|
Gavelkind
Gavelkind () was a system of land tenure chiefly associated with the Celtic law in Ireland and Wales and with the legal traditions of the English county of Kent. The word may have originated from the Old Irish phrases ''Gabhaltas-cinne'' or ''Gavail-kinne'', which meant "family settlement" (Modern Gaelic ''gabhail-cine''). The term came to describe all tenure and inheritance practices where land was divided equally among sons or other heirs. Kent's inheritance pattern was a system of partible inheritance and bears a resemblance to Salic patrimony. As such, it may bear witness to a wider Germanic tradition that was probably ancient. Over the centuries, various acts were passed to disgavel individual manors, but the custom was only fully abolished in England and Wales by the Administration of Estates Act 1925.Elton. The tenures of Kent. ch. XVI – Disgavelled Lands Gavelkind in Kent Before the abolition of gavelkind tenure by the Administration of Estates Act 1925, all land i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyfraith Hywel
''Cyfraith Hywel'' (; ''Laws of Hywel''), also known as Welsh law ( la, Leges Walliæ), was the system of law practised in medieval Wales before its final conquest by England. Subsequently, the Welsh law's criminal codes were superseded by the Statute of Rhuddlan in AD 1284 and its civil codes by Henry VIII's series of Laws in Wales Acts between 1535 and 1542. Welsh law was a form of Celtic law with many similarities to the Brehon law of Ireland and particularly the customs and terminology of the Britons of Strathclyde. It was passed down orally by jurists and bards and, according to tradition, only first codified during the reign of Hywel Dda in the mid-10th century. The earliest surviving manuscripts, however, are in Latin, date from the early 13th century, and show marked regional differences.Wade-Evans, Arthur. ''Welsh Medieval Law''. Oxford Univ., 1909. Accessed 1 Feb 2013. The law is only known to have been revised by a few rulers (particularly Bleddyn ap Cynfyn, who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partible Inheritance
Partible inheritance is a system of inheritance in which property is apportioned among heirs. It contrasts in particular with primogeniture, which was common in feudal society and requires that the whole or most of the inheritance passes to the eldest son, and with agnatic seniority, which requires the succession to pass to next senior male. Partible inheritance systems are common ones to be found in legal systems based on both common law and the Napoleonic Code. In the latter case, there may be a further requirement implying division according to a scheme, such as equal shares for legitimate children. Partible inheritance has been common in ancient Celtic and Germanic tribal societies, an example of the latter pattern is the so-called Salic patrimony. Historically speaking, non-partible inheritance has been associated with monarchies and the wish for landed estates to be kept together as units. In the Middle Ages, the partible inheritance systems, for example, of the Meroving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Tenure
In common law systems, land tenure, from the French verb "tenir" means "to hold", is the legal regime in which land owned by an individual is possessed by someone else who is said to "hold" the land, based on an agreement between both individuals. It determines who can use land, for how long and under what conditions. Tenure may be based both on official laws and policies, and on informal local customs (insofar higher law does allow that). In other words, land tenure implies a system according to which land is held by an individual or the actual tiller of the land but this person does not have legal ownership. It determines the holder's rights and responsibilities in connection with their holding. The sovereign monarch, known in England as The Crown, held land in its own right. All land holders are either its tenants or sub-tenants. ''Tenure'' signifies a legal relationship between tenant and lord, arranging the duties and rights of tenant and lord in relationship to the land. Ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estate (law)
An estate, in common law, is the net worth of a person at any point in time, alive or dead. It is the sum of a person's assets – legal rights, interests and entitlements to property of any kind – less all liabilities at that time. The issue is of special legal significance on a question of bankruptcy and death of the person. (See inheritance.) Depending on the particular context, the term is also used in reference to an estate in land or of a particular kind of property (such as real estate or personal estate). The term is also used to refer to the sum of a person's assets only. The equivalent in civil law legal systems is patrimony. Bankruptcy Under United States bankruptcy law, a person's estate consists of all assets or property of any kind available for distribution to creditors. However, some assets are recognized as exempt to allow a person significant resources to restart his or her financial life. In the United States, asset exemptions depend on various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Yorke (antiquary)
Philip Yorke (30 July 1743 – 19 February 1804) was a Welsh politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1775 and 1792 and an antiquary who developed an interest in Welsh history and genealogy relatively late in life. He was the author of ''The Royal Tribes of Wales'' (1799). Background The son of Simon Yorke (1696–1767) and Dorothy Hutton (1717–1787), he was born at Erddig, not far from Wrexham (Denbighshire, Wales). He was related to Philip Yorke, first earl of Hardwicke, who was uncle to Simon's father Simon Yorke. His mother, Dorothy, was a daughter of Matthew Hutton of Newnham, Hertfordshire. After receiving his basic education in Wanstead and at Newcome's School in Hackney, he went to Eton College and subsequently in 1762 to Benet College, Cambridge, where he was awarded an MA degree in 1765. He proceeded to Lincoln's Inn in 1762 and was 'called to the bar' in 1767. He took delight in classical literature, and became a fellow of the Society of Antiquaries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcher Lords
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales. A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in France) before the introduction of the title of "marquess" in Britain; no Marcher lord ever bore this rank. In this context the word ''march'' means a border region or frontier, and is cognate with the verb "to march", both ultimately derived from Proto-Indo-European ''*mereg-'', "edge" or "boundary". The greatest Marcher lords included the earls of Chester, Gloucester, Hereford, Pembroke and Shrewsbury (see also English earls of March). County palatine Some strong earldoms along the Welsh border were granted the privileged status of county palatine shortly after the Norman Conquest, but only that based on Chester survived for a long period. The term particularly applies to Anglo-Norman lords in Wales, who had complete jurisdiction over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman England
England in the High Middle Ages includes the history of England between the Norman Conquest in 1066 and the death of King John, considered by some to be the last of the Angevin kings of England, in 1216. A disputed succession and victory at the Battle of Hastings led to the conquest of England by William of Normandy in 1066. This linked the crown of England with possessions in France and brought a new aristocracy to the country that dominated landholding, government and the church. They brought with them the French language and maintained their rule through a system of castles and the introduction of a feudal system of landholding. By the time of William's death in 1087, England formed the largest part of an Anglo-Norman empire, ruled by nobles with landholdings across England, Normandy and Wales. William's sons disputed succession to his lands, with William II emerging as ruler of England and much of Normandy. On his death in 1100 his younger brother claimed the throne as Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hywel Dda
Hywel Dda, sometimes anglicised as Howel the Good, or Hywel ap Cadell (died 949/950) was a king of Deheubarth who eventually came to rule most of Wales. He became the sole king of Seisyllwg in 920 and shortly thereafter established Deheubarth, and proceeded to gain control over the entire country from Prestatyn to Pembroke. As a descendant of Rhodri Mawr through his father Cadell, Hywel was a member of the Dinefwr branch of the dynasty. He was recorded as King of the Britons in the ''Annales Cambriæ'' and the ''Annals of Ulster''. Hywel is highly esteemed among other medieval Welsh rulers. His name is particularly linked with the codification of traditional Welsh law, which were thenceforth known as the Laws of Hywel Dda. The latter part of his name (''Dda'', lit. "Good") refers to the fact that his laws were just and good. The historian Dafydd Jenkins sees in them compassion rather than punishment, plenty of common sense and recognition of the rights of women. Hywel Dda w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bards
In Celtic cultures, a bard is a professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron (such as a monarch or chieftain) to commemorate one or more of the patron's ancestors and to praise the patron's own activities. With the decline of a living bardic tradition in the modern period, the term has loosened to mean a generic minstrel or author (especially a famous one). For example, William Shakespeare and Rabindranath Tagore are respectively known as "the Bard of Avon" (often simply "the Bard") and "the Bard of Bengal".Oxford Dictionary of English, s.v. ''bard'', n.1. In 16th-century Scotland, it turned into a derogatory term for an itinerant musician; nonetheless it was later romanticised by Sir Walter Scott (1771–1832). Etymology The English term ''bard'' is a loan word from the Celtic languages: Gaulish: ''bardo-'' ('bard, poet'), mga, bard and ('bard, poet'), wlm, bardd ('singer, poet'), Middle Breton: ''barz'' ('mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie J
Leslie may refer to: * Leslie (name), a name and list of people with the given name or surname, including fictional characters Families * Clan Leslie, a Scottish clan with the motto "grip fast" * Leslie (Russian nobility), a Russian noble family of Scottish origin Places Canada * Leslie, Saskatchewan * Leslie Street, a road in Toronto and York Region, Ontario ** Leslie (TTC), a subway station ** Leslie Street Spit, an artificial spit in Toronto United States * Leslie, Arkansas *Leslie, Georgia *Leslie, Michigan *Leslie, Missouri *Leslie, West Virginia * Leslie, Wisconsin *Leslie Township, Michigan *Leslie Township, Minnesota Elsewhere * Leslie Dam, a dam in Warwick, Queensland, Australia * Leslie, Mpumalanga, South Africa * Leslie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland, see List of listed buildings in Leslie, Aberdeenshire * Leslie, Fife, Scotland, UK Other uses * Leslie speaker system * Leslie Motor Car company * Leslie Controls, Inc. * Leslie (singer) (born 1985), French singer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
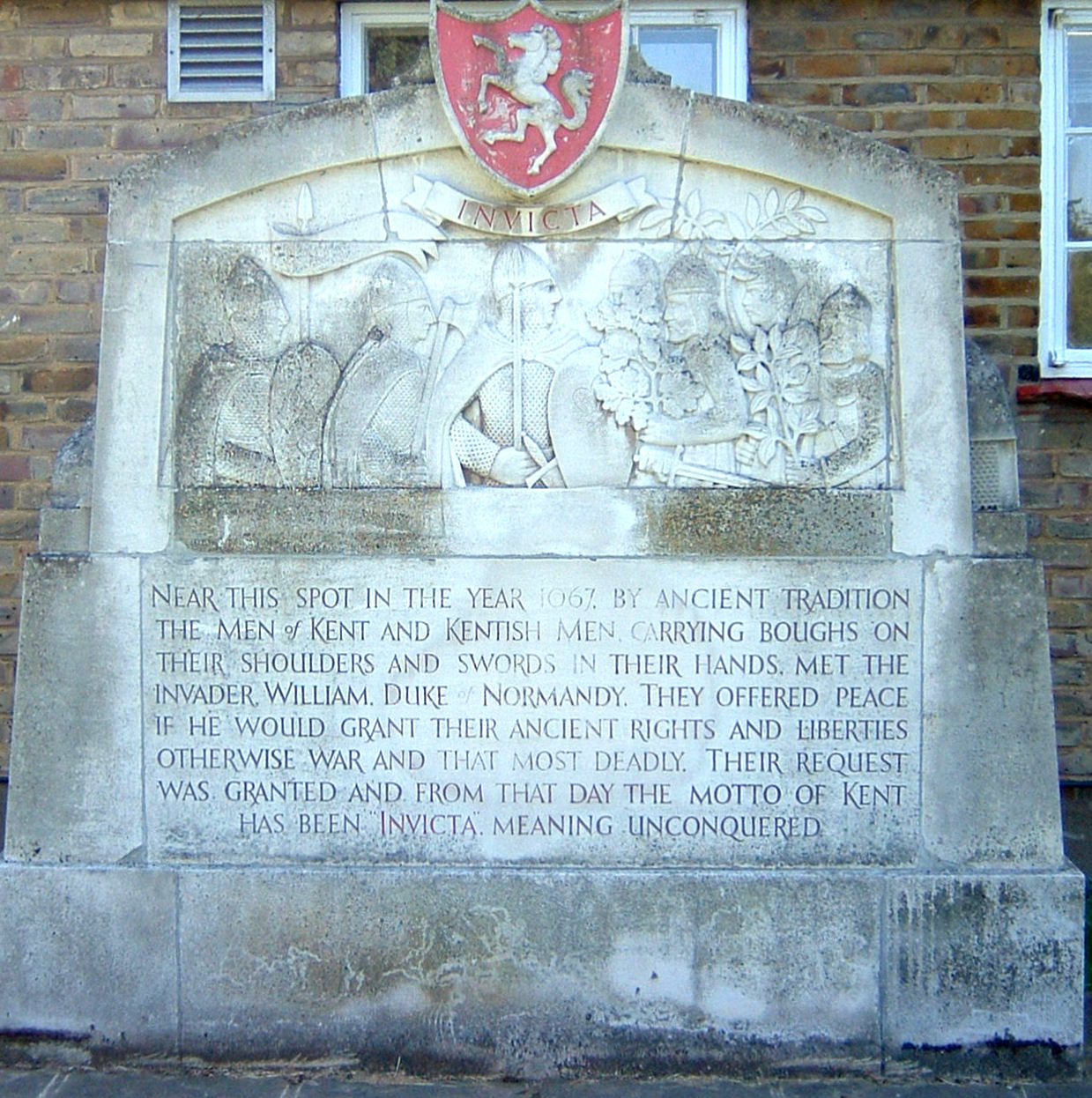
William The Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Normandy, king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 1087. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle to establish his throne, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading an army of Normans to victory over the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose. William was the son of the unmarried Duke Robert I of Normandy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relative. In most contexts, it means the inheritance of the firstborn son (agnatic primogeniture); it can also mean by the firstborn daughter (matrilineal primogeniture). Description The common definition given is also known as male-line primogeniture, the classical form popular in European jurisdictions among others until into the 20th century. In the absence of male-line offspring, variations were expounded to entitle a daughter or a brother or, in the absence of either, to another collateral relative, in a specified order (e.g. male-preference primogeniture, Salic primogeniture, semi-Salic primogeniture). Variations have tempered the traditional, sole-beneficiary, right (such as French appanage) or, in the West since World War II, eliminate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Judge_cropped.jpg)