|
G-quadruplexes
In molecular biology, G-quadruplex secondary structures (G4) are formed in nucleic acids by sequences that are rich in guanine. They are helical in shape and contain guanine tetrads that can form from one, two or four strands. The unimolecular forms often occur naturally near the ends of the chromosomes, better known as the telomeric regions, and in transcriptional regulatory regions of multiple genes, both in microbes and across vertebrates including oncogenes in humans. Four guanine bases can associate through Hoogsteen hydrogen bonding to form a square planar structure called a guanine tetrad (G-tetrad or G-quartet), and two or more guanine tetrads (from G-tracts, continuous runs of guanine) can stack on top of each other to form a G-quadruplex. The placement and bonding to form G-quadruplexes is not random and serve very unusual functional purposes. The quadruplex structure is further stabilized by the presence of a cation, especially potassium, which sits in a central c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine Tetrad
In molecular biology, a guanine tetrad (also known as a G-tetrad or G-quartet) is a structure composed of four guanine bases in a square planar array. They most prominently contribute to the structure of G-quadruplexes, where their hydrogen bonding stabilizes the structure. Usually, there are at least two guanine tetrads in a G-quadruplex, and they often feature Hoogsteen-style hydrogen bonding. Guanine tetrads are formed by sequences rich in guanine, such as GGGGC. They may also play a role in the dimerization of non-endogenous RNAs to facilitate the replication of some viruses. Guanine tetrads dimerize through their 5' ends since it is more energetically favorable. They can be stabilized by central cations, such as lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, or caesium. However, they still form a variety of different structures. Guanine tetrads are not always stable, but the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA can assist in stability of the guanine tetrads themselves. Guanine tetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiparallel (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, two biopolymers are antiparallel if they run parallel (geometry), parallel to each other but with opposite directionality (molecular biology), directionality (alignments). An example is the two complementarity (molecular biology), complementary strands of a DNA nucleic acid double helix, double helix, which antiparallel vectors, run in opposite directions alongside each other. Nucleic acids Nucleic acid molecules have a phosphoryl (5') end and a hydroxyl (3') end. This notation follows from IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, organic chemistry nomenclature, and can be used to define the movement of enzymes such as DNA polymerases relative to the DNA strand in a non-arbitrary manner. G-quadruplexes G-quadruplexes, also known as G4 DNA are secondary structures found in nucleic acids that are rich in guanine. These structures are normally located at the telomeres (the ends of the Chromosome, chromosomes). The G-quadruplex can either be parallel or antiparallel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
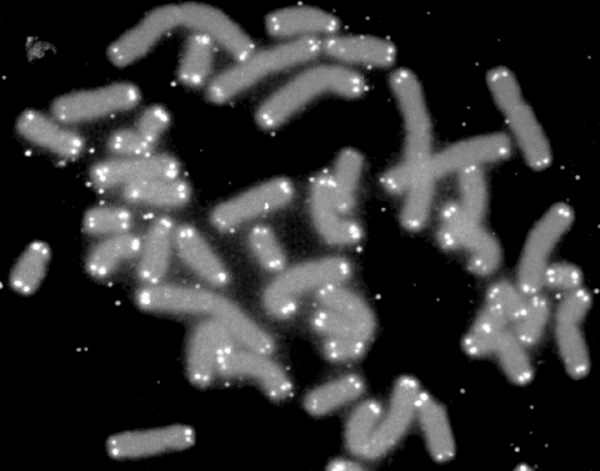
Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of DNA, chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery The existence of a special structure at the ends of chromosomes was independently proposed in 1938 by Hermann Joseph Muller, studying the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', and in 1939 by Barbara McClintock, working with maize. Muller observed that the ends of irradiated fruit fly chromosomes did not present alterations such as deletions or inversions. He hypothesized the presence of a protective cap, which he coined "telomeres", from the Greek ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomeric
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery The existence of a special structure at the ends of chromosomes was independently proposed in 1938 by Hermann Joseph Muller, studying the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', and in 1939 by Barbara McClintock, working with maize. Muller observed that the ends of irradiated fruit fly chromosomes did not present alterations such as deletions or inversions. He hypothesized the presence of a protective cap, which he coined "telomeres", from the Greek ''telos'' (end) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoogsteen Base Pair
A Hoogsteen base pair is a variation of base-pairing in nucleic acids such as the A•T pair. In this manner, two nucleobases, one on each strand, can be held together by hydrogen bonds in the major groove. A Hoogsteen base pair applies the N7 position of the purine base (as a hydrogen bond acceptor) and C4 amino group (as a donor), which bind the Watson–Crick (N3–C4) face of the pyrimidine base. History Ten years after James Watson and Francis Crick published their model of the DNA double helix, Karst Hoogsteen reported a crystal structure of a complex in which analogues of A and T formed a base pair that had a different geometry from that described by Watson and Crick. Similarly, an alternative base-pairing geometry can occur for G•C pairs. Hoogsteen pointed out that if the alternative hydrogen-bonding patterns were present in DNA, then the double helix would have to assume a quite different shape. Hoogsteen base pairs are observed in alternative structures such as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aaron Klug
Sir Aaron Klug (11 August 1926 – 20 November 2018) was a British biophysicist and chemist. He was a winner of the 1982 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his development of crystallographic electron microscopy and his structural elucidation of biologically important nucleic acid-protein complexes. Early life and education Klug was born in Želva, in Lithuania, to Jewish parents Lazar, a cattleman, and Bella (née Silin) Klug, with whom he emigrated to South Africa at the age of two. He was educated at Durban High School. Paul de Kruif's 1926 book, '' Microbe Hunters'', aroused his interest in microbiology. Klug was part of the Hashomer Hatzair Jewish Zionist youth movement in South Africa. He started to study microbiology, but then moved into physics and maths, graduating with a Bachelor of Science degree at the University of the Witwatersrand, in Johannesburg. He studied physics under Reginald W. James and obtained his Master of Science degree at the University of Cape Town. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimolecular
In chemistry, molecularity is the number of molecules that come together to react in an elementary reaction, elementary (single-step) reactionAtkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry. Oxford University Press, 2014 and is equal to the sum of Stoichiometry, stoichiometric coefficients of reactants in the elementary reaction with effective collision (Activation energy, sufficient energy) and correct orientation. Depending on how many molecules come together, a reaction can be unimolecular, bimolecular or even trimolecular. The kinetic order of any elementary reaction or reaction step is ''equal'' to its molecularity, and the rate equation of an elementary reaction can therefore be determined by inspection, from the molecularity. The kinetic order of a complex (multistep) reaction, however, is not necessarily equal to the number of molecules involved. The concept of molecularity is only useful to describe elementary reactions or steps. Unimolecular reactions In a unimolecular r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA repair#DNA damage, DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30 nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |