|
Geodesic Airframe
A geodetic airframe is a type of construction for the airframes of aircraft developed by United Kingdom, British aeronautical engineer Barnes Wallis in the 1930s (who sometimes spelt it "geodesic"). Earlier, it was used by Prof. Schütte for the Schütte Lanz Airship SL 1 in 1909. It makes use of a space frame formed from a spirally crossing basket-weave of load-bearing members.Buttler, p.93 The principle is that two geodesic, geodesic arcs can be drawn to intersect on a curving surface (the fuselage) in a manner that the Torsion (mechanics), torsional load on each cancels out that on the other.Buttler, p.94 Early examples The "diagonal rider" structural element was used by Joshua Humphreys in the Original six frigates of the United States Navy, first US Navy sail frigates in 1794. Diagonal riders are viewable in the interior hull structure of the preserved USS Constitution, USS ''Constitution'' on display in Boston Harbor. The structure was a pioneering example of placing "no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Warwick Geodesic Fuselage
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 1867, acquired more businesses, and began branching out into military hardware and shipbuilding. In 1911, the company expanded into aircraft manufacturer, aircraft manufacture and opened a flying school. They expanded even further into electrical and railway manufacturing, and in 1928 acquired an interest in the Supermarine. Beginning in the 1960s, various parts of the company were nationalised, and in 1999 the rest of the company was acquired by Rolls-Royce Holdings, Rolls-Royce plc, which sold the defence arm to Alvis plc. The Vickers name lived on in Alvis Vickers, until the latter was acquired by BAE Systems in 2004 to form BAE Systems Platforms & Services, BAE Systems Land Systems. History Early history Vickers was formed in Sheffiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
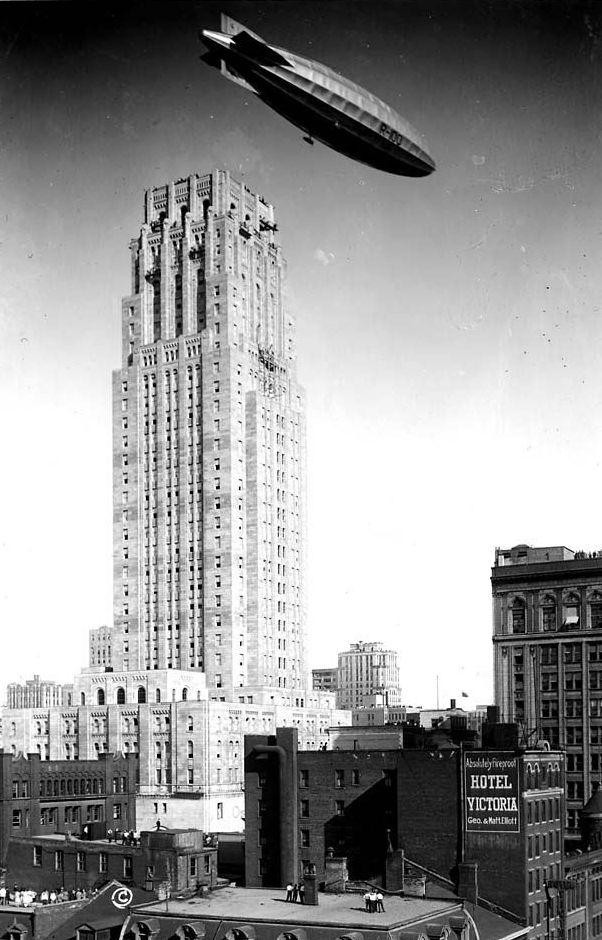
R100
His Majesty's Airship R100 was a privately designed and built British rigid airship made as part of a two-ship competition to develop a commercial airship service for use on British Empire routes as part of the Imperial Airship Scheme. The other airship, the R101, was built by the British Air Ministry, but both airships were funded by the Government. R100 was built by the Airship Guarantee Company, a specially created subsidiary of the armaments firm Vickers-Armstrongs, led by Commander Dennis Burney. The design team was headed by Barnes Wallis, later famous for his invention of the bouncing bomb. The design team also included Nevil Shute Norway as the senior stress engineer. R100 first flew in December 1929. It made a series of trial flights and a successful return crossing of the Atlantic in July–August 1930, but following the crash of R101 in October 1930 the Imperial Airship Scheme was terminated and R100 was broken up for scrap. Background R100 was built as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesic (other)
A geodesic is a curve representing in some sense the shortest path between two points on a surface. Geodesic may also refer to: * Geodesic (general relativity), generalization of the notion of a "straight line" to curved spacetime * An adjective meaning "related to geodesy", the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's geometric shape * Geodesic dome, a hemispherical lattice-shell structure made from triangles, the shape of which is called a geodesic polyhedron A geodesic polyhedron is a convex polyhedron made from triangles. They usually have icosahedral symmetry, such that they have 6 triangles at a vertex, except 12 vertices which have 5 triangles. They are the dual of corresponding Goldberg po ... See also * * Geodetic (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesic Dome
A geodesic dome is a hemispherical thin-shell structure (lattice-shell) based on a geodesic polyhedron. The rigid triangular elements of the dome distribute stress throughout the structure, making geodesic domes able to withstand very heavy loads for their size. History The first geodesic dome was designed after World War I by Walther Bauersfeld, chief engineer of Carl Zeiss Jena, an optical company, for a planetarium to house his planetarium projector. An initial, small dome was patented and constructed by the firm of Dykerhoff and Wydmann on the roof of the Carl Zeiss Werke in Jena, Germany. A larger dome, called "The Wonder of Jena", opened to the public on July 18, 1926. Twenty years later, Buckminster Fuller coined the term "geodesic" from field experiments with artist Kenneth Snelson at Black Mountain College in 1948 and 1949. Although Fuller was not the original inventor, he is credited with the U.S. popularization of the idea for which he received on 29 J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
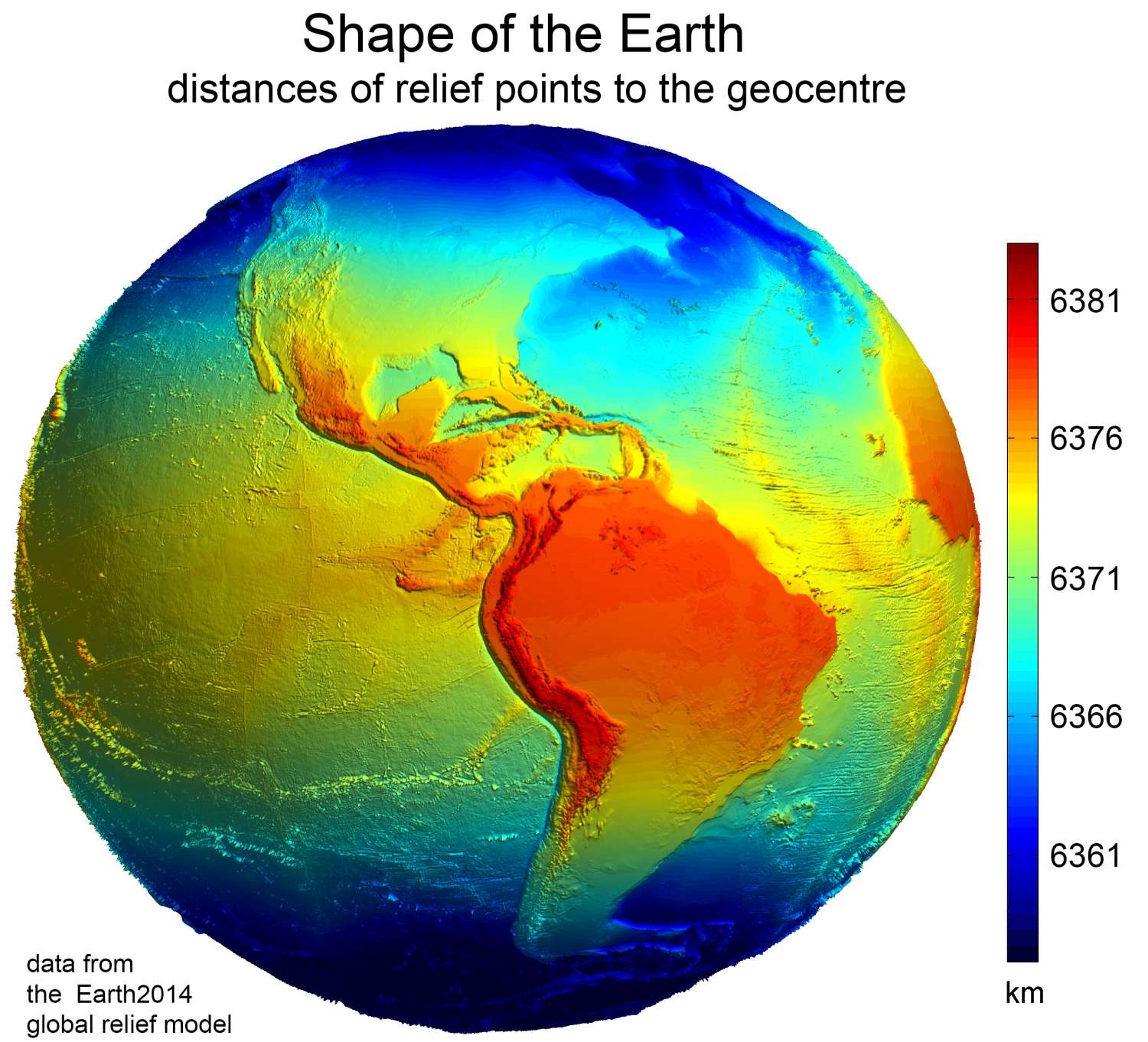
Figure Of The Earth
In geodesy, the figure of the Earth is the size and shape used to model planet Earth. The kind of figure depends on application, including the precision needed for the model. A spherical Earth is a well-known historical approximation that is satisfactory for geography, astronomy and many other purposes. Several models with greater accuracy (including ellipsoid) have been developed so that coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns. Motivation Earth's topographic surface is apparent with its variety of land forms and water areas. This topographic surface is generally the concern of topographers, hydrographers, and geophysicists. While it is the surface on which Earth measurements are made, mathematically modeling it while taking the irregularities into account would be extremely complicated. The Pythagorean concept of a spherical Earth offers a simple surface that is easy to deal with mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Principle
Balance Types of balance in visual design * Symmetry Hierarchy/Dominance/Emphasis Scale/proportion Scale in design Increasing an element's scale in a design piece increases its value in terms of hierarchy and makes it to be seen first compared to other elements while decreasing an element's scale reduces its value. See also * Composition (visual arts) * Gestalt laws of grouping * Interior design * Landscape design * Pattern language * Elements of art * Principles of art * Color theory Notes References *Kilmer, R., & Kilmer, W. O. (1992). Designing Interiors. Orland, FL: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Inc. . *Nielson, K. J., & Taylor, D. A. (2002). Interiors: An Introduction. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. *Pile, J.F. (1995; fourth edition, 2007). Interior Design. New York: Harry N. Abrams, Inc. Abrams, formerly Harry N. Abrams, Inc. (HNA), is an American publisher of art and illustrated books, children's books, and stationery. The enterprise is a subsidiary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers VC
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 1867, acquired more businesses, and began branching out into military hardware and shipbuilding. In 1911, the company expanded into aircraft manufacture and opened a flying school. They expanded even further into electrical and railway manufacturing, and in 1928 acquired an interest in the Supermarine. Beginning in the 1960s, various parts of the company were nationalised, and in 1999 the rest of the company was acquired by Rolls-Royce plc, which sold the defence arm to Alvis plc. The Vickers name lived on in Alvis Vickers, until the latter was acquired by BAE Systems in 2004 to form BAE Systems Land Systems. History Early history Vickers was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law George Naylor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant. Linen is very strong and absorbent, and it dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. Linen textiles can be made from flax plant fiber, yarn, as well as woven and knitted. Linen also has other distinctive characteristics, such as its tendency to wrinkle. It takes significantly longer to harvest than a material like cotton, although both are natural fibers. It is also more difficult to weave than cotton. Linen textiles appear to be some of the oldest in the world; their history goes back many thousands of years. Dyed flax fibers found in a cave in the Caucasus (present-day Georgia (country), Georgia) suggest the use of woven linen fabrics from wild flax may date back over 30,000 years. Linen was used in ancient civilizations including Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt, and linen is mentioned in the Bible. In the 18th century and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Dope
Aircraft dope is a plasticised lacquer that is applied to fabric-covered aircraft. It tightens and stiffens fabric stretched over airframes, which renders them airtight and weatherproof, increasing their durability and lifespan.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 170. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. The technique has been commonly applied to both full-size and flying models of aircraft. Attributes Doping techniques have been employed in aircraft construction since the dawn of heavier-than-air flight; the fabric of the ground-breaking Wright Flyer had benefitted from doping, as did many of the aircraft that soon followed. Without the application of dope, fabric coverings lacked durability while being highly flammable, both factors rendering them far less viable. By the 1910s, a wide variety of doping agents had entered widespread use while entirely original formulas were being regularly introduced in the industry. Typical doping agent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duralumin
Duralumin (also called duraluminum, duraluminium, duralum, dural(l)ium, or dural) is a trade name for one of the earliest types of age hardening, age-hardenable aluminium–copper alloys. The term is a combination of ''Düren'' and ''aluminium'' . Its use as a trade name is obsolete. Today the term mainly refers to aluminium-copper alloys, designated as the 2000 series by the international alloy designation system (IADS), as with 2014 aluminium alloy, 2014 and 2024 aluminium alloy, 2024 alloys used in airframe fabrication. Duralumin was developed in 1909 in Germany. Duralumin is known for its strength and hardness, making it suitable for various applications, especially in the aviation and aerospace industry. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, which can be mitigated by using alclad-duralum materials. History Duralumin was developed by the German metallurgist Alfred Wilm at private military-industrial laboratory (Center for Scientific-Technical Research) in Neubabelsberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Windsor
The Vickers Windsor was a Second World War British four-engine heavy bomber, intended for high altitude flight. The Windsor was designed by Barnes Wallis and Rex Pierson at the Vickers-Armstrongs factory at Brooklands. Three prototype aircraft were built but planned production was cancelled due to the end of the war. Design and development As a possible replacement for the pre-war Vickers Wellington medium bomber, Vickers had proposed a series of designs. The first, to meet the same specification as the Bristol Buckingham and Air Ministry Specification B.11/41, was for a high speed twin-engined medium bomber, with remote controlled turrets in engine nacelles and guns in the nose. This was considered to be neither fast enough to be a fast bomber nor well armed enough to be a normal medium bomber. A four-engined development of the same design was also drawn up. The official position was that the Wellington was becoming obsolete but as the Vickers factories were set up only for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Warwick
The Vickers Warwick was a British twin-engined bomber aircraft developed and operated during the Second World War that was primarily used in other roles. In line with the naming convention followed by other RAF heavy bombers of the era, it was named after a British city or town, in this case Warwick. The Warwick was the largest British twin-engined aircraft to see use during the Second World War. The Warwick was designed and manufactured by Vickers-Armstrongs during the late 1930s. It was intended to serve as a larger counterpart to the Vickers Wellington bomber. The two aircraft share similar construction and design principles but development of the Warwick was delayed by a lack of suitable engines. Its first flight was on 13 August 1939 but delays to its intended powerplant and by the time adequate engines were available, it was obsolete.Barfield 1972, p. 145. The Warwick entered production during 1942 and squadron service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). Barely a dozen airc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |