|
Glossary Of Power Generation
The following is a list of common definitions related to power generation. __NOTOC__ A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z References External linksStanwell Corporation - Glossary {{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140317121950/http://www.aemo.com.au/Glossary/ , date=2014-03-17 Energy production Power Generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its d ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Intensity
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, C and C being stable, while C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual ability to form polymers at the temperatures commonly encountered on Earth, enables this element to serve as a common element of all known life. It is the second most abundant element in the human body by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion Valve
A thermal expansion valve or thermostatic expansion valve (often abbreviated as TEV, TXV, or TX valve) is a component in vapor-compression refrigeration and air conditioning systems that controls the amount of refrigerant released into the evaporator and is intended to regulate the superheat of the refrigerant that flows out of the evaporator to a steady value. Although often described as a "thermostatic" valve, an expansion valve is not able to regulate the evaporator's temperature to a precise value. The evaporator's temperature will vary only with the evaporating pressure, which will have to be regulated through other means (such as by adjusting the compressor's capacity). Thermal expansion valves are often referred to generically as "metering devices", although this may also refer to any other device that releases liquid refrigerant into the low-pressure section but does not react to temperature, such as a capillary tube or a pressure-controlled valve. Theory of operation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Water
Hard water is water that has a high mineral content (in contrast with "soft water"). Hard water is formed when water percolates through deposits of limestone, chalk or gypsum, which are largely made up of calcium and magnesium carbonates, bicarbonates and sulfates. Drinking hard water may have moderate health benefits. It can pose critical problems in industrial settings, where water hardness is monitored to avoid costly breakdowns in boilers, cooling towers, and other equipment that handles water. In domestic settings, hard water is often indicated by a lack of foam formation when soap is agitated in water, and by the formation of limescale in kettles and water heaters. Wherever water hardness is a concern, water softening is commonly used to reduce hard water's adverse effects. Origins Natural rainwater, snow and other forms of precipitation typically have low concentrations of divalent cations such as calcium and magnesium. They may have small concentrations of ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force, electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change Alternating current, AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
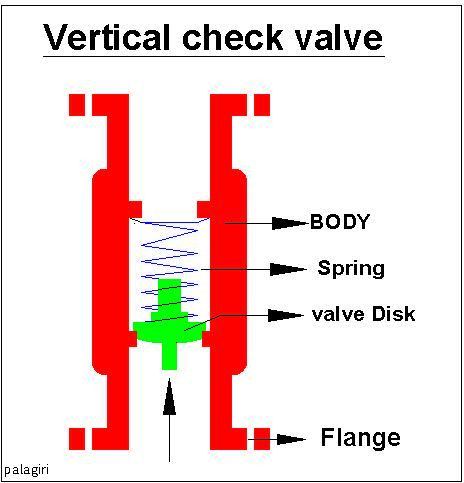
Non-return Valve
A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction. Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave. There are various types of check valves used in a wide variety of applications. Check valves are often part of common household items. Although they are available in a wide range of sizes and costs, check valves generally are very small, simple, and inexpensive. Check valves work automatically and most are not controlled by a person or any external control; accordingly, most do not have any valve handle or stem. The bodies (external shells) of most check valves are made of plastic or metal. An important concept in check valves is the cracking pressure which is the minimum differential upstream pressure between inlet and outlet at which the valve will operate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure. Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size of the vessel, the contents, working pressure, mass constraints, and the number of items required. Pressure vessels can be dangerous, and fatal accidents have occurred in the history of their development and operation. Consequently, pressure vessel design, manufacture, and operation are regulated by engineering authorities backed by legislation. For these reasons, the definition of a pressure vessel varies from country to country. The design involves parameters such as maximum safe operating pressure and temperature, safety factor, corrosion allowance and minimum design temperature (for brittle fracture). Construction is tested using nondestructive testing, such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and pressure tests. Hydrostatic pressure t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulverizer
Comminution is the reduction of solid material A material is a matter, substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an Physical object, object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical property, physical ...s from one average particle size to a smaller average particle size, by Crusher, crushing, Mill (grinding), grinding, cutting, Vibrator (mechanical), vibrating, or other processes. Comminution is related to pulverization and grinding. All use mechanical devices, and many types of mill (grinding), mills have been invented. Concomitant with size reduction, comminution increases the surface area of the solid. For example, a pulverizer mill is used to Pulverized coal-fired boiler, pulverize coal for combustion in the steam-generating furnaces of Coal-fired power station, coal power plants. A cement mill produces finely ground ingredients for portland cement. A hammer mill is used on farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impulse Turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator.Munson, Bruce Roy, T. H. Okiishi, and Wade W. Huebsch. "Turbomachines." Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. 6th ed. Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons, 2009. Print. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Gas, steam, and water turbines have a casing around the blades that contains and controls the working fluid. Modern steam turbines frequently employ both reaction and impulse in the same unit, typically varying the degree of reaction and impulse from the blade root to its periphery. History Hero of Alexandria demonstrated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brayton Cycle
The Brayton cycle, also known as the Joule cycle, is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of certain heat engines that have air or some other gas as their working fluid. It is characterized by isentropic process, isentropic compression and expansion, and isobaric process, isobaric heat addition and rejection, though practical engines have adiabatic process, adiabatic rather than isentropic steps. The most common current application is in airbreathing jet engines and gas turbine engines. The engine cycle is named after George Brayton (1830–1892), the American engineer, who developed the Brayton Ready Motor in 1872, using a piston compressor and piston expander. An engine using the cycle was originally proposed and patented by Englishman John Barber (engineer), John Barber in 1791, using a reciprocating compressor and a turbine expander. There are two main types of Brayton cycles: closed and open. In a closed cycle, the working gas stays inside the engine. Heat i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
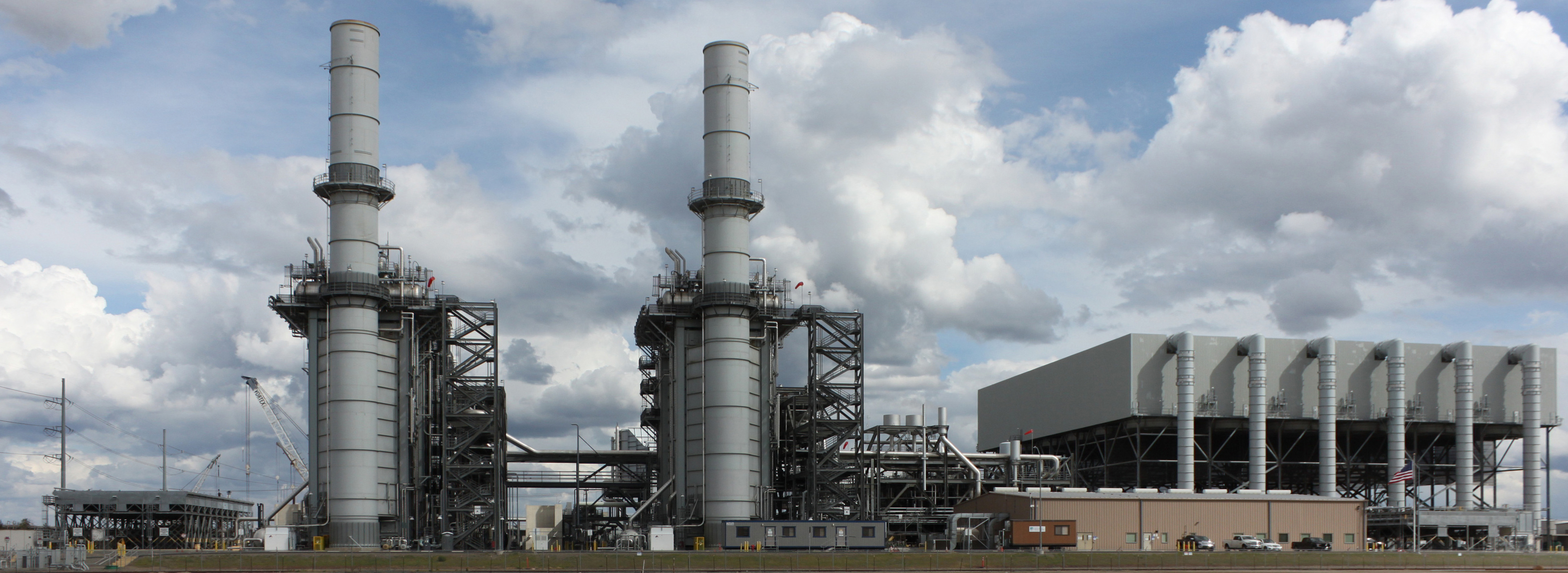
Combined Cycle Gas Turbine
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plant, which is a kind of gas-fired power plant. The same principle is also used for marine propulsion, where it is called a combined gas and steam (COGAS) plant. Combining two or more thermodynamic cycles improves overall efficiency, which reduces fuel costs. The principle is that after completing its cycle in the first engine, the working fluid (the exhaust) is still hot enough that a second subsequent heat engine can extract energy from the heat in the exhaust. Usually the heat passes through a heat exchanger so that the two engines can use different working fluids. By generating power from multiple streams of work, the overall efficiency can be increased by 50–60%. That is, from an overall efficiency of the system of say ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Continuous Rating
In electrical engineering and mechanical engineering, the power rating of equipment is the highest power input allowed to flow through particular equipment. According to the particular discipline, the term ''power'' may refer to electrical or mechanical power. A power rating can also involve average and maximum power, which may vary depending on the kind of equipment and its application. Power rating limits are usually set as a guideline by the manufacturers, protecting the equipment, and simplifying the design of larger systems, by providing a level of operation under which the equipment will not be damaged while allowing for a certain safety margin. Equipment types Dissipative equipment In equipment that primarily dissipates electric power or converts it into mechanical power, such as resistors, and speakers, the power rating given is usually the maximum power that can be safely dissipated by the equipment. The usual reason for this limit is heat, although in certa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |