|
Garífuna
The Garifuna people ( or ; pl. Garínagu in Garifuna) are a people of mixed free African and indigenous American ancestry that originated in the Caribbean island of Saint Vincent and speak Garifuna, an Arawakan language, and Vincentian Creole. The Garifuna are the descendants of indigenous Arawak, Kalinago (Island Carib), and Afro-Caribbean people. The founding population of the Central American diaspora, estimated at 2,500 to 5,000 persons, were transplanted to the Central American coast from the Commonwealth Caribbean island of Saint Vincent, which was known to the Garinagu as ''Yurumein'', in the Windward Islands in the British West Indies in the Lesser Antilles. Small Garifuna communities still live in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The Garifuna diaspora abroad includes communities in Honduras, in the United States, and in Belize. Name In the Garifuna language, the endonym ''Garínagu'' refers to the people as a whole and the term ''Garífuna'' refers to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawakan Language
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock. Name The name ''Maipure'' was given to the family by Filippo S. Gilij in 1782, after the Maipure language of Venezuela, which he used as a basis of his comparisons. It was renamed after the culturally more important Arawak language a century later. The term ''Arawak'' took over, until its use was extended by North American scholars to the broader Macro-Arawakan pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Honduras; to the southeast by El Salvador and to the south by the Pacific Ocean. With an estimated population of around million, Guatemala is the most populous country in Central America and the 11th most populous country in the Americas. It is a representative democracy with its capital and largest city being Nueva Guatemala de la Asunción, also known as Guatemala City, the most populous city in Central America. The territory of modern Guatemala hosted the core of the Maya civilization, which extended across Mesoamerica. In the 16th century, most of this area was conquered by the Spanish and claimed as part of the viceroyalty of New Spain. Guatemala attained independence in 1821 from Spain and Mexico. In 1823, it became part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean, which owes its name to them. They lived throughout northeastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the notion of a mass emigration and conquest; the Kalinago language appears not to have been Cariban, but like that of their neighbors, the Taíno. Irving Rouse an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garifuna Language
Garifuna (Karif) is a minority language widely spoken in villages of Garifuna people in the western part of the northern coast of Central America. It is a member of the Arawakan language family but an atypical one since it is spoken outside the Arawakan language area, which is otherwise now confined to the northern parts of South America, and because it contains an unusually high number of loanwords, from both Carib languages and a number of European languages because of an extremely tumultuous past involving warfare, migration and colonization. The language was once confined to the Antillean islands of St. Vincent and Dominica, but its speakers, the Garifuna people, were deported by the British in 1797 to the north coast of Honduras from where the language and Garifuna people has since spread along the coast south to Nicaragua and north to Guatemala and Belize. Parts of Garifuna vocabulary are split between men's speech and women's speech, and some concepts have two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Guiana (now Guyana) and Trinidad and Tobago. Other territories include Bermuda, and the former British Honduras (now Belize). The colonies were also at the center of the transatlantic slave trade, around 2.3 million slaves were brought to the British Caribbean. Before the decolonisation period in the later 1950s and 1960s the term was used to include all British colonies in the region as part of the British Empire. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent , image_name = , image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada. , image_alt = , locator_map = , location = Caribbean Sea North Atlantic Ocean , coordinates = , area_km2 = 3232.5 , total_islands = 90+ , major_islands = Carriacou Dominica GrenadaMartinique Petite MartiniqueSaint Lucia Saint Vincent , highest_mount = Morne Diablotins, Dominica , elevation_m = 1,447 , country = Dominica , country_largest_city = Roseau , country1 = Grenada , country1_largest_city = St. George's , country2 = Martinique , country2_largest_city = Fort-de-France , country3 = Saint Lucia , country3_largest_city = Castries , country4 = Saint Vincent and the Grenadines , country4_largest_city = Kingstown , density_km2 = 227 , population = 854,000 , ethnic_groups = The Windward Islands are the southern, generally larger islands of the Lesser Antilles. Part of the West Indies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Caribbean
The Commonwealth Caribbean is the region of the Caribbean with English-speaking countries and territories, which once constituted the Caribbean portion of the British Empire and are now part of the Commonwealth of Nations. The term includes many independent island nations, British Overseas Territories and some mainland nations. It is also known as the English-speaking Caribbean, Anglophone Caribbean or Anglo-Caribbean. The term is now used in preference over the older term ''British West Indies'', which was used to describe the British colonies in the West Indies during decolonisation and following independence from the United Kingdom. ''Anglo-Caribbean'' and ''British Commonwealth Caribbean'' also became preferred replacement terms to ''British West Indies''. Countries and territories The Commonwealth Caribbean consists of countries and territories, which include Caribbean islands or parts of mainland North and South America surrounding the Caribbean Sea. Independent is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greater Antilles and northern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. All these groups spoke related Arawakan languages. Name Early Spanish explorers and administrators used the terms ''Arawak'' and ''Caribs'' to distinguish the peoples of the Caribbean, with ''Carib'' reserved for indigenous groups that they considered hostile and ''Arawak'' for groups that they considered friendly. In 1871, ethnologist Daniel Garrison Brinton proposed calling the Caribbean populace "Island Arawak" due to their cultural and linguistic similarities with the mainland Arawak. Subsequent scholars shortened this convention to "Arawak", creating confusion between the island and mainland groups. In the 20th century, scholars such as Irving Rouse resumed using "Taíno" for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Vincent (Antilles)
Saint Vincent is a volcanic island in the Caribbean. It is the largest island of the country Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and is located in the Caribbean Sea, between Saint Lucia and Grenada. It is composed of partially submerged volcanic mountains. Its largest volcano and the country's highest peak, La Soufrière, is active, with the latest episode of volcanic activity having begun in December 2020 and intensifying in April 2021. There were major territory wars between the indigenous population of the Black Caribs, also called the Garifuna, and Great Britain in the 18th century, before the island was ceded to the British in 1763 and again in 1783. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines gained independence from the United Kingdom on 27 October 1979 and became part of the British Commonwealth of Nations thereafter. Approximately 130,000 people currently live on the island, and the population saw significant migration to the UK in the early 1900s and between the 1940s and 1980s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous People Of The Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, states, kingdoms, republics, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigenous peoples; some countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African People
The population of Africa has grown rapidly over the past century and consequently shows a large youth bulge, further reinforced by a low life expectancy of below 50 years in some African countries. Total population as of 2020 is estimated at more than 1.3 billion, with a growth rate of more than 2.5% p.a. The total fertility rate (births per woman) for Sub-Saharan Africa is 4.7 as of 2018, the highest in the world according to the World Bank. The most populous African country is Nigeria with over 206 million inhabitants as of 2020 and a growth rate of 2.6% p.a. Population Genetics History Alternative Estimates of African Population, 0–1998 AD (in thousands) Source: Maddison and others. (University of Groningen). Shares of Africa and World Population, 0–2018 AD (% of world total) Source: Maddison and others (University of Groningen) and others. Vital Statistics 1950–2021AD Registration of vital events in most of Africa is incomplete. The website Our World in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
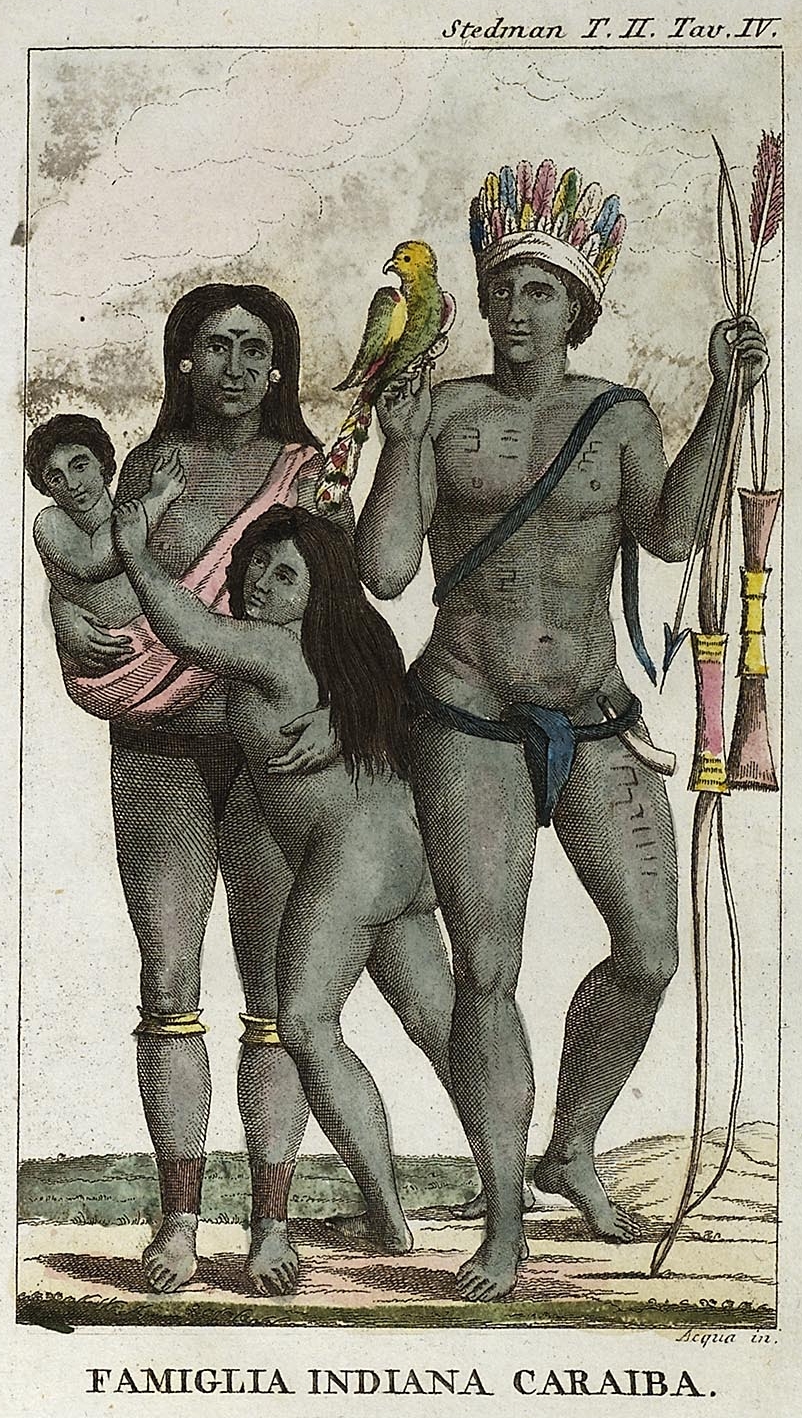



_2007.jpg)