|
Frederick P. Salvucci
Frederick "Fred" Peter Salvucci (born April 8, 1940) is an American civil engineer and educator, who specializes in transportation issues. Salvucci was the Secretary of Transportation for the Commonwealth of Massachusetts under Governor Michael Dukakis, serving a total of 12 years. He was a Senior Lecturer of Transportation Planning and Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Career Born in Brighton, Salvucci graduated from Boston Latin School in 1957. He then attended the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he received his Bachelor of Science in 1961 and his Master of Science in 1962, both in civil engineering with a specialization in transportation. At MIT, he was a member of Chi Epsilon and the American Society of Civil Engineers. From 1964 to 1965, he spent a year abroad as a Fulbright Scholar at the University of Naples Federico II, where he studied investments in transportation to stimulate economic development in high poverty areas of Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton, Boston
Brighton is a former town and current neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts, United States, located in the northwestern corner of the city. It is named after the English city of Brighton. Initially Brighton was part of Cambridge, and known as "Little Cambridge". Brighton separated from Cambridge in 1807 after a bridge dispute, and was annexed to Boston in 1874. For much of its early history, it was a rural town with a significant commercial center at its eastern end. The neighborhood of Allston was also formerly part of the town of Brighton, but is now often considered to be separate, leading to the name Allston–Brighton for the combined area. This historic center of Brighton is the Brighton Center Historic District. The Aberdeen section of Brighton was designated as a local architectural conservation district by the Boston Landmarks Commission in 2001. History In 1630, land comprising present-day Allston–Brighton and Newton was assigned to Watertown. In 1634, the Massach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulbright Scholar
The Fulbright Program, including the Fulbright–Hays Program, is one of several United States Cultural Exchange Programs with the goal of improving intercultural relations, cultural diplomacy, and intercultural competence between the people of the United States and other countries, through the exchange of persons, knowledge, and skills. Via the program, competitively-selected American citizens including students, scholars, teachers, professionals, scientists, and artists may receive scholarships or grants to study, conduct research, teach, or exercise their talents abroad; and citizens of other countries may qualify to do the same in the United States. The program was founded by United States Senator J. William Fulbright in 1946 and is considered to be one of the most widely recognized and prestigious scholarships in the world. The program provides approximately 8,000 grants annually – roughly 1,600 to U.S. students, 1,200 to U.S. scholars, 4,000 to foreign students, 900 to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Park Square (Boston)
Park Square in downtown Boston, Massachusetts is bounded by Stuart, Charles Street South, Boylston, and Arlington Streets. It is the home of the Boston Four Seasons Hotel, the Boston Park Plaza, and nearly a dozen restaurants. To the north across Boylston Street is the Boston Public Garden. To the east is the Washington Street Theatre District. The Bay Village neighborhood is to the south, and Back Bay is to the west. At one time, the terminus of the Boston and Providence Railroad was in the square; however, after South Station opened, the terminal was closed. A statue commemorating US emancipation of slaves was installed in Park Square in 1879 and removed in December 2020. From 1964 to 1974, the University of Massachusetts Boston campus was located in Park Square. A small street in the district was renamed "Park Plaice" in honor of Legal Sea Foods, a local restaurant. Education Boston Public Schools operates area district public schools. Boston Renaissance Charter Public Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MBTA
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (abbreviated MBTA and known colloquially as "the T") is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network includes the MBTA subway with three metro lines (the Blue, Orange, and Red lines), two light rail lines (the Green and Ashmont–Mattapan lines), and a five-line bus rapid transit system (the Silver Line); MBTA bus local and express service; the twelve-line MBTA Commuter Rail system, and several ferry routes. In , the system had a ridership of , or about per weekday as of , of which the rapid transit lines averaged and the light rail lines , making it the fourth-busiest rapid transit system and the third-busiest light rail system in the United States. As of , average weekday ridership of the commuter rail system was , making it the sixth-busiest commuter rail system in the U.S. The MBTA is the successor of several previous public a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MBTA Commuter Rail
The MBTA Commuter Rail system serves as the commuter rail arm of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's transportation coverage of Greater Boston in the United States. Trains run over of track to 141 different stations, with 58 stations on the north side and 83 stations on the south. It is operated under contract by Keolis, which took over operations on July 1, 2014, from the Massachusetts Bay Commuter Railroad Company (MBCR). In , the system had a ridership of , or about per weekday as of , making it the sixth-busiest commuter rail system in the U.S., behind the three New York-area systems, the Chicago-area system, and the Philadelphia-area system. The line's characteristic purple-trimmed coaches operate as far south as North Kingstown, Rhode Island, and as far north as Newburyport and as far west as Fitchburg, both in Massachusetts. Trains originate at two major terminals in Boston—South Station and North Station—with both transportation hubs offering conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Corridor (Boston)
The Southwest Corridor or Southwest Expressway was a project designed to bring an eight-lane highway into the City of Boston from a direction southwesterly of downtown. It was supposed to connect with Interstate 95 (I-95) at Route 128. As originally designed, it would have followed the right of way of the former Penn Central/New Haven Railroad mainline (current Amtrak Northeast Corridor) running from Readville, north through Roslindale, Forest Hills and Jamaica Plain, where it would have met the also-cancelled I-695 (Inner Belt Expressway). The 50-foot-wide (15 m) median for the uncompleted "Southwest Expressway" would have carried the southwest stretch of the MBTA Orange Line within it, replacing the Washington Street Elevated railway's 1901/1909-built elevated railbed. Another highway, the four-lane South End Bypass, was proposed to run along the railroad corridor between I-695 in Roxbury and I-90 near Back Bay. History Early railroad history The Boston and Providence Railroa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange Line (MBTA)
The Orange Line is a rapid transit line operated by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) as part of the MBTA subway system. The line runs south on the surface from Oak Grove station in Malden, Massachusetts through Malden and Medford, paralleling the Haverhill Line, then crosses the Mystic River on a bridge into Somerville, then into Charlestown. It passes under the Charles River and runs through Downtown Boston in the Washington Street Tunnel. The line returns to the surface in the South End, then follows the Southwest Corridor southwest in a cut through Roxbury and Jamaica Plain to Forest Hills station. The Orange Line operates during normal MBTA service hours (all times except late nights) with six-car trains. A 120-car fleet built in 1979–1981 is being replaced with a 152-car CRRC fleet from 2018 to 2023. The Orange Line is fully grade-separated; trains are driven by operators with automatic train control for safety. Wellington Carhouse in Medford is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alewife (MBTA Station)
Alewife station is a Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) intermodal transit station in the North Cambridge neighborhood of Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is the northwest terminal of the rapid transit Red Line (part of the MBTA subway system) and a hub for several MBTA bus routes. The station is at the confluence of the Minuteman Bikeway, Alewife Linear Park, Fitchburg Cutoff Path, and Alewife Greenway off Alewife Brook Parkway adjacent to Massachusetts Route 2, with a five-story parking garage for park and ride use. The station has three bike cages. Alewife station is named after nearby Alewife Brook Parkway and Alewife Brook, themselves named after the alewife fish. The Fitchburg Railroad (now the MBTA Commuter Rail Fitchburg Line) opened through North Cambridge in 1842, followed by the now-closed Lexington Branch and Fitchburg Cutoff branch lines. An extension of the 1912-opened Cambridge–Dorchester line to North Cambridge was first proposed in the 1930s, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quincy Center Station
Quincy Center station is an intermodal transit station in Quincy, Massachusetts. It is a transfer station between the MBTA Red Line subway, MBTA Commuter Rail's Old Colony Lines and Greenbush Line, and a number of MBTA bus routes. It is located between Hancock Street and Burgin Parkway in the Quincy Center district. Opened in 1971, the station was covered by a large parking garage which was closed in 2012 due to structural problems. A project to remove and replace the garage is under way. All buses and trains are accessible from the Hancock Street entrance. Access from Burgin Parkway was formerly through the garage; a new accessible entrance will be added as part of the current project. History Old Colony Railroad The Old Colony Railroad opened its main line from South Boston to Plymouth on November 10, 1845. Quincy station was located at Quincy Square behind the town hall. New station buildings – low brick structures very similar to the extant building at – were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Line (MBTA)
The Red Line is a rapid transit line operated by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) as part of the MBTA subway system. The line runs south and east underground from Alewife station in North Cambridge through Somerville and Cambridge, surfacing to cross the Longfellow Bridge then returning to tunnels under Downtown Boston. It continues underground through South Boston, splitting into two branches on the surface at JFK/UMass station. The Ashmont branch runs southwest through Dorchester to Ashmont station, where the connecting light rail Ashmont–Mattapan High Speed Line (shown as part of the Red Line on maps, but operated separately) continues to Mattapan station. The Braintree branch runs southwest through Quincy and Braintree to Braintree station. The Red Line operates during normal MBTA service hours (all times except late nights) with six-car trains. The 218-car active fleet consists of three orders of cars built in 1969–70, 1987–89, and 1993–9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clean Air Act (United States)
The Clean Air Act (CAA) is the United States' primary federal air quality law, intended to reduce and control air pollution nationwide. Initially enacted in 1963 and amended many times since, it is one of the United States' first and most influential modern environmental laws. As with many other major U.S. federal environmental statutes, the Clean Air Act is administered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), in coordination with state, local, and tribal governments. EPA develops extensive administrative regulations to carry out the law's mandates. The associated regulatory programs are often technical and complex. Among the most important, the National Ambient Air Quality Standards program sets standards for concentrations of certain pollutants in outdoor air; the National Emissions Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants program sets standards for emissions of particular hazardous pollutants from specific sources. Other programs create requirements for vehicle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
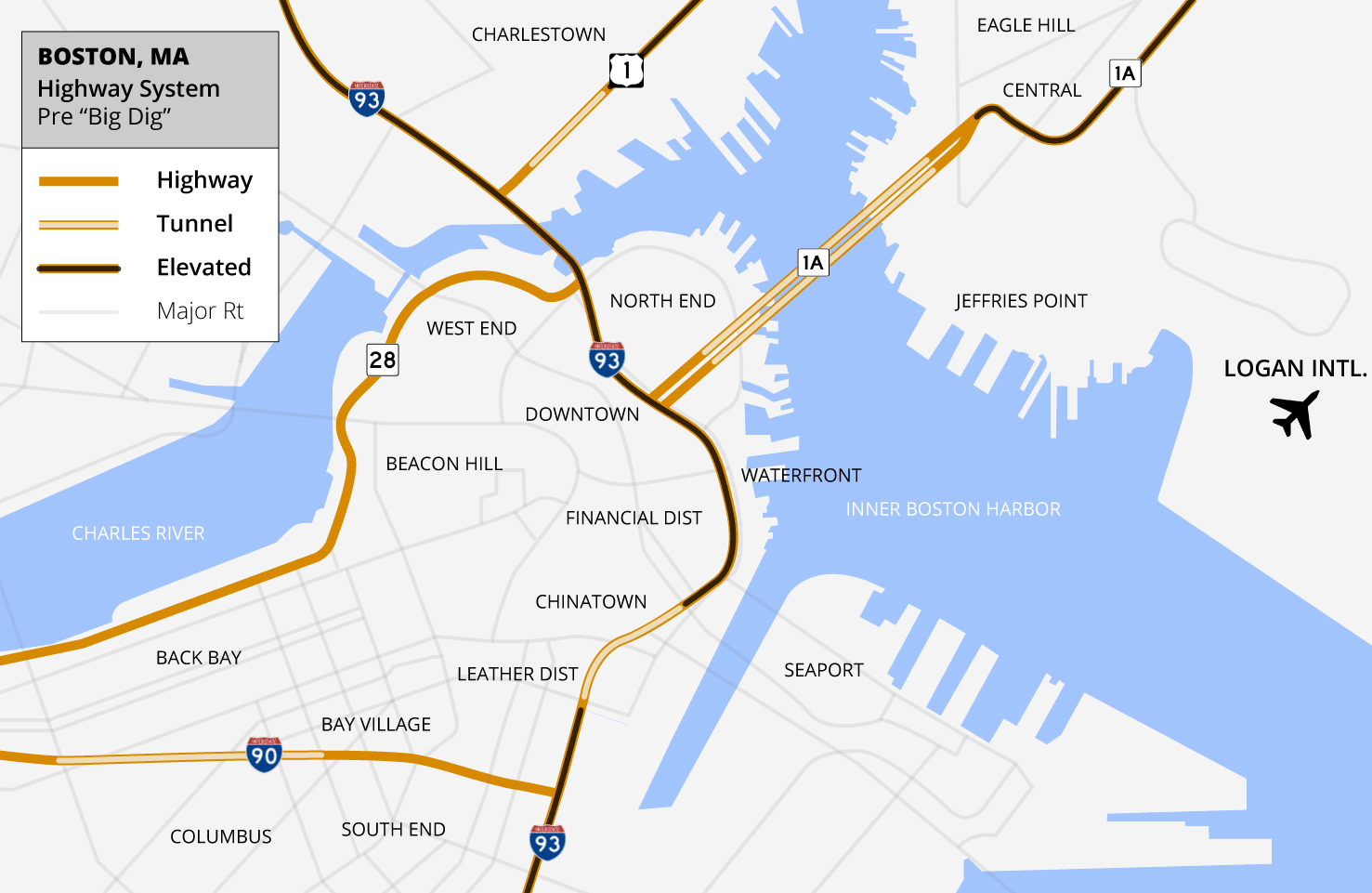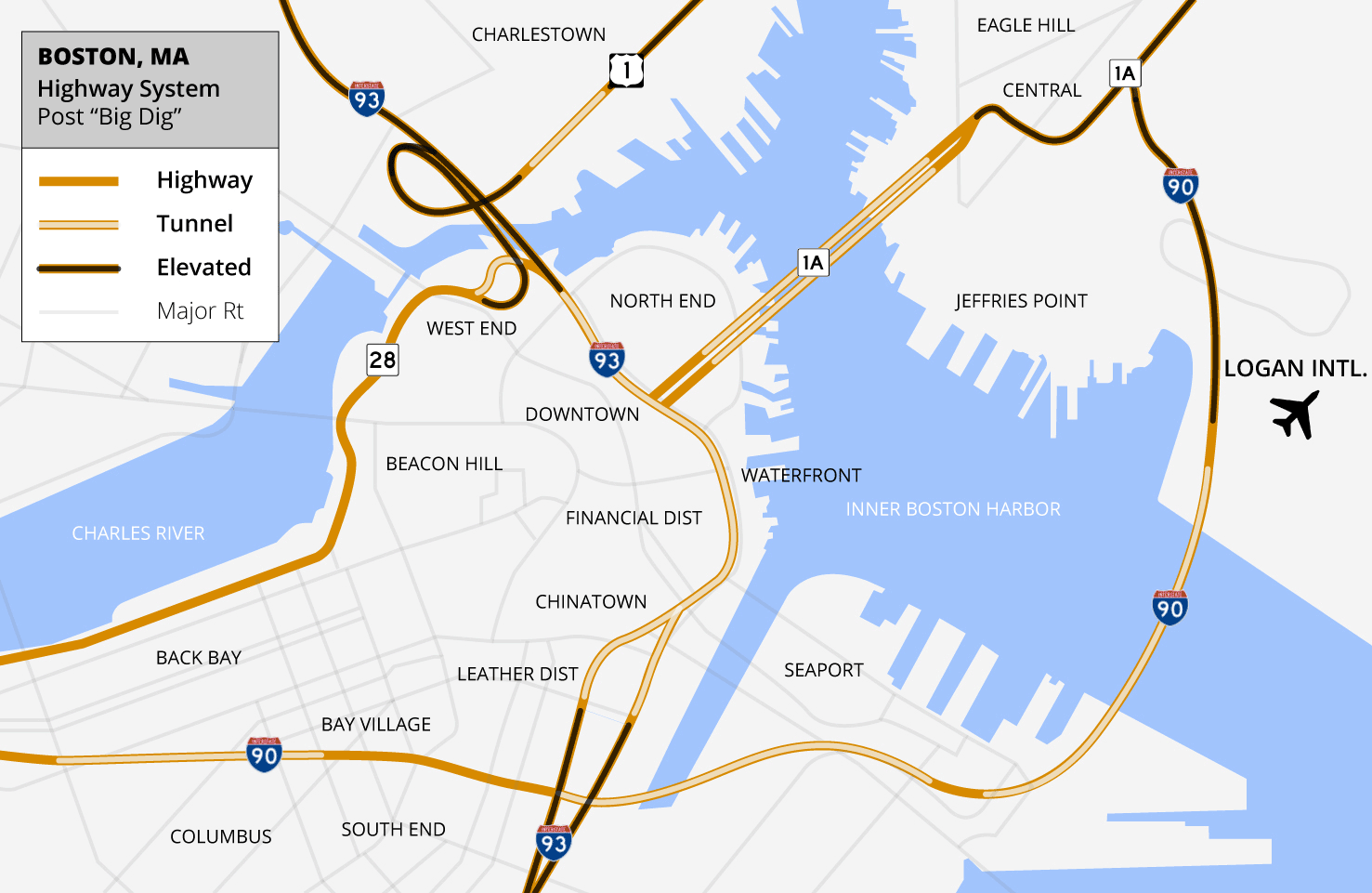
Big Dig (Boston, Massachusetts)
The Central Artery/Tunnel Project (CA/T Project), commonly known as the Big Dig, was a megaproject in Boston that rerouted the Central Artery of Interstate 93 (I-93), the chief highway through the heart of the city, into the 1.5-mile (2.4 km) tunnel named the Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Tunnel. The project also included the construction of the Ted Williams Tunnel (extending I-90 to Logan International Airport), the Leonard P. Zakim Bunker Hill Memorial Bridge over the Charles River, and the Rose Kennedy Greenway in the space vacated by the previous I-93 elevated roadway. Initially, the plan was also to include a rail connection between Boston's two major train terminals. Planning began in 1982; the construction work was carried out between 1991 and 2006; and the project concluded on December 31, 2007, when the partnership between the program manager and the Massachusetts Turnpike Authority ended. The Big Dig was the most expensive highway project in the United States, and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |