|
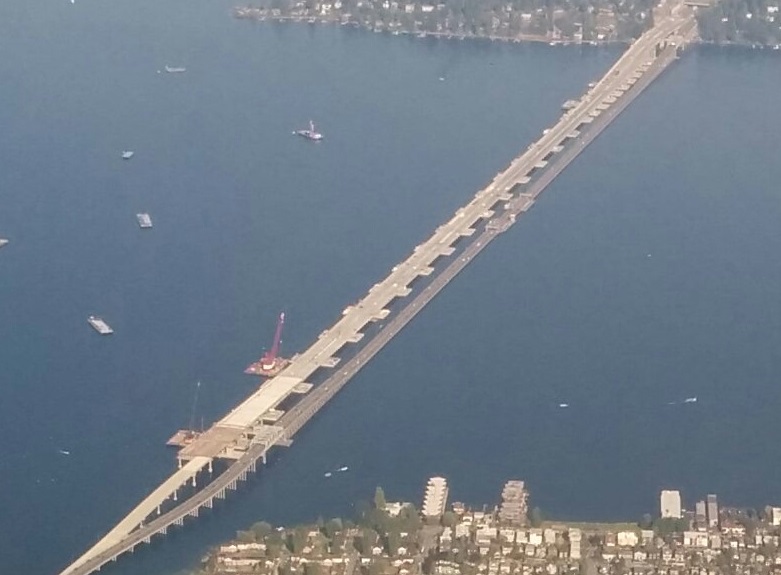
Governor Albert D. Rosellini Bridge—Evergreen Point
The Evergreen Point Floating Bridge, also known as the 520 Bridge and officially the Governor Albert D. Rosellini Bridge, is a floating bridge that carries Washington State Route 520 across Lake Washington from Seattle to its eastern suburbs. The floating span is the longest floating bridge in the world, as well as the world's widest measuring at its midpoint. It is a toll bridge and uses electronic collection. The bridge opened in April 2016 and replaced the original Evergreen Point Floating Bridge at the site, which was shorter and four lanes wide. The original bridge was vulnerable to earthquakes and strong wind events, which would frequently shut down traffic. Planning for a replacement began in 1997 and was approved in 2011; the $4.65 billion budget was derived from state gas taxes and federal sources, as well as toll revenue. Construction of the 77 concrete pontoons began in 2011 and on-site assembly began in 2014. The Evergreen Point Floating Bridge carries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Washington
Lake Washington () is a large freshwater lake adjacent to the city of Seattle, Washington, United States. It is the largest lake in King County, Washington, King County and the second largest natural lake in the state of Washington (state), Washington, after Lake Chelan. It borders the cities of Seattle on the west, Bellevue, Washington, Bellevue and Kirkland, Washington, Kirkland on the east, Renton, Washington, Renton on the south, and Kenmore, Washington, Kenmore on the north, and encloses Mercer Island, Washington, Mercer Island. The lake is fed by the Sammamish River at its north end and the Cedar River (Washington), Cedar River at its south. Lake Washington has been known to the Duwamish people, Duwamish and other Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples living on the lake for millennia as (lit. "lake" in Lushootseed). At the time of European settlement, it was recorded as At-sar-kal in a map sketched by engineer Abiel W. Tinkham; and the Chinook Jargon name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1964 State Highway Renumbering (Washington)
The 1964 state highway renumbering was a reorganization of state highways in the U.S. state of Washington. The new system, based on sign routes (SR, later changed to state routes), replaced the primary and secondary highway system implemented in 1937. It was first signed in January 1964 and codified into the Revised Code of Washington in 1970. History The former numbering system of primary and secondary state highways, using lettered suffixes and unnamed branches, created confusion for motorists as the system expanded. The system also ignored, or conflicted with, the federal highway system and the then-developing Interstate Highway System. The state highway department originally planned for a major highway renumbering in 1957, expanding on the existing primary and secondary system with numbers as high as 59, but serious consideration of a full-scale renumbering began in 1962. It had the specific goal of replacing letter suffixes with two- and three-digit numbers, which wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate 5 Express Lanes
Interstate 5 (I-5) is an Interstate Highway on the West Coast of the United States that serves as the region's primary north–south route. It spans across the state of Washington, from the Oregon state border at Vancouver, through the Puget Sound region, to the Canadian border at Blaine. Within the Seattle metropolitan area, the freeway connects the cities of Tacoma, Seattle, and Everett. I-5 is the only interstate to traverse the whole state from north to south and is Washington's busiest highway, with an average of 274,000 vehicles traveling on it through Downtown Seattle on a typical day. The segment in Downtown Seattle is also among the widest freeways in the United States, at 13 lanes, and includes a set of express lanes that reverse direction depending on time of the day. Most of the freeway is four lanes in rural areas and six to eight lanes in suburban areas, including a set of high-occupancy vehicle lanes in the latter. I-5 also has three related auxiliary Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google News Archive
Google News Archive is an extension of Google News providing free access to scanned archives of newspapers and links to other newspaper archives on the web, both free and paid. Some of the news archives date back to 18th century. There is a timeline view available, to select news from various years. History The archive went live on June 6, 2006, after Google acquired PaperofRecord.com, originally created by Robert J. Huggins and his team at Cold North Wind, Inc. The acquisition was not publicly announced by Cold North Wind until 2008. While the service initially provided a simple index of other web pages, on September 8, 2008, Google News began to offer indexed content from scanned newspapers. The depth of chronological coverage varies. Newspapers were thought to have escaped copyright obligations of news articles because of Google's method of publishing the archives as searchable image files of the actual newspaper pages, rather than as pure text of articles. In 2011, Goo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American not-for-profit organization, not-for-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association, and produces news reports that are distributed to its members, major U.S. daily newspapers and radio and television broadcasters. Since the award was established in 1917, the AP has earned 59 Pulitzer Prizes, including 36 for photography. The AP is also known for its widely used ''AP Stylebook'', its AP polls tracking National Collegiate Athletic Association, NCAA sports, sponsoring the National Football League's annual awards, and its election polls and results during Elections in the United States, US elections. By 2016, news collected by the AP was published and republished by more than 1,300 newspapers and broadcasters. The AP operates 235 news bureaus in 94 countries, and publishes in English, Spanish, and Arabic. It also operates the AP Radio Network, which provides twice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellensburg Daily Record
''The Daily Record'' is an American daily newspaper published in Ellensburg, Washington. The ''Record'' is published four days a week with an afternoon edition each Tuesday through Thursday and a weekend edition is delivered on Saturday mornings. It has a circulation of 2,619. History This newspaper is a successor to the ''Kittitas County Localizer'', first published on July 12, 1883. After the official founding of the town of Ellensburg, that paper became the ''Ellensburg Localizer''. On July 1, 1909, the paper, now under the ownership of William S. Zimmerman and J.C. "Cliff" Kaynor, changed its name to the ''Evening Record''. It is from this event that the modern edition of the newspaper marks its birth. Kaynor bought Zimmerman's share in 1912 and continued as the paper's sole publisher for nearly fifty years. The paper's name was changed to ''The Ellensburg Daily Record'' on April 23, 1938, and on March 14, 1973, the paper became simply ''The Daily Record'' to reflect its ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest Windstorm
Pacific Northwest windstorms, sometimes colloquially known as Big Blows, are extratropical cyclones which form in the Pacific basin, and affect land areas in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and British Columbia, Canada. They form as cyclonic windstorms associated with areas of low atmospheric pressure that track across the North Pacific Ocean towards western North America. Deep low pressure areas are relatively common over the North Pacific. They are most common in the winter months. On average, the month when most windstorms form is November or December. The closest analogue to these storms are European windstorms, which develop over the eastern portion of the North Atlantic Ocean as opposed to the North Pacific. Nor'easters, a similar class of extratropical cyclones, commonly affect the east coast of North America. While the storms on the East Coast are named "nor'easters", the Pacific Northwest windstorms are not called "nor'westers" because the cyclones' primary wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storm Surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the normal tidal level, and does not include waves. The main meteorological factor contributing to a storm surge is high-speed wind pushing water towards the coast over a long fetch. Other factors affecting storm surge severity include the shallowness and orientation of the water body in the storm path, the timing of tides, and the atmospheric pressure drop due to the storm. As extreme weather becomes more intense and the sea level rises due to climate change, storm surges are expected to cause more risk to coastal populations. Communities and governments can adapt by building hard infrastructure, like surge barriers, soft infrastructure, like coastal dunes or mangroves, improving coastal construction practices and building social strat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibration
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the oscillations can only be analysed statistically (e.g. the movement of a tire on a gravel road). Vibration can be desirable: for example, the motion of a tuning fork, the reed in a woodwind instrument or harmonica, a mobile phone, or the cone of a loudspeaker. In many cases, however, vibration is undesirable, wasting energy and creating unwanted sound. For example, the vibrational motions of engines, electric motor An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to gene ...s, or any Machine, mechanical device in operation are typically unwanted. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HistoryLink
HistoryLink is an online encyclopedia of Washington (state), Washington state history. The site has more than 8,100 entries and attracts 23,000 weekly visitors. It has 500 biographies and more than 14,000 images. The non-profit historical organization History Ink produces HistoryLink.org, stating that it is the nation's first online encyclopedia of local and state history created expressly for the Internet. Walt Crowley was the founding president and executive director. History In 1997, Crowley discussed preparing a Seattle-King County, Washington, King County historical encyclopedia for the 2001 sesquicentennial of the Denny Party. His wife Marie McCaffrey suggested publishing the encyclopedia on the Internet. They and Paul Dorpat incorporated History Ink on November 10, 1997, with seed money from Patsy Bullitt Collins, Priscilla "Patsy" Collins, by birth a member of Seattle's wealthy and prominent Bullitt family. The prototype of HistoryLink.org debuted on May 1, 1998, and att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
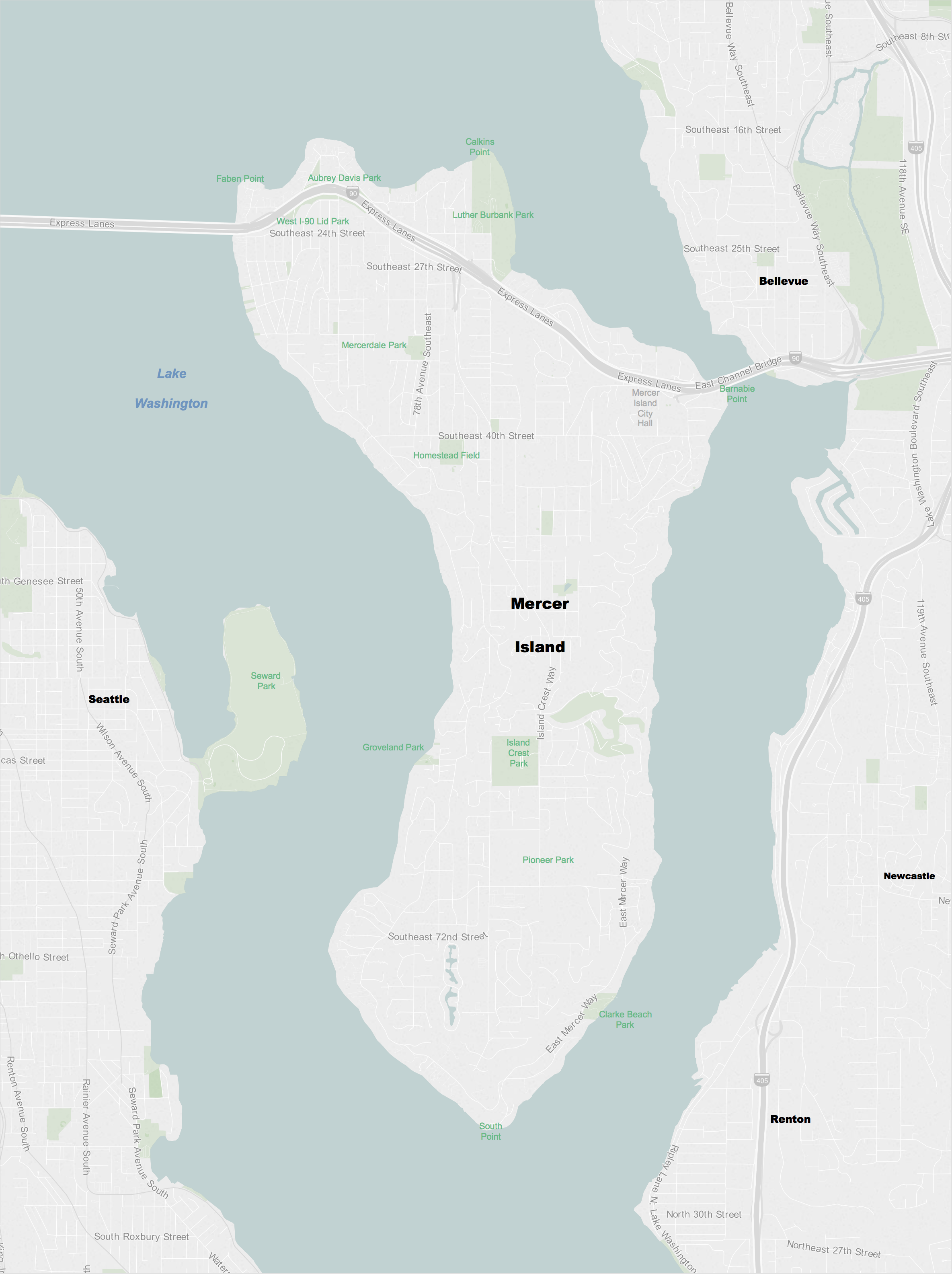
Mercer Island, Washington
Mercer Island is a city in King County, Washington, United States, located on an island of the same name in the southern portion of Lake Washington. Mercer Island is in the Seattle metropolitan area, with Seattle to its west and Bellevue to its east. The island is connected to the mainland on both sides by bridges carrying Interstate 90, with the city of Seattle to the west and the city of Bellevue to the east. The Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge and the parallel Homer M. Hadley Memorial Bridge are floating bridges that span Lake Washington and carry, respectively, eastbound and westbound lanes of Interstate 90 and connect Mercer Island to the northern portion of Seattle's South End. I-90 traverses the northern portion of Mercer Island and is then carried from the island to Bellevue over the East Channel of Lake Washington by the East Channel Bridge. Mercer Island is located closer to Bellevue than it is to Seattle, and is therefore often considered to be part of King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |