|
GRO J1655−40
GRO J1655−40 is a binary star consisting of an evolved F-type primary star and a massive, unseen companion, which orbit each other once every 2.6 days in the constellation of Scorpius. Gas from the surface of the visible star is accreted onto the dark companion, which appears to be a stellar black hole with several times the mass of the Sun. The optical companion of this low-mass X-ray binary is a subgiant F star. Along with GRS 1915+105, GRO J1655−40 is one of at least two galactic "microquasars" that may provide a link between the supermassive black holes generally believed to power extragalactic quasars and more local accreting black hole systems. In particular, both display the radio jets characteristic of many active galactic nuclei. The distance from the Solar System is probably about 11,000 light years, or approximately half-way from the Sun to the Galactic Center, but a closer distance of ~2800 ly is not ruled out. GRO J1655−40 and its companion are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GRO J1655-40 (CGRO)
{{disambiguation ...
GRO or Gro may refer to: Organisations * General Register Office * General Register Office (Northern Ireland) Technology and science * Generic receive offload, in computer networking * GRO structure file format, used by GROMACS Transportation * Girona–Costa Brava Airport (IATA code), Spain * J. Douglas Galyon Depot (Station code), North Carolina, US * Rota International Airport (FAA LID code), Northern Mariana Islands Other uses * Green River Ordinance (band), an American rock band * Gro (given name) * Gró, a figure in Norse mythology * Groma language (ISO 639-3 code) - language spoken by some Tibetans See also * Compton Gamma Ray Observatory The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) was a space observatory detecting photons with photon energy, energies from 20 kElectronvolt#Properties, eV to 30 GeV, in Earth orbit from 1991 to 2000. The observatory featured four main tel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relativistic Jet
An astrophysical jet is an astronomical phenomenon where outflows of ionised matter are emitted as extended beams along the axis of rotation. When this greatly accelerated matter in the beam approaches the speed of light, astrophysical jets become relativistic jets as they show effects from special relativity. The formation and powering of astrophysical jets are highly complex phenomena that are associated with many types of high-energy astronomical sources. They likely arise from dynamic interactions within accretion disks, whose active processes are commonly connected with compact central objects such as black holes, neutron stars or pulsars. One explanation is that tangled magnetic fields are organised to aim two diametrically opposing beams away from the central source by angles only several degrees wide Jets may also be influenced by a general relativity effect known as frame-dragging. Most of the largest and most active jets are created by supermassive black holes (SMBH) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microquasars
A microquasar, a smaller version of a quasar, is a compact region surrounding a stellar black hole with a mass several times that of its Binary star#Cataclysmic variables and X-ray binaries, companion star, observable in sufficient details, in Milky Way, our own or nearby galaxy. The matter being pulled from the companion star forms an accretion disk around the black hole. This accretion disk may become so hot, due to friction, that it begins to emit X-rays. The disk also projects narrow streams or "Astrophysical jet, jets" of subatomic particles at near-Speed of light, light speed, generating a strong radio wave emission. Overview In 1979, SS 433, in our own galaxy, became the first microquasar to be discovered, when Margon et al. observed its relativistic jets. It was thought to be the most exotic case until similar objects such as GRS 1915+105 were confirmed in 1994. In some cases, blobs or "knots" of brighter plasma (physics), plasma within the jets appear to be traveling fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Black Holes
Stellar means anything related to one or more stars (''stella''). The term may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Stellar'' (magazine), an Irish lifestyle and fashion magazine * Stellar Loussier, a character from ''Mobile Suit Gundam SEED Destiny'' * Dr. Stellar, a Big Bang Comics superhero * ''Stellar 7'', a game for the Apple II computer system * ''Stellar'' (film), a Canadian film Music * Stellar (group), a South Korean girl group * Stellar (New Zealand band), a New Zealand-based rock band * Stellar (musical artist), an American singer, songwriter, and producer * "Stellar" (song), a 2000 song by Incubus * Stellar Awards, awards for the gospel music industry Brands and enterprises * Stellar (payment network), a system for sending money through the internet * Stellar Group (construction company), a construction company in Florida, United States * Hasselblad Stellar, a compact digital camera * Hyundai Stellar, an automobile model * O2 XDA Stellar, an HTC mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Binaries
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 picometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range of 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for broken bones) and materials science (e.g., identification of some chemical elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
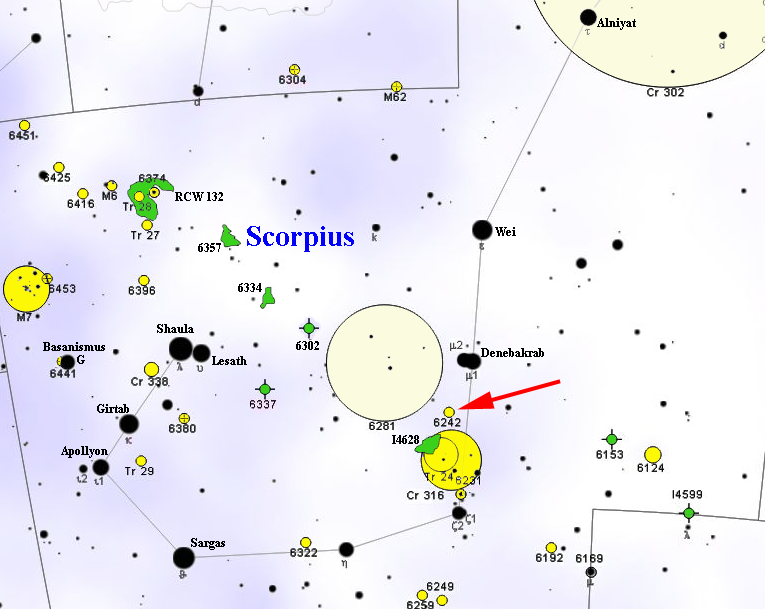
NGC 6242
NGC 6242 is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation Scorpius. It can be viewed with binoculars or a telescope at about 1.5° to the south-southeast of the double star Mu Scorpii. This cluster was discovered by French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in 1752 from South Africa. It is located at a distance of approximately from the Sun, just to the north of the Sco OB 1 association. The cluster has an estimated age of 77.6 million years. A microquasar with the designation GRO J1655-40 GRO or Gro may refer to: Organisations * General Register Office * General Register Office (Northern Ireland) Technology and science * Generic receive offload, in computer networking * GRO structure file format, used by GROMACS Transportation * G ... is located in the vicinity of NGC 6242 and is moving away from the cluster with a runaway space velocity of . It may have originated in the cluster during a supernova explosion ago. References External links * * SEDS– NGC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nearest Known Black Holes
This is a list of known black holes that are close to the Solar System. It is thought that most black holes are solitary, but black holes in binary or larger systems are much easier to detect. Solitary black holes can generally only be detected by measuring their gravitational distortion of the light from more distant objects. As of February 2022, only one isolated black hole has been confirmed, OGLE-2011-BLG-0462, around 5,200 light-years away. The nearest known black hole is Gaia BH1, which was discovered in September 2022 by a team led by Kareem El-Badry. Gaia BH1 is 1,560 light-years away from Earth in the direction of the constellation Ophiuchus. For comparison, the nearest star to the Sun (Proxima Centauri) is about away, and the Milky Way galaxy is approximately 100,000 light-years in diameter. List Nearest black hole record holders This is a succession of black holes that have been known as the nearest black hole. See also * List of black holes * List of most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasi-periodic Oscillation
In X-ray astronomy, quasi-periodic oscillation (QPO) is the manner in which the X-ray light from an astronomical object flickers about certain frequencies. In these situations, the X-rays are emitted near the inner edge of an accretion disk in which gas swirls onto a compact object such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole. The QPO phenomenon promises to help astronomers understand the innermost regions of accretion disks and the masses, radii, and spin periods of white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. QPOs could help test Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity which makes predictions that differ most from those of Newtonian gravity when the gravitational force is strongest or when rotation is fastest (when a phenomenon called the Lense–Thirring effect comes into play). However, the various explanations of QPOs remain controversial and the conclusions reached from their study remain provisional. A QPO is identified by performing a power spectrum of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. The last supernova directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not long after Tycho's Supernova in 1572, both of which were visible to the naked eye. The supernova remnant, remnants of more recent supernovae have been found, and observations of supernovae in other galaxies suggest they occur in the Milky Way on average about three times every century. A supernova in the Milky Way would almost certainly be observable through mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Neighborhood
The Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC), also known as the Local Fluff, is an interstellar cloud roughly across, through which the Solar System is moving. This feature overlaps with a region around the Sun referred to as the solar neighborhood. It is unknown whether the Sun is embedded in the Local Interstellar Cloud, or is in the region where the Local Interstellar Cloud is interacting with the neighboring G-Cloud. Like the G-Cloud and others, the LIC is part of the Very Local Interstellar Medium which begins where the heliosphere and interplanetary medium end, the furthest that probes have traveled. Structure The Solar System is located within a structure called the Local Bubble, a low-density region of the galactic interstellar medium. Within this region is the Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC), an area of slightly higher hydrogen density. It is estimated that the Solar System entered the LIC within the past 10,000 years. It is uncertain whether the Sun is still inside of the LIC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several List of Milky Way's satellite galaxies, satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact Astronomical radio source, radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius (constellation), Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula. There are around 10 million stars within one parsec of the Galactic Center, dominated by red giants, with a significant population of massive supergiants and Wolf–Rayet stars from star formation in the region around 1 million years ago. The core stars are a small part within the much wider central region, called ''galactic bulge''. Discovery Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |