural population. The island of Gotland and the other areas of the province of Gotland make up less than one percent of Sweden's total land area. The county formed by the archipelago is the second smallest by area and is the least populated in Sweden. In spite of the small size due to its narrow width, the driving distance between the furthermost points of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
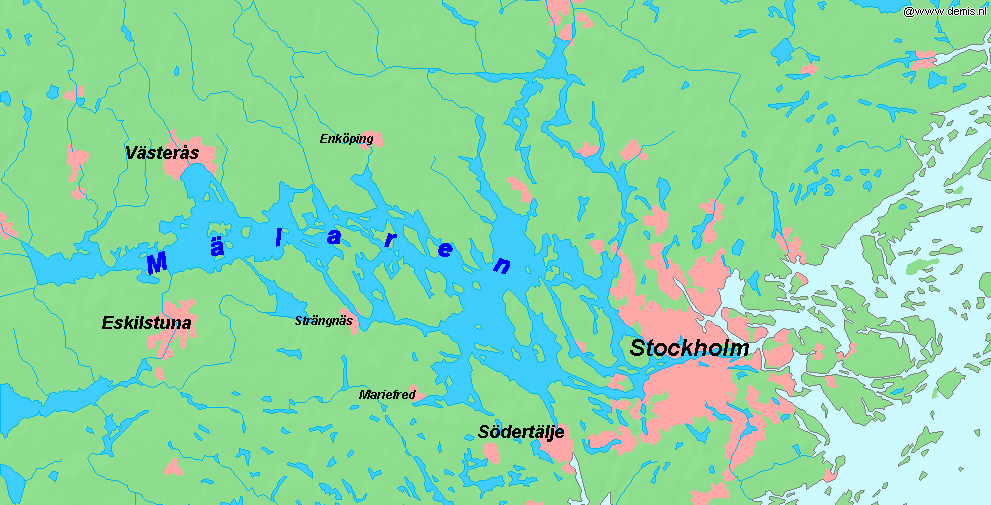
Mälaren
Mälaren ( , , or ), historically referred to as Lake Malar in English, is the third-largest freshwater lake in Sweden (after Vänern and Vättern). Its area is and its greatest depth is 64 m (210 ft). Mälaren spans from east to west. The lake drains, from south-west to north-east, into the Baltic Sea through its natural outlets Norrström and Söderström (as it flows around Stadsholmen island) and through the artificial Södertälje Canal and Hammarbyleden waterway. The easternmost bay of Mälaren, in central Stockholm, is called Riddarfjärden. The lake is located in Svealand and bounded by the provinces of Uppland, Södermanland and Västmanland. The two largest islands in Mälaren are Selaön () and Svartsjölandet (). Mälaren is low-lying and mostly relatively shallow. Being a quite narrow and shallow lake, Mälaren has bridge crossings between Eskilstuna and Västerås with two crossings on the western end at Kvicksund and three separate bridges between St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birger Nerman
Birger Nerman (6 October 188822 August 1971) was a Swedish archaeologist, historian and philologist who specialized in the history and culture of Iron Age Sweden. Nerman was educated at Uppsala University, where he began his career as a lecturer in Nordic philology. He participated in archaeological excavations on Stone Age and Iron Age Sweden, and became noted for his efforts to combine archaeological and philological evidence. Areas investigated by Nerman include Gamla Uppsala and Gotland. From 1923 to 1925, Nerman was professor of archaeology at the University of Dorpat, during which he made contributions to the development of archaeology in Estonia. In subsequent years, he conducted excavations at Grobiņa and other places, with the aim of investigating relations between Sweden and the eastern Baltic in the Iron Age. Nerman was director of the Swedish History Museum from 1938 to 1954, during which he organized several exhibitions on Swedish history. He was a Swedish natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology. Climate The climate is mainly Oceanic climate (Cfb), Humid continental climate (Dfb), Subarctic climate (Dfc and Dsc) and Tundra (ET). Geography Northern Europe might be defined roughly to include some or all of the following areas: British Isles, Fennoscandia, the peninsula of Jutland, the Baltic region, Baltic plain that lies to the east, and the many islands that lie offshore from mainland northern Europe and the main European continent. In some cases, Greenland is also included, although it is only politically European, comprising part of the Kingdom of Denmark, and not considered to be geographically in Europe. The area is partly mountainous, including the northern volcanic islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
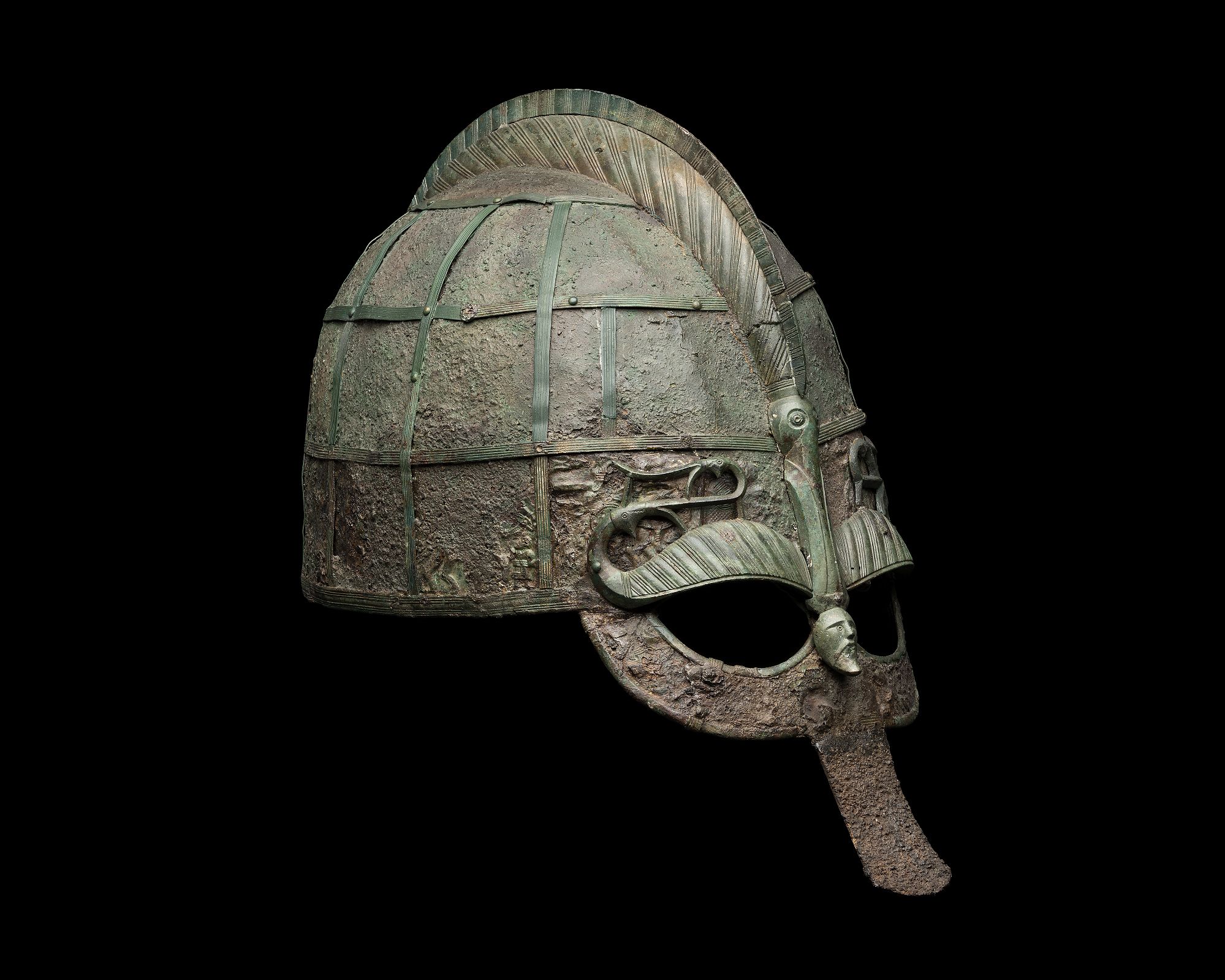
Vendel Age
In Scandinavian prehistory, sometimes specifically Swedish prehistory, the Vendel Period, or Vendel Age (; ) appears between the Migration Period and the Viking Age. The name is taken from the rich boat inhumation cemetery at Vendel parish church, Uppland. Unlike the preceding and succeeding eras, the Vendel Period left very few precious metal artifacts or runic inscriptions. Instead, it is extremely rich in animal art on copper-alloy objects. It is also known for '' guldgubbar'', tiny embossed gold foil images, and elaborate helmets with embossed decoration similar to the one found at Sutton Hoo in England. During the period, Swedish expeditions began to explore the waterways of territories which later became Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. The Elder Futhark writing system was abandoned in favor of the Younger Futhark, virtually simultaneously over the whole of Scandinavia. Some runestones survive, most notably those at Rök and Sparlösa, both from . Other written sourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |