|
Grave Circle B, Mycenae
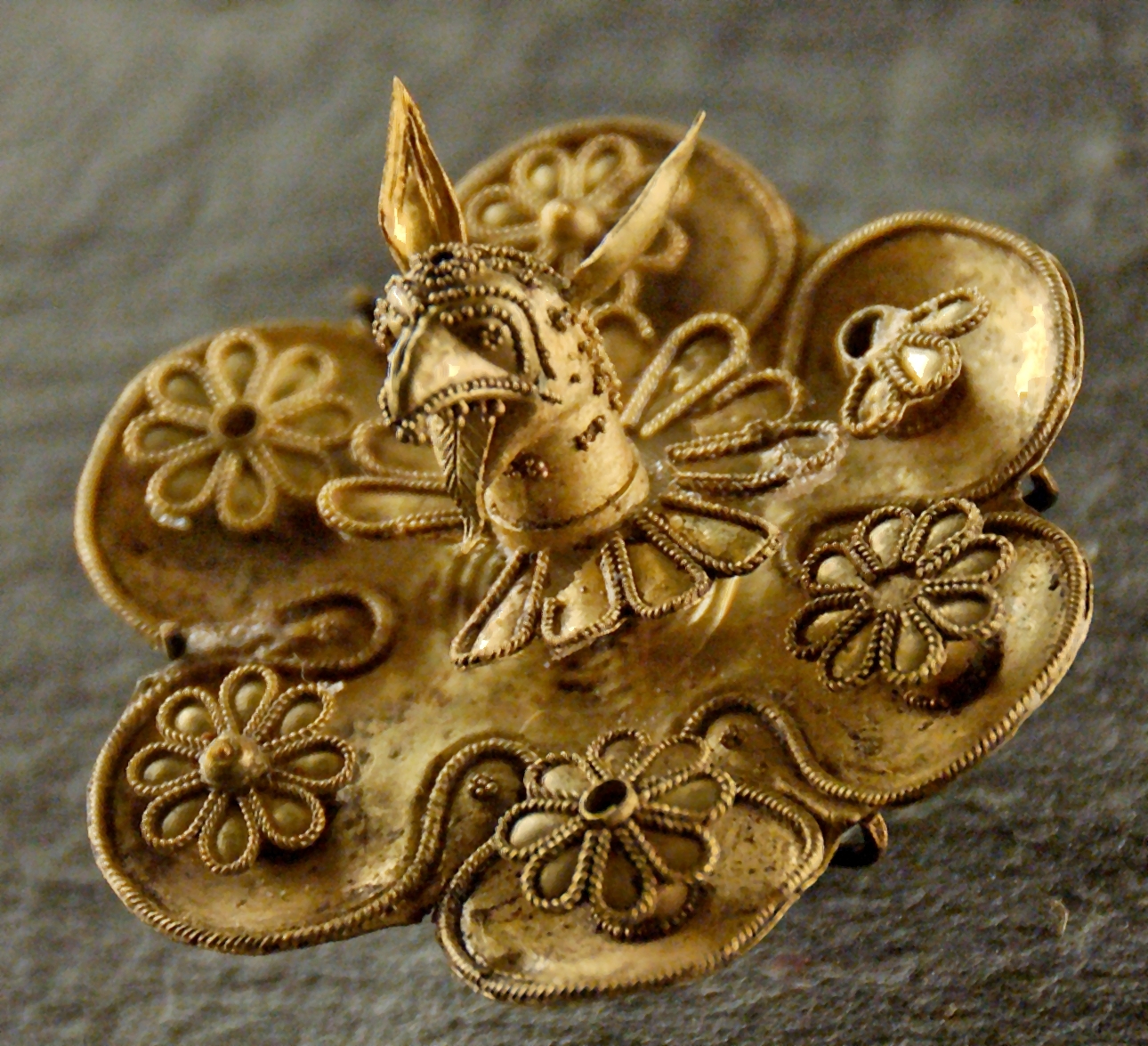
Grave Circle B in Mycenae is a 17th–16th century BCE royal cemetery situated outside the late Bronze Age citadel of Mycenae, southern Greece. This burial complex was constructed outside the fortification walls of Mycenae and together with Grave Circle A represent one of the major characteristics of the early phase of the Mycenaean civilization. Structure Grave Circle B, with a diameter of , is situated at a distance of west of the Lion Gate, the main entrance of Mycenae.. The burial structure was enclosed by a circular stone wall, thick and high... The Circle hosts a total of 26 graves; 14 of which are shaft graves and the rest simple cists. A total of 24 persons were found in the shafts, while six of the shaft graves were family tombs in which several occupants were found. Most shafts were marked by a pile of stones and on four of them stelae were erected. The latter were up to high. Two of the stelae, on graves Alpha and Gamma, were engraved with hunting scenes.. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; ; or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines, Greece, Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos; and south of Corinth. The site is inland from the Saronic Gulf and built upon a hill rising above sea level. In the second millennium BC, Mycenae was one of the major centres of Greek civilisation, a military stronghold which dominated much of southern Greece, Crete, the Cyclades and parts of southwest Anatolia. The period of History of Greece, Greek history from about 1600 BC to about 1100 BC is called Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean in reference to Mycenae. At its peak in 1350 BC, the citadel and lower town had a population of 30,000 and an area of . The first correct identification of Mycenae in modern literature was in 1700, during a survey conducted by the Venetian engineer Francesco Vandeyk on behalf of Francesco Grimani, the Provveditore Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Vessel In The Shape Of Swans, Rock Crystal Mycenae 16 C BC, NAMA 8638 080842
{{disambiguation ...
Small means of insignificant size. Small may also refer to: Science and technology * SMALL, an ALGOL-like programming language * ''Small'' (journal), a nano-science publication * <small>, an HTML element that defines smaller text Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * Small, in the British children's show Big & Small Other uses * Small (surname) * List of people known as the Small * "Small", a song from the album ''The Cosmos Rocks'' by Queen + Paul Rodgers See also * Smal (other) * Smalls (other) Smalls may refer to: * Smalls (surname) * Camp Robert Smalls, a United States Naval training facility * Fort Robert Smalls, a Civil War redoubt * Smalls Creek, a northern tributary of the Parramatta River * Smalls Falls, a waterfall in Maine, USA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In The 16th Century BC
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient DNA
Ancient DNA (aDNA) is DNA isolated from ancient sources (typically Biological specimen, specimens, but also environmental DNA). Due to degradation processes (including Crosslinking of DNA, cross-linking, deamination and DNA fragmentation, fragmentation) ancient DNA is more degraded in comparison with present-day genetic material. Genetic material has been recovered from paleo/archaeological and historical skeletal material, Mummy, mummified tissues, archival collections of non-frozen medical specimens, preserved plant remains, ice and from permafrost cores, marine and lake sediments and Excavation (archaeology), excavation dirt. Even under the best preservation conditions, there is an upper boundary of 0.4–1.5 million years for a sample to contain sufficient DNA for sequencing technologies. The oldest DNA sequenced from physical specimens are from mammoth molars in Siberia over 1 million years old. In 2022, two-million-year-old genetic material was recovered from sediments in G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The University of Manchester is considered a red brick university, a product of the civic university movement of the late 19th century. The current University of Manchester was formed in 2004 following the merger of the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology (UMIST) and the Victoria University of Manchester. This followed a century of the two institutions working closely with one another. Additionally, the university owns and operates major cultural assets such as the Manchester Museum, The Whitworth art gallery, the John Rylands Library, the Tabley House, Tabley House Collection and the Jodrell Bank Observatory – a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology had its origins in the Manchester Mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George E
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Papadimitriou
John K. Papadimitriou (; – April 11, 1963) was a Greek archaeologist. Along with George E. Mylonas, George Mylonas, he excavated Grave Circle B, Mycenae, Grave Circle B, the oldest known monumentalized burials at the Bronze Age site of Mycenae. The son of a schoolteacher, Papadimitriou studied archaeology and literature at the University of Athens. He served briefly in the Hellenic Navy and entered upon an academic career, before taking a post with the Greek Archaeological Service in 1929. Early in his career, he excavated on Corfu and at Nicopolis, and published two short studies on archaeological history. He also studied abroad at the Humboldt University of Berlin, Friedrich Wilhelms University in Berlin, which awarded him a doctorate in 1935. During the Axis occupation of Greece, Papadimitriou joined the Communism, communist-led National Liberation Front (Greece), National Liberation Front; his left-wing views attracted suspicion and sometimes hostility from the Greek e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Clytemnestra
The Tomb of Clytemnestra was a Mycenaean tholos type tomb built in c. 1250 BC. A number of architectural features such as the semi-column were largely adopted by later classical monuments of the first millennium BC, both in the Greek and Latin world. The Tomb of Clytemnestra with its imposing façade is together with the Treasury of Atreus the most monumental tomb of that type. The tomb is named after Clytemnestra, the wife of king Agamemnon, mythical ruler of Mycenae and leader of the Greeks in the Trojan War. However, it has been also suggested by modern scholars that this might have been Agamemnon's tomb or even that the tomb was never occupied due to the destruction of Mycenae which occurred during that time. Chronology and classification Tholos type tombs emerged in Mycenaean Greece in c. 1500-1450 BC as the resting places of the local royal families. They consisted of large circular burial chambers with high vaulted roofs and a straight entry passage (dromos) lined with ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beehive Tomb
A beehive tomb, also known as a tholos tomb (plural tholoi; from , ''tholotoi táphoi'', "domed tomb(s)"), is a burial structure characterized by its false dome created by corbelling, the superposition of successively smaller rings of mudbricks or, more often, stones. The resulting structure resembles a beehive, hence the traditional English name. Tholoi were used for burial in several cultures in the Mediterranean and West Asia, but in some cases they were used for different purposes such as homes (Cyprus), rituals (Bulgaria, Syria), and even fortification (Spain, Sardinia). Although Max Mallowan used the same name for the circular houses belonging to the Neolithic culture of Tell Halaf (Iraq, Syria and Turkey), there is no relationship between them. Greece In Greece, the vaulted ''tholoi'' are a monumental Late Bronze Age development. Their origin is a matter of considerable debate: were they inspired by the tholoi of Crete which were first used in the Early Minoan p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grave Circle B 1
A grave is a location where a dead body (typically that of a human, although sometimes that of an animal) is buried or interred after a funeral. Graves are usually located in special areas set aside for the purpose of burial, such as graveyards or cemeteries. In some religions, it is believed that the body must be burned or cremated for the soul to survive; in others, the complete decomposition of the body is considered to be important for the rest of the soul (see bereavement). Description The formal use of a grave involves several steps with associated terminology. ;Grave cut The excavation that forms the grave. Excavations vary from a shallow scraping to removal of topsoil to a depth of or more where a vault or burial chamber is to be constructed. However, most modern graves in the United States are only deep as the casket is placed into a concrete box (see burial vault) to prevent a sinkhole, to ensure the grave is strong enough to be driven over, and to prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mask Of Agamemnon
The Mask of Agamemnon is a gold funerary mask which was discovered at the Bronze Age site of Mycenae in southern Greece. The mask, displayed in the National Archaeological Museum of Athens, has been described by the historian Cathy Gere as the "''Mona Lisa'' of prehistory". German archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann, who discovered the artifact in 1876, believed that he had found the body of the Mycenaean king Agamemnon, leader of the Achaeans in the ancient Greek epic of the Trojan War, the ''Iliad''. Modern archaeological research suggests that the mask dates to about the 16th century BC, pre-dating the period of the mythical Trojan War by 300–400 years. Discovery Schliemann found the gold funeral mask in 1876, in a shaft tomb designated Grave V, at the site Grave Circle A, Mycenae."Behind the Mask of Agamemnon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrum
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially and is also known as "Colored gold#Green gold, green gold".Emsley, John (2003Nature's building blocks: an A–Z guide to the elements Oxford University Press. p. 168. . Electrum was used as early as the third millennium BC in the Old Kingdom of Egypt, sometimes as an exterior coating to the pyramidion, pyramidia atop ancient Egyptian pyramids and obelisks. It was also used in the making of ancient Beaker (archaeology) , drinking vessels. The first known metal coins made were of electrum, dating back to the end of the 7th century or the beginning of the 6th century BC. Etymology The name ''electrum'' is the Latinized form of the Greek language, Greek word ἤλεκτρον (''ḗlektron''), mentioned in the ''Odyssey'', referring to a metallic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |