|
Gating Orders
Gating may refer to: Neurobiology *Gating (electrophysiology), the opening (activation) or closing (deactivation) of ion channels * Sensory gating, an automatic process by which the brain adjusts to stimuli * Synaptic gating, neural circuits suppressing inputs through synapses Technology *Gating (telecommunication), a process of selectively modifying signals * Gating system metalwork, a process in casting * Gating signal, a signal that provides a time window *Clock gating, a power-saving techniques used in synchronous circuits *Power gating, a power-saving technique for circuits *Noise gate, a term in audio signal processing *Frequency-resolved optical gating, a term related to auto correlation in optics * Gating (cytometry), manually selecting a population during flow cytometry analysis *Gating mechanism, an architectural motif in neural networks. Other See also *Gate (other) A gate is an opening in a wall or fence fitted with a moveable barrier allowing it to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gating (electrophysiology)
In electrophysiology, the term gating refers to the opening (activation) or closing (by deactivation or inactivation) of ion channels. This change in conformation is a response to changes in transmembrane voltage. When ion channels are in a 'closed' (non-conducting) state, they are impermeable to ions and do not conduct electrical current. When ion channels are in their open state, they conduct electrical current by allowing specific types of ions to pass through them, and thus, across the plasma membrane of the cell. Gating is the process by which an ion channel transitions between its open and closed states. A variety of cellular changes can trigger gating, depending on the ion channel, including changes in voltage across the cell membrane (voltage-gated ion channels), chemicals interacting with the ion channel (ligand-gated ion channels), changes in temperature, stretching or deformation of the cell membrane, addition of a phosphate group to the ion channel (phosphorylation), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Gating
Sensory gating describes neural processes of filtering out redundant or irrelevant stimuli from all possible environmental stimuli reaching the brain. Also referred to as gating or filtering, sensory gating prevents an overload of information in the higher-order centers of the brain. Sensory gating can also occur in different forms through changes in both perception and sensation, affected by various factors such as "arousal, recent stimulus exposure, and selective attention." Although sensory gating is largely automatic, it also occurs within the context of attention processing as the brain selectively seeks for goal-relevant information. Previous studies have shown a correlation between sensory gating and different cognitive functions, but there is not yet a solid evidence implying that the relationship between sensory gating and cognitive functions are modality-independent. Cocktail party effect The cocktail party effect illustrates how the brain inhibits input from environmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
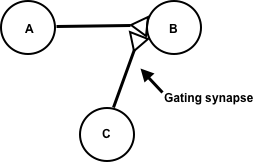
Synaptic Gating
Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation). Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gating (telecommunication)
In telecommunication, the term gating has the following meanings: #The process of selecting only those portions of a wave between specified time intervals or between specified amplitude limits. #The controlling of signals by means of combinational logic elements. #A process in which a predetermined set (mathematics), set of conditions, when established, permits a second process to occur. Telecommunications engineering Signal processing {{Telecomm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate (casting)
In metalworking and jewelry making, casting is a process in which a liquid metal is delivered into a mold (usually by a crucible) that contains a negative impression (i.e., a three-dimensional negative image) of the intended shape. The metal is poured into the mold through a hollow channel called a sprue. The metal and mold are then cooled, and the metal part (the ''casting'') is extracted. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Casting processes have been known for thousands of years, and have been widely used for sculpture (especially in bronze), jewelry in precious metals, and weapons and tools. Highly engineered castings are found in 90 percent of durable goods, including cars, trucks, aerospace, trains, mining and construction equipment, oil wells, appliances, pipes, hydrants, wind turbines, nuclear plants, medical devices, defense products, toys, and more. Traditional techniques include los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gating Signal
Signal gating is a concept commonly used in the field of electronics and signal processing. It refers to the process of controlling the flow of signals based on certain conditions or criteria. The goal of signal gating is to selectively allow or block the transmission of signals through a circuit or system. In signal gating, a gating signal is used to modulate the passage of the main signal. The gating signal acts as a control mechanism, determining when the main signal can pass through the gate and when it is blocked. The gating signal can be generated by various means, such as an external trigger, a specific voltage level, or a specific frequency range. Signal gating is often employed in applications where precise control over the transmission of signals is required. Here are a few examples of how signal gating is used in different fields: 1. Telecommunications: In telecommunications systems, signal gating is used to regulate the flow of data packets. By opening and closing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Gating
In computer architecture, clock gating is a popular power management technique used in many synchronous circuits for reducing dynamic power dissipation (a significant source of power dissipation in digital designs), by removing the clock signal when the circuit, or a subpart of it, is idle. Clock gating Energy conservation, saves power by pruning part of the Clock_signal#Distribution, clock tree distribution, at the cost of adding more logic to a circuit. Pruning the clock turns off portions of the circuitry so that the Flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops in them do not switch state, as switching the state consumes power. When not switched, the switching power consumption is reduced. This technique is particularly effective in systems with significant idle time or predictable periods of inactivity within specific module Essential details Digital circuits consume power through multiple mechanisms, typically categorised into dynamic and static components. The equation can describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Gating
Power gating is a technique used in integrated circuit An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ... design to reduce power consumption, by shutting off the current to blocks of the circuit that are not in use. In addition to reducing stand-by or leakage power, power gating has the benefit of enabling Iddq testing. Overview Power gating affects design architecture more than clock gating. It increases time delays, as power gated modes have to be safely entered and exited. Architectural trade-offs exist between designing for the amount of leakage power saving in low power modes and the energy dissipation to enter and exit the low power modes. Shutting down the blocks can be accomplished either by software or hardware. Driver software can schedule the power down operations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise Gate
A noise gate or simply gate is an electronic device or software that is used to control the amplitude, volume of an audio signal. Comparable to a limiter, which attenuates signals ''above'' a threshold, such as loud attacks from the start of musical notes, noise gates attenuate signals that register ''below'' the threshold. However, noise gates attenuate signals by a fixed amount, known as the range. In its simplest form, a noise gate allows a main signal to pass through only when it is above a set threshold: the gate is ''open''. If the signal falls below the threshold, no signal is allowed to pass (or the signal is substantially attenuated): the gate is ''closed''. A noise gate is used when the level of the signal is above the level of the unwanted noise. The threshold is set above the level of the noise, and so when there is no main signal, the gate is closed. A common application is with electric guitar to remove hum and hiss noise caused by distortion effects units. A nois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency-resolved Optical Gating
Frequency-resolved optical gating (FROG) is a general method for measuring the Spectral density, spectral phase of Ultrashort pulse, ultrashort laser pulses, which range from subfemtosecond to about a nanosecond in length. Invented in 1991 by Rick Trebino and Daniel J. Kane, FROG was the first technique to solve this problem, which is difficult because, ordinarily, to measure an event in time, a shorter event is required with which to measure it. For example, to measure a soap bubble popping requires a strobe light with a shorter duration to freeze the action. Because ultrashort laser pulses are the shortest events ever created, before FROG, it was thought by many that their complete measurement in time was not possible. FROG, however, solved the problem by measuring an "auto-spectrogram" of the pulse, in which the pulse gates itself in a nonlinear optical medium and the resulting gated piece of the pulse is then spectrally resolved as a function of the delay between the two pulse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gating (cytometry)
A gate in cytometry Cytometry is the measurement of number and characteristics of cell (biology), cells. Variables that can be measured by cytometric methods include cell size, cell counting, cell count, cell morphology (shape and structure), cell cycle phase, DNA c ... is a set of value limits (boundaries) that serve to isolate a specific group of cytometric events from a large set. Gates can be defined by discrimination analysis, or can simply be drawn around a given set of data points on a printout and then converted to a computer-useful form. Gates can be implemented with a physical blinder. Gates may be used either to selectively gather data or to segregate data for analysis. Division Gates are divided mathematically into inclusive gates and exclusive gates. Inclusive gates select data that falls within the limits set, while exclusive gates select data that falls outside the limits. Live gate A live gate is a term used for a process that prevents the acquisition by the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gating Mechanism
In neural networks, the gating mechanism is an architectural motif for controlling the flow of activation and gradient signals. They are most prominently used in recurrent neural networks (RNNs), but have also found applications in other architectures. RNNs Gating mechanisms are the centerpiece of long short-term memory (LSTM). They were proposed to mitigate the vanishing gradient problem often encountered by regular RNNs. An LSTM unit contains three gates: * An input gate, which controls the flow of new information into the memory cell * A forget gate, which controls how much information is retained from the previous time step * An output gate, which controls how much information is passed to the next layer. The equations for LSTM are: \begin \mathbf_t &= \sigma(\mathbf_t \mathbf_ + \mathbf_ \mathbf_ + \mathbf_i) \\ \mathbf_t &= \sigma(\mathbf_t \mathbf_ + \mathbf_ \mathbf_ + \mathbf_f) \\ \mathbf_t &= \sigma(\mathbf_t \mathbf_ + \mathbf_ \mathbf_ + \mathbf_o) \\ \tilde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |