|
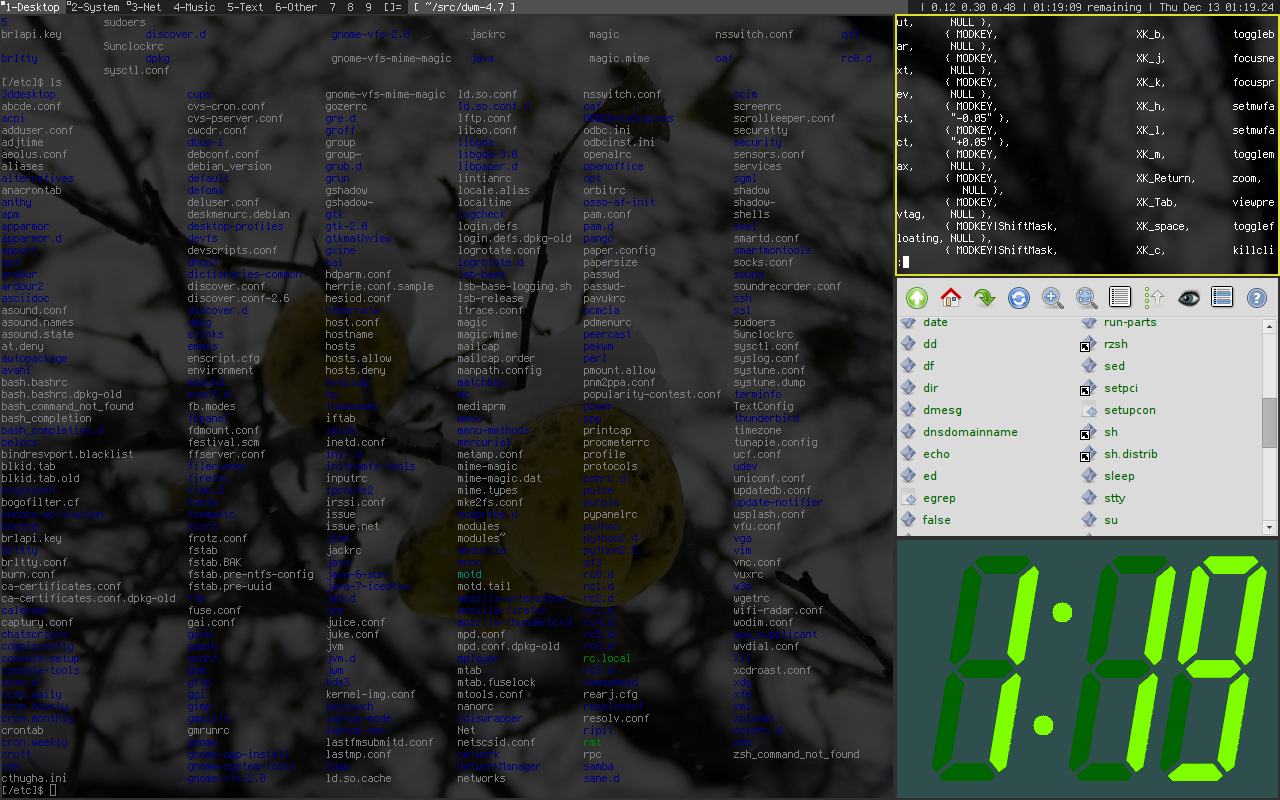
GNU Emacs
GNU Emacs is a text editor and suite of free software tools. Its development began in 1984 by GNU Project founder Richard Stallman, based on the Emacs editor developed for Unix operating systems. GNU Emacs has been a central component of the GNU project and a flagship project of the free software movement. The program's tagline is "the extensible self-documenting text editor." Most functionality in GNU Emacs is implemented in user-accessible Emacs Lisp, allowing deep extensibility directly by users and through community-contributed packages. Its built-in features include a file browser and editor (Dired), an advanced calculator (Calc), an email client and news reader (Gnus), a Language Server Protocol integration, and the productivity system Org-mode. A large community of users have contributed extensions such as the Git interface Magit, the Vim (text editor), Vim emulation layer Evil, several search frameworks, the window manager EXWM, and tools for working with a wide range of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magit
Magit ( or ) is an interface to the Git version control system, available as a GNU Emacs package written in Emacs Lisp. It is available through the MELPA package repository, on which it is the most-downloaded non-library package, with over 4.3 million downloads as of September 2024. Like many graphical user interfaces, Magit provides a visual interface to represent version control actions; however, it uses a keyboard-centric model, and also functions as a text-based user interface. The issue of key-memorization is mitigated through use of a popup menu which displays the actions available to the user — serving as a Mnemonics, mnemonic aid. History Magit was created by Marius Vollmer in 2008, with Jonas Bernoulli assuming the role of maintainer in 2013. Since its release, Magit has seen a high degree of Open-source software development, community involvement, with 350 individuals having contributed code to this free software project as of September 2020. In 2018 Magit under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNOME 3
GNOME 3 is the third major release of the GNOME desktop environment. A major departure from technologies implemented by its predecessors, GNOME 3 introduced a dramatically different user interface. It was the first GNOME release to utilize a unified graphical shell known as GNOME Shell. It also introduced support for the Wayland display protocol and added integration with other key technologies such as Flatpak during its development lifecycle. While loose planning began as early as 2004, it was not officially announced until 2008, and received an initial release in 2011. It was superseded by GNOME 40 in 2021. Features Much of GNOME 3's user interface changes were based-on attempts at simplification and rethinking of traditional desktop computing workflows. Eschewing the beige colors present in GNOME 2 in favor of a modern black and gray, a new look and feel was implemented, which became known as Adwaita. Possibly the single-most significant feature change that GNOME 3 int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public Licenses (GNU GPL or simply GPL) are a series of widely used free software licenses, or ''copyleft'' licenses, that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, or modify the software. The GPL was the first copyleft license available for general use. It was originally written by Richard Stallman, the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The licenses in the GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. The GPL is more restrictive than the GNU Lesser General Public License, and even more distinct from the more widely used permissive software licenses such as BSD, MIT, and Apache. Historically, the GPL license family has been one of the most popular software licenses in the free and open-source software (FOSS) domai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David A
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; page 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Stallman - Fête De L'Humanité 2014 - 010
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", " Dick", " Dickon", " Dickie", "Rich", " Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Anderse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EXWM
In computing, a tiling window manager is a window manager with the organization of the screen often dependant on mathematical formulas to organise the windows into a non-overlapping frame. This is opposed to the more common approach used by stacking window managers, which allow the user to drag windows around, instead of windows snapping into a position. This allows for a different style of organization, although it departs from the traditional desktop metaphor. History Xerox PARC The first Xerox Star system (released in 1981) tiled application windows, but allowed dialog boxes and property windows to overlap. Later, Xerox PARC also developed CEDAR (released in 1982), the first windowing system using a tiled window manager. Various vendors Next in 1983 came Andrew WM, a complete tiled windowing system later replaced by X11. Microsoft's Windows 1.0 (released in 1985) also used tiling (see sections below). In 1986 came Digital Research's GEM 2.0, a windowing system for the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vim (text Editor)
Vim (; : "Vim is pronounced as one word, like Jim, not vi-ai-em. It's written with a capital, since it's a name, again like Jim." ''vi improved'') is a free and open-source, screen-based text editor program. It is an improved Clone (computing), clone of Bill Joy's vi (text editor), vi. Vim's author, Bram Moolenaar, derived Vim from a port of the Stevie (text editor), Stevie editor for Amiga and released a version to the public in 1991. Vim is designed for use both from a command-line interface and as a standalone application in a graphical user interface. Since its release for the Amiga, cross-platform development has made it available on #Availability, many other systems. In 2018, it was voted the most popular editor amongst ''Linux Journal'' readers; in 2015 the Stack Overflow developer survey found it to be the third most popular text edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Org-mode
Mode (also: ''org-mode''; ) is a mode for document editing, formatting, and organizing within the free software text editor GNU Emacs and its derivatives, designed for notes, planning, and authoring. The name is used to encompass plain text files ("org files") that include simple marks to indicate levels of a hierarchy (such as the outline of an essay, a topic list with subtopics, nested computer code, etc.), and an editor with functions that can read the markup and manipulate hierarchy elements (expand/hide elements, move blocks of elements, check off to-do list items, etc.). Org Mode was created by Carsten Dominik in 2003, originally to organize his own life and work, and since the first release numerous other users and developers have contributed to this free software package. Emacs has included Org Mode as a major mode by default since 2006. Bastien Guerry is the maintainer since 2010, in cooperation with an active development community. Since its success in Emacs, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Server Protocol
The Language Server Protocol (LSP) is an open, JSON-RPC-based protocol for use between source code editors or integrated development environments (IDEs) and servers that provide "language intelligence tools": programming language-specific features like code completion, syntax highlighting and marking of warnings and errors, as well as refactoring routines. The goal of the protocol is to allow programming language support to be implemented and distributed independently of any given editor or IDE. In the early 2020s, LSP quickly became a "norm" for language intelligence tools providers. History LSP was originally developed for Microsoft Visual Studio Code and is now an open standard. On June 27, 2016, Microsoft announced a collaboration with Red Hat and Codenvy to standardize the protocol's specification. Its specification is hosted and developed on GitHub. Background Modern IDEs provide programmers with sophisticated features like code completion, refactoring, navigating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnus
Gnus (), or Gnus Network User Services, is a message reader which is part of GNU Emacs. It supports reading and composing both e-mail and news and can also act as an RSS reader, web processor, and directory browser for both local and remote filesystems. Gnus blurs the distinction between news and e-mail, treating them both as "articles" that come from different sources. News articles are kept separate by group, and e-mail can be split into arbitrary groups, similar to folders in other mail readers. In addition, Gnus is able to use a number of web-based sources as inputs for its groups. Features Some Gnus features: * a range of backends that support any or all of: ** reading email from the local filesystem, or over a network via IMAP or POP3 ** reading web pages via an RSS feed ** treating a directory of files, either local or remote (via FTP or other method) as articles to browse ** reading Usenet News, including the Gmane and Gwene mail-to-news archives of mailing lists ** s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dired
Dired (for Directory Editor) is a computer program for editing file system directories. It typically runs inside the Emacs text editor as a specialized mode, though standalone versions have been written. Dired was the file manager, or visual editor of file system information. The first version of Dired was written as a stand-alone program independently in 1972 by Dave Lebling at Project MAC, and circa 1974 by Stan Kugell at the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (SAIL). It was incorporated into GNU Emacs from the earliest versions, and re-implemented in C and C++ on other operating systems. When run in Emacs, dired displays an ls-like file listing in an Emacs buffer. The list can be navigated using standard navigation commands. Several Emacs Lisp scripts have been developed to extend Dired in Emacs. In combination with Tramp it is able to access remote file systems for editing files by means of SSH, FTP, telnet and many other protocols, as well as the capabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems ( SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE ( HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). The early versions of Unix—which are retrospectively referred to as " Research Unix"—ran on computers such as the PDP-11 and VAX; Unix was commonly used on minicomputers and mainframes from the 1970s onwards. It distinguished itself from its predecessors as the first portable operating system: almost the entire operating system is written in the C programming language (in 1973), which allows U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |