|
GPR55
G protein-coupled receptor 55 also known as GPR55 is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''GPR55'' gene. GPR55, along with GPR119 and GPR18, have been implicated as novel cannabinoid receptors. History GPR55 was identified and cloned for the first time in 1999. Later it was identified by an in silico screen as a putative cannabinoid receptor because of a similar amino acid sequence in the binding region. Research groups from Glaxo Smith Kline and Astra Zeneca characterized the receptor extensively because it was hoped to be responsible for the blood pressure lowering properties of cannabinoids. GPR55 is indeed activated by endogenous and exogenous cannabinoids such as plant and synthetic cannabinoids but GPR-55 knockout mice generated by a research group from Glaxo Smith Kline showed no altered blood pressure regulation after administration of the cannabidiol-derivative abnormal cannabidiol. Signal cascade GPR55 is coupled to the G-protein G1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abnormal Cannabidiol
Abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) is a synthetic regioisomer of cannabidiol, which unlike most other cannabinoids produces vasodilator effects, lowers blood pressure, and induces cell migration, cell proliferation and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in microglia, but without producing any psychoactive or sedative effects. Abn-CBD can be found as an impurity in synthetic cannabidiol. Receptor activity It has been shown that the actions of abnormal cannabidiol are mediated through a site separate from the cannabinoid receptor 1, CB1 and cannabinoid receptor 2, CB2 receptors, which responds to abnormal cannabidiol, O-1602, and the endogenous ligands: anandamide (AEA), N-arachidonoyl glycine (NAGly) and N-arachidonoyl L-serine. Multiple lines of evidence support the proposed identification of this novel target in microglia as the previously orphan receptor GPR18. Another possible target of abnormal cannabidiol is GPR55, which has also received much attention as a putative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
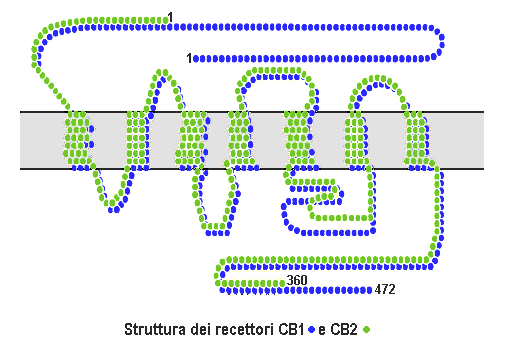
Cannabinoid Receptor
Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system of vertebrates a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains. Cannabinoid receptors are activated by three major groups of ligands: * Endocannabinoids; * Phytocannabinoids (plant-derived such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) produced by cannabis); * Synthetic cannabinoids (such as HU-210). All endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is expressed mainly in the brain (central nervous system or "CNS"), but also in the lungs, liver and kidneys. The CB2 receptor is expressed mainly in the immune system, in hematopoietic cells, and in parts of the brain. The protein sequences of CB1 and CB2 receptors are about 44% similar. When on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysophosphatidylinositol
Lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI, lysoPI), or L-α-lysophosphatidylinositol, is an endogenous lysophospholipid and endocannabinoid neurotransmitter. LPI, along with its 2-arachidonoyl- derivative, 2-arachidonoyl lysophosphatidylinositol (2-ALPI), have been proposed as the endogenous ligands of GPR55. Recent studies have shown that the fatty acyl composition of LPI influences neuroinflammatory responses in primary neuronal cultures, highlighting its potential role in neuroinflammation. See also * Phosphatidylinositol Phosphatidylinositol or inositol phospholipid is a biomolecule. It was initially called "inosite" when it was discovered by Léon Maquenne and Johann Joseph von Scherer in the late 19th century. It was discovered in bacteria but later also found ... * Cannabinoid receptor References Endocannabinoids Neurotransmitters Phospholipids Inositol {{biochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found primarily in the ''Cannabis'' plant or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in Cannabis (drug), cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include aminoalkylindoles, 1,5-diarylpyrazoles, qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPR18
''N''-Arachidonyl glycine receptor (NAGly receptor), also known as G protein-coupled receptor 18 (GPR18), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPR18'' gene. Along with the other previously orphan receptors GPR55 and GPR119, GPR18 has been found to be a receptor for endogenous lipid neurotransmitters, several of which also bind to cannabinoid receptors. It has been found to be involved in the regulation of intraocular pressure. Research supports the hypothesis that GPR18 is the abnormal cannabidiol receptor and N-arachidonoyl glycine, the endogenous lipid metabolite of anandamide, initiates directed microglial migration in the CNS through activation of GPR18, though recent evidence demonstrates that NAGly was not shown to be a GPR18 agonist in rat sympathetic neurons. Resolvin D2 (RvD2), a member of the specialized proresolving mediators (SPM) class of polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites, is an activating ligand for GPR18; RvD2 and its activation of GPR18 contribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found primarily in the ''Cannabis'' plant or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 100 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include aminoalkylindoles, 1,5-diarylpyrazoles, quinolines, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-1602
O-1602 is a synthetic compound most closely related to abnormal cannabidiol, and more distantly related in structure to cannabinoid drugs such as THC. O-1602 does not bind to the classical cannabinoid receptors CB1 or CB2 with any significant affinity, but instead is an agonist at several other receptors which appear to be related to the cannabinoid receptors, particularly GPR18 and GPR55. These previously orphan receptors have been found to be targets for a number of endogenous and synthetic cannabinoid compounds, and are thought to be responsible for most of the non-CB1, non-CB2 mediated effects that have become evident in the course of cannabinoid research. O-1602 produces some effects shared with classical cannabinoid compounds such as analgesic and antiinflammatory effects and appetite stimulation, but it does not produce sedation or psychoactive effects, and has several actions in the gut and brain that are not shared with typical cannabinoid agonists. See also * Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP-55940
55,940 is a synthetic cannabinoid which mimics the effects of naturally occurring THC (one of the psychoactive compounds found in cannabis). CP 55,940 was created by Pfizer in 1974 but was never marketed. It is currently used as a research tool to study the endocannabinoid system. Pharmacology CP 55,940 is 45 times more potent than Δ9-THC, and fully antagonized by rimonabant (SR141716A). It is considered a full agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors and has Ki values of 0.58 nM and 0.68 nM respectively, but is an antagonist at GPR55, the putative "CB3" receptor. CP 55,940 binding has been detected in the cytosol of rat brain cerebral cortex. It can upregulate 5-HT2A receptors in mice. In vitro studies CP 55,940 induced cell death in NG 108-15 Mouse neuroblastoma x Rat glioma hybrid brain cancer (genetically engineered mouse x rat brain cancer) cells. In vivo studies CP 55,940 showed protective effects on rat brain mitochondria upon paraquat exposure. It a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP 55,940
55,940 is a synthetic cannabinoid which mimics the effects of naturally occurring THC (one of the psychoactive compounds found in cannabis). CP 55,940 was created by Pfizer in 1974 but was never marketed. It is currently used as a research tool to study the endocannabinoid system The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system composed of endocannabinoids, which are neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors, and cannabinoid receptor proteins that are expressed throughout the central nervous system ( .... Pharmacology CP 55,940 is 45 times more potent than Δ9-THC, and fully antagonized by rimonabant (SR141716A). It is considered a full agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors and has Ki values of 0.58 nM and 0.68 nM respectively, but is an antagonist at GPR55, the putative "CB3" receptor. CP 55,940 binding has been detected in the cytosol of rat brain cerebral cortex. It can upregulate 5-HT2A receptors in mice. In vitro studies CP 55, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPR119
G protein-coupled receptor 119 also known as GPR119 is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''GPR119'' gene. GPR119, along with GPR55 and GPR18, have been implicated as novel cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacology GPR119 is expressed predominantly in the pancreas and gastrointestinal tract in rodents and humans, as well as in the brain in rodents. Activation of the receptor has been shown to cause a reduction in food intake and body weight gain in rats. GPR119 has also been shown to regulate incretin and insulin hormone secretion. As a result, new drugs acting on the receptor have been suggested as novel treatments for obesity and diabetes. Ligands A number of endogenous, synthetic and plant derived ligands for this receptor have been identified: * 2-Oleoylglycerol (2OG) * Anandamide * AR-231,453 * MBX-2982 * Oleoylethanolamide (OEA) (Endogenous Ligand) * PSN-375,963 * PSN-632,408 Human microbiota and GPR119 activation Commensal bacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |