|
Grishma
Grishma () the Sanskrit word meaning summer. This is one of the six seasons ( ritu), each lasting two months, the others being: Vasanta (spring), Varsha (monsoon), Sharada (autumn), Hemanta (pre-winter), and Shishira (winter). It falls in the two months of Jyeshtha and Ashadha of the Hindu calendar, or April and May of the Gregorian calendar. It is preceded by Vasanta, the spring season, and followed by Varsha, the rainy season The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Rainy Season may also refer to: * ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King * "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni * '' .... References Sources *Selby, Martha Ann (translator). ''The Circle of Six Seasons'', Penguin, New Delhi, 2003, * Raghavan, V. ''Ṛtu in Sanskrit literature'', Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri Kendriya Sanskrit Vidyapeetha, Delhi, 1972. Hindu calendar {{Hinduism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ratha Yatra
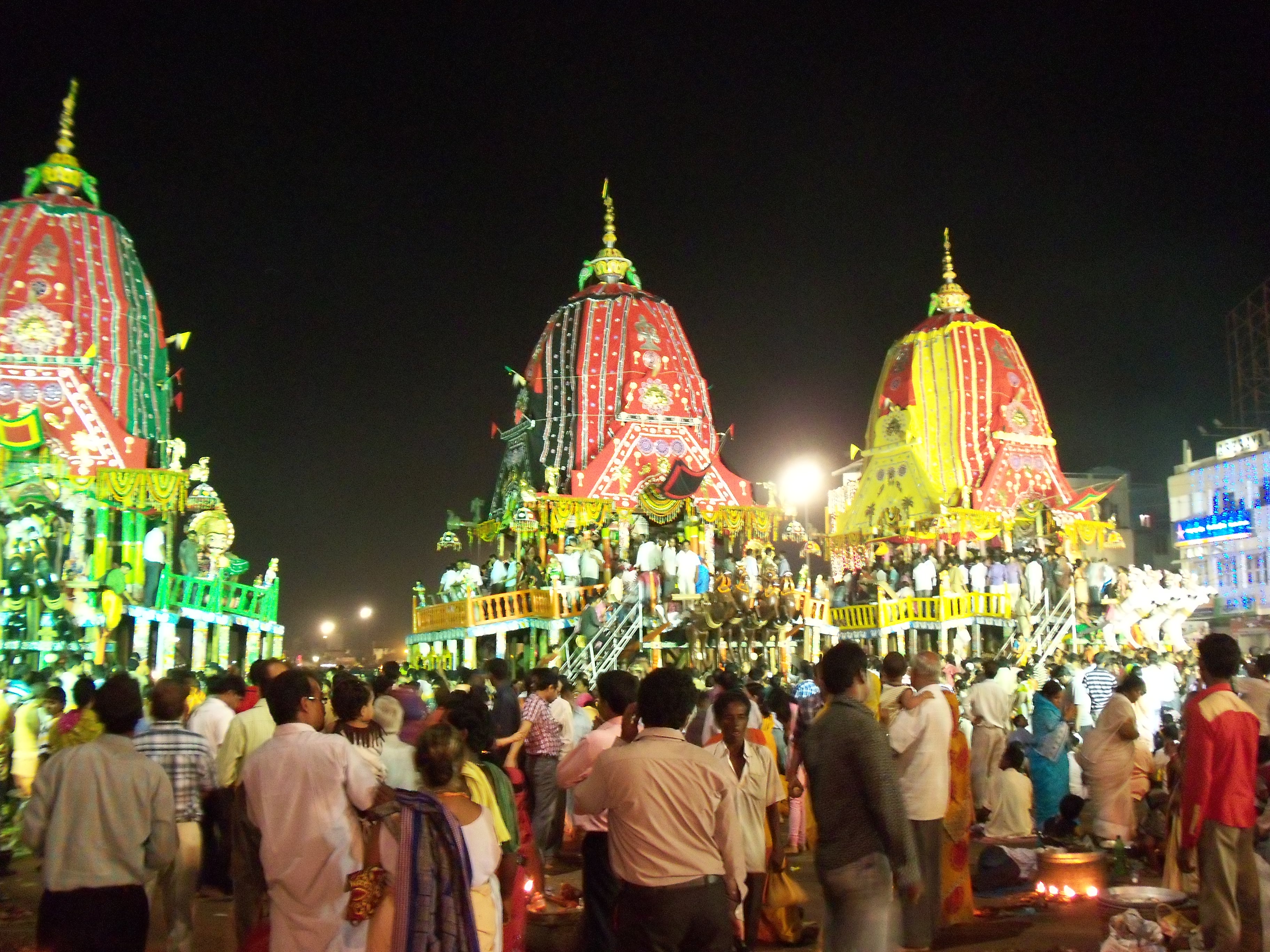
Ratha Yatra (), or chariot festival, is any public procession in a chariot. They are held annually during festivals in India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka. The term also refers to the popular annual Ratha Yatra of Puri that involves a public procession with a chariot with deities Jagannath (Vishnu avatar), Balabhadra (his brother), Subhadra (his sister), and Sudarshana Chakra (his weapon) on a ratha, which is a wooden deula-shaped chariot. Ratha Yatra processions have been historically common in Vishnu-related (Jagannath, Rama, Krishna) traditions in Hinduism across India, in Shiva-related traditions, saints and goddesses in Nepal, with Tirthankaras in Jainism, as well as tribal folk religions found in the eastern states of India. Notable Ratha Yatras in India include the Ratha Yatra of Puri, the Dhamrai Ratha Yatra in Bangladesh and the Ratha Yatra of Mahesh. Hindu communities outside India, such as in Singapore, celebrate Ratha Yatra such as those associated with Jagannat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Winter
Winter is the coldest and darkest season of the year in temperate and polar climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures define different dates as the start of winter, and some use a definition based on weather. When it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. Winter typically brings precipitation that, depending on a region's climate, is mainly rain or snow. The moment of winter solstice is when the Sun's elevation with respect to the North or South Pole is at its most negative value; that is, the Sun is at its farthest below the horizon as measured from the pole. The day on which this occurs has the shortest day and the longest night, with day length increasing and night length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice. The earliest sunset and latest sunrise dates outs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spring (season)
Spring, also known as springtime, is one of the four temperate seasons, succeeding winter and preceding summer. There are various technical definitions of spring, but local usage of the term varies according to local climate, cultures and customs. When it is spring in the Northern Hemisphere, it is autumn in the Southern Hemisphere and vice versa. At the spring equinox, also called the vernal equinox, Daytime (astronomy), days and nights are approximately twelve hours long, with daytime length increasing and nighttime length decreasing as the season progresses until the summer solstice. The spring equinox is in March in the Northern Hemisphere and in September in the Southern Hemisphere, while the summer solstice is in June in the Northern Hemisphere and in December in the Southern Hemisphere. Spring and "springtime" refer to the season, and also to ideas of rebirth, rejuvenation, renewal, resurrection and regrowth. Subtropical and tropical areas have climates better described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gregorian Calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It went into effect in October 1582 following the papal bull issued by Pope Gregory XIII, which introduced it as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years slightly differently to make the average calendar year 365.2425 days long rather than the Julian calendar's 365.25 days, thus more closely approximating the 365.2422-day tropical year, "tropical" or "solar" year that is determined by the Earth's revolution around the Sun. The rule for leap years is that every year divisible by four is a leap year, except for years that are divisible by 100, except in turn for years also divisible by 400. For example 1800 and 1900 were not leap years, but 2000 was. There were two reasons to establish the Gregorian calendar. First, the Julian calendar was based on the estimate that the average solar year is exactly 365.25 days long, an overestimate of a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
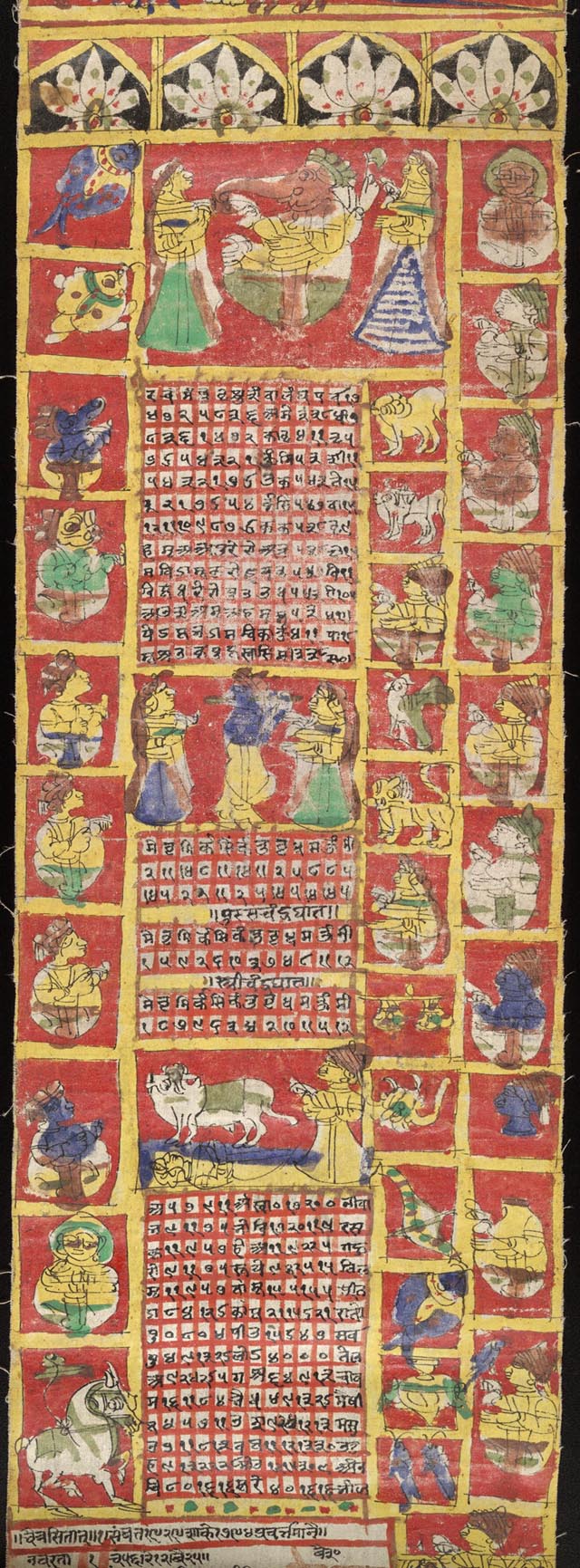
Hindu Calendar
The Hindu calendar, also called Panchangam, Panchanga (), is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a similar underlying concept for timekeeping based on sidereal year for solar cycle, solar cycle and adjustment of lunar cycles in every three years, but differ in their relative emphasis to moon cycle or the sun cycle and the names of months and when they consider the New Year to start. Of the various regional calendars, the most studied and known Hindu calendars are the Shaka era, Shalivahana Shaka (Based on the Shalivahana, King Shalivahana, also the Indian national calendar) found in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region of Southern India and the Vikram Samvat (Bikrami) found in Nepal and the North and Central regions of India – both of which emphasize the lunar cycle. Their new year starts in spring. In regions such as Tamil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ashadha
Ashadha or Aashaadha or Adi () is a month of the Hindu calendar that corresponds to June/July in the Gregorian calendar. In India's national civil calendar, this month is the fourth month of the year, beginning on 22 June and ending on 22 July. In Hindu astrology, Ashada begins with the Sun's entry into Gemini. It is the first of the two months that comprise the monsoon season. The corresponding month in the Bengali calendar is the third month. In lunar religious calendars, Ashadha begins on a new moon and is usually the fourth month of the year. Events Festivals Rath Yatra that is dedicated to Jagannath is held in the month of Asadha every year in Puri and other places. Guru Purnima, a festival dedicated to the Guru, is celebrated on the Purnima (Full Moon) day of the month. Prior to it Shayani Ekadashi, is observed on the eleventh lunar day (Ekadashi) of the bright fortnight (Shukla paksha). "" is an important festival in Tamil Nadu and auspicious for Amman. In many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jyeshta
Jyeshtha or Jyēṣṭha (; ''jēṭ''; ''zeth''; ''Jyeṣṭha'') is a month of the Hindu calendar. In India's national civil calendar, Jyestha is the third month of the year. Known as ''Joishtho'' ( ''Jyôishţhô'') in Bengali, it is the second month of the Bengali calendar. In lunar religious calendars, Jyēṣṭha begins on the new moon and is the third month of the year. Traditionally, Jyēṣṭha is associated with high summer, and corresponds to May–JuneHenderson, Helene. (Ed.) (2005) ''Holidays, festivals, and celebrations of the world dictionary'' Third edition. Electronic edition. Detroit: Omnigraphics, p. xxix. in the Gregorian calendar. In Tamil, the month is known as Āni, the third month of the solar calendar that begins in mid-June. In Hindu astrology, Jyēṣṭha begins with the Sun's entry into Taurus, and is the second month of the year. Festivals * Shani Dev Jayanti is celebrated on New Moon day i.e. Amavasya of Jyeshtha month. * Ganga Dussehra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shishira (season)
Shishira () is the Ritu (Indian season), season of winter in the Hindu calendar. It comprises the months of Pausha and Magha (month), Magha or mid-January to mid-March in the Gregorian calendar. References Sources *Selby, Martha Ann (translator). ''The Circle of Six Seasons'', Penguin, New Delhi, 2003, * Raghavan, V. ''Ṛtu in Sanskrit literature'', Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri Kendriya Sanskrit Vidyapeetha, Delhi, 1972. Hindu calendar Seasons {{hinduism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hemanta (season)
Hemanta () is the season of early winter in the Hindu calendar. It is one of the six seasons (Ritu (Indian season), ritu), each lasting two months, the others being Vasanta (season), Vasanta (spring), Grishma (summer), Sharada (season), Sharada (autumn), Varsha (season), Varsha (monsoon), and Shishira (season), Shishira (winter). It falls in the two months of Agrahayana and Pausha of the Hindu calendar, or November and December of the Gregorian calendar. It is preceded by Sharada, the autumn season, and followed by Shishira, the winter season. References Hindu calendar Seasons {{Hinduism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Autumn
Autumn, also known as fall (especially in US & Canada), is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September (Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Southern Hemisphere). Autumn is the season when the duration of daylight becomes noticeably shorter and the temperature cools considerably. Day length decreases and night length increases as the season progresses until the winter solstice in December (Northern Hemisphere) and June (Southern Hemisphere). One of its main features in temperate climates is the striking change in colour of the leaves of deciduous trees as they prepare to shed. Date definitions Some cultures regard the autumnal equinox as "mid-autumn", while others with a longer temperature lag treat the equinox as the start of autumn. In the English-speaking world of high latitude countries, autumn traditionally began with Lammas Day and ended around Hallowe'en, the approximate mid-poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sharada (season)
Sharada or Śāradā is the autumn season in the Hindu calendar. It roughly corresponds to the months of Bhadrapada and Ashvina, or Ashvina and Kartika, and the western months of mid-September to mid-November. Sharada is preceded by Varsha and followed by Hemanta. Occasions Sharad Navaratri is marked on the first nine days of the season, regarded to be auspicious. Sharad Purnima is the full moon day in the month of Ashvina, which commemorates the performance of the rasalila dance by the deity Krishna Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c .... References Sources *Selby, Martha Ann (translator). ''The Circle of Six Seasons'', 2003, * Raghavan, V. ''Ṛtu in Sanskrit literature'', Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri from Nepal, 1972. Hindu calendar Autumn {{Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |