|
Grandson, Switzerland
Grandson () is a municipality in the district of Jura-Nord Vaudois in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland. It is situated on the south-west tip of Lake Neuchâtel, about 25 km (15 miles) north of Lausanne. It was part of the Kingdom of Upper Burgundy until the death of Rudolph III of Burgundy (993-1032), also King of Lower Burgundy, the last in the male line, when it was united with the Holy Roman Empire. On 2 March 1476, during the Burgundian Wars, Charles the Bold was defeated here in the Battle of Grandson. History The Grandson family is first mentioned in the second half of the 11th century as ''Grancione''. The town was first mentioned around 1100 as ''de castro Grancione''. Around 1126 it was mentioned as ''castri Grandissoni'' and in 1154 it was called ''apud Grantionem''. Prehistoric settlements In May 1895 a farmer discovered a buried underground menhir weighing about three tons and about tall in Les Echâtelards. The monolith now stands in the vicini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jura-North Vaudois District
Jura-Nord Vaudois District (french: district du Jura-Nord vaudois) is a district in Vaud canton of Switzerland. Its capital is Yverdon-les-Bains. Geography Jura-Nord vaudois has an area, , of . Of this area, or 47.6% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 44.1% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 7.0% is settled (buildings or roads) and or 1.3% is unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data accessed 25 March 2010. Demographics Jura-Nord vaudois has a population () of . In there were 605 live births to Swiss citizens and 195 births to non-Swiss citizens, and in same time span there were 608 deaths of Swiss citizens and 48 non-Swiss citizen deaths. Ignoring immigration and emigratio ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
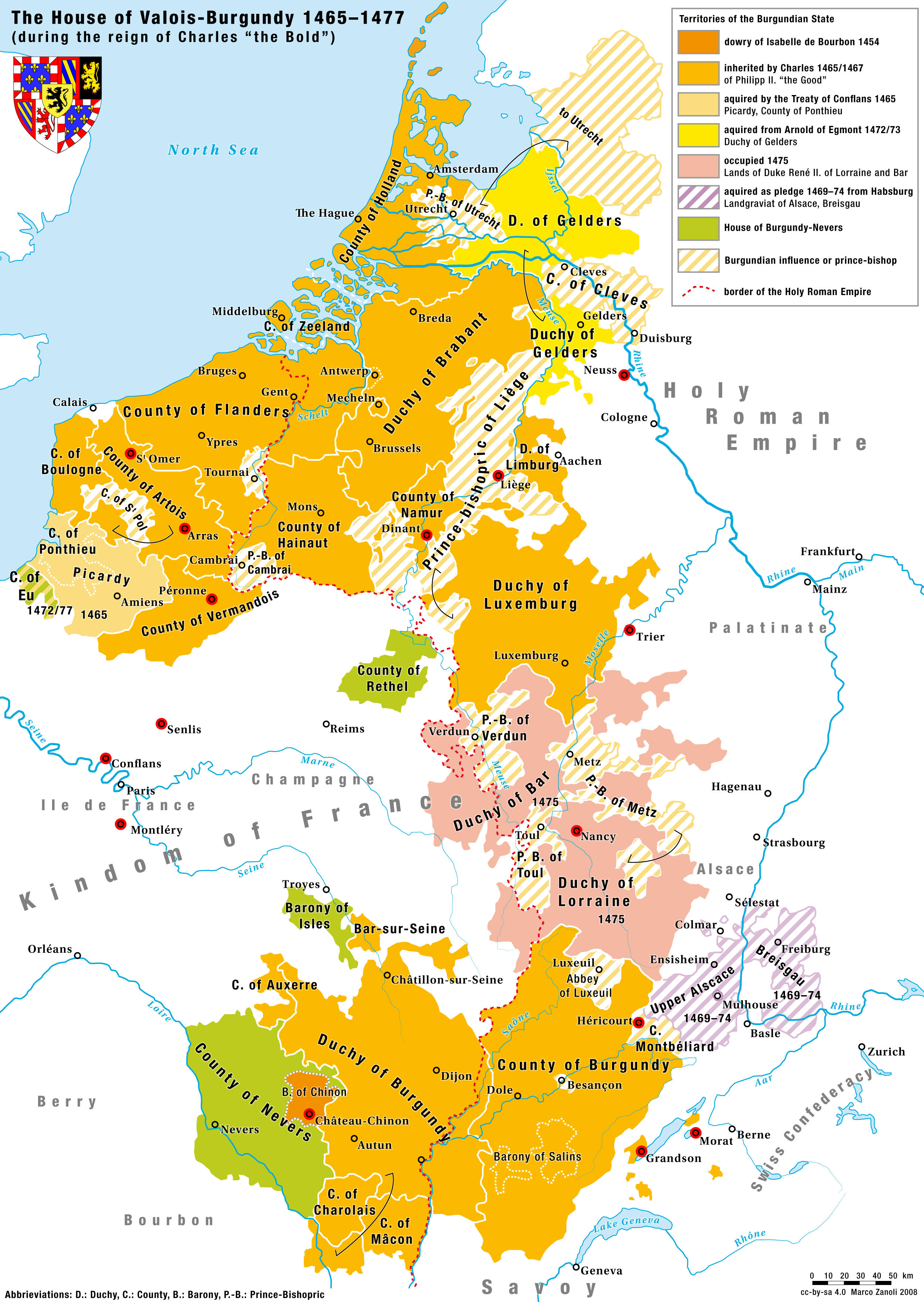
Charles The Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. Charles's main objective was to be crowned king by turning the growing Burgundian State into a territorially continuous kingdom. He declared himself and his lands independent, bought Alsace, Upper Alsace and conquered County of Zutphen, Zutphen, Duchy of Guelders, Guelders and Duchy of Lorraine, Lorraine, uniting at last Burgundian northern and southern possessions. This caused the enmity of several European powers and triggered the Burgundian Wars. Charles's early death at the Battle of Nancy at the hands of Swiss mercenaries fighting for René II, Duke of Lorraine, was of great consequence in European history. The Burgundian domains, long wedged between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire, were divided, but the precise disposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG , caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal , abbreviation = OSB , formation = , motto = (English: 'Pray and Work') , founder = Benedict of Nursia , founding_location = Subiaco Abbey , type = Catholic religious order , headquarters = Sant'Anselmo all'Aventino , num_members = 6,802 (3,419 priests) as of 2020 , leader_title = Abbot Primate , leader_name = Gregory Polan, OSB , main_organ = Benedictine Confederation , parent_organization = Catholic Church , website = The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict ( la, Ordo Sancti Benedicti, abbreviated as OSB), are a monastic religious order of the Catholic Church following the Rule of Saint Benedict. They are also sometimes called the Black Monks, in reference to the colour of their religious habits. They w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandson Castle
Grandson Castle (french: Château de Grandson ) is a medieval castle in the Swiss municipality of Grandson in the canton of Vaud. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance. History The Lords of Grandson were first mentioned in the second half of the 11th century, when the castle was built. It was sited on the shore of Lake Neuchâtel to control the coast road. The House of Grandson sired a number of powerful scions, including bishops of Basel, Lausanne, Toul and Verdun Over the following century, as the Lords of Grandson expanded their power, they often came into conflict with the nearby monastery of Romainmôtier. In the 13th century the castle was rebuilt by Otto I of Grandson. Otto I is the most famous of the Lords of Grandson. He was a close friend of Prince Edward of England and accompanied him in 1271 on the Crusades to the Holy Land. He participated on the side of the English king in the conquest of Wales in 1283. In 1291 he commanded the Crusader arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland In The Roman Era
The territory of modern Switzerland was a part of the Roman Republic and Empire for a period of about six centuries, beginning with the step-by-step conquest of the area by Roman armies from the 2nd century BC and ending with the Fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. The mostly Celtic tribes of the area were subjugated by successive Roman campaigns aimed at control of the strategic routes from Italy across the Alps to the Rhine and into Gaul, most importantly by Julius Caesar's defeat of the largest tribal group, the Helvetii, in the Gallic Wars in 58 BC. Under the '' Pax Romana'', the area was smoothly integrated into the prospering Empire, and its population assimilated into the wider Gallo-Roman culture by the 2nd century AD, as the Romans enlisted the native aristocracy to engage in local government, built a network of roads connecting their newly established colonial cities and divided up the area among the Roman provinces. Roman civilization be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia ( Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jura Water Correction
The correction of the waters of the Swiss Jura consisted of a wide series of hydrological undertakings carried out in Switzerland in the region of the three lakes: Lake Morat connected to Lake Neuchatel by the Broye Canal, the latter connected to Lake Bienne by the Thielle Canal, an area called the " Seeland”. These projects included the operations of cleaning, restoration and diversion of rivers. The main works took place in three distinct phases during the 19th and 20th centuries. The correction has helped regulate the hydrology. It limits the risk of flooding, particularly in the areas covered by the Aare. It has also added vast areas of valuable agricultural land through the drying out and subsequent sanitization and improvement of the swamps which used to lie between these three lakes. Many rivers have been corrected in Switzerland, for example the Rhône, which has undergone several adjustments between the 19th century and present day. However, the realignments in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stilt House
Stilt houses (also called pile dwellings or lake dwellings) are houses raised on stilts (or piles) over the surface of the soil or a body of water. Stilt houses are built primarily as a protection against flooding; they also keep out vermin. The shady space under the house can be used for work or storage. Arctic Houses where permafrost is present, in the Arctic, are built on stilts to keep permafrost under them from melting. Permafrost can be up to 70% water. While frozen, it provides a stable foundation. However, if heat radiating from the bottom of a home melts the permafrost, the home goes out of level and starts sinking into the ground. Other means of keeping the permafrost from melting are available, but raising the home off the ground on stilts is one of the most effective ways. Indo-Pacific Raised rectangular houses are one of the cultural hallmarks of the Austronesian peoples and are found throughout the regions in Island Southeast Asia, Island Melanesia, Micron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |