|
Fossil Bluff
Fossil Bluff is a seasonal British aircraft refuelling station located on the east coast of Alexander Island in Antarctica. In operation since 1961, its facilities provide fuel, storage, and ancillary support for British exploration and operations during the summer season, October through March. The site is adjacent to a natural, north–south travelling route along the George VI Ice Shelf. Fossil Bluff is a collection of buildings and facilities, at the centre of which lies Fossil Bluff Station. Geography Fossil Bluff hut sits at the foot of a scree-covered ridge overlooking George VI Sound which separates mountainous Alexander Island from Palmer Land. George VI Ice Shelf occupies the sound and provides a north–south route for travelling parties except in high summer when the ice shelf's surface is flooded with meltwater. To the west and north-west lie Planet Heights, an extensive range of mountains rising to over . Immediately to the west lies Giza Peak and the snow-free P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wynyard, Tasmania
Wynyard ( /ˈwɪnjɚd/) ''wi-nyuhd'') is a rural town located on the North West coast of Tasmania, Australia. Wynyard is situated west of Burnie. As of the 2021 census, Wynyard has an estimated population of 6,296 The town is a regional hub servicing the surrounding rural areas, the adjacent Burnie Wynyard Airport provides commercial flights to Melbourne and other districts. The main council offices for the Waratah-Wynyard local government area are located in Wynyard. History Three ex-convict Alexander brothers established a settlement, Alexandria, on the west, or Table Cape, side of the Inglis River in the 1850s. They bought large areas of farmland on Table Cape and built several small ships for produce and timber trading. Shortly afterwards, Wynyard town, on the east side of the river, was laid out, but lagged well behind Alexandria which had a church and several shops including a blacksmith and general store. After the Inglis River was bridged in 1861, Alexandria began to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kg Hut New View
KG, Kg, kG or kg may refer to: Units of measurement * kg, the kilogram, the SI base unit of mass * kG or kGs, the kilogauss, a unit of measurement of magnetic induction People * KG (wrestler), ring name of Syuri (born 1989) * K. G. Cunningham (born 1939), Australian radio presenter and cricketer * Kevin Garnett (born 1976), nicknamed KG, American basketball player * Kyle Gass (born 1960), nicknamed KG, American musician of Tenacious D * Kagiso Rabada (born 1995), nicknamed KG, South African cricketer Places * Bad Kissingen, Germany, vehicle registration code KG * Kragujevac, Serbia, vehicle registration code KG * Kyrgyzstan, ISO 3166 country code KG ** .kg, Internet country code top-level domain for Kyrgyzstan Transportation * , a Venezuelan airline, IATA airline designator KG * Ship's center of gravity above keel Other uses * ''K.G.'' (album), a 2020 album by King Gizzard & the Lizard Wizard * , the highest state court in Berlin, Germany * , a military combat formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethelbert Ridge
Ethelbert Ridge () is a ridge composed of igneous rocks within the Fossil Bluff groups of sedimentary rocks located east-southeast of Mount Alfred. It was originally named "Saddleback Ridge" informally by British Antarctic Survey geologist Alastair Linn because of its pronounced saddleback appearance when viewed from the south. It was later formally named for Ethelbert, son of Ethelwulf, the Saxon King of the West Saxons and Kentishmen, and effectively King of England The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiw ... from 860–866. This continues the naming of features in the area after Saxon Kings of England. References Ridges of Alexander Island {{AlexanderIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belemnite Valley
Belemnite Valley () is a valley in Antarctica, northwest of Fossil Bluff Base and bounded to the north by Eros Glacier. It is mostly snow and ice free with a central meltwater stream. It has been referred to as "Hollow Valley" in scientific reports in the early 1960s, and is sometimes referred to today as "Happy Valley". The name "Belemnite Valley" was proposed due to the preponderance of Belemnite Belemnitida (or the belemnite) is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to ...s found in the exposed rock in the valley. References Valleys of Antarctica Valleys of Alexander Island {{AlexanderIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airports In Antarctica
__TOC__ List , 18/36Ice , - valign=top , Palmer SkiwayHeliport , , NZ12 , , Anvers Island , , 01/19Snow , - valign=top , Patriot Hills Blue-Ice Runway , , SCPZ , , Ellsworth Mountains , , 24MIce , - valign=top , Pegasus Field(serving McMurdo Station and Scott Base) , , NZPG , , Ross Island , , 15/33Ice08/26Ice (skiway) , - valign=top , Perseus RunwayTemporary Airfield , , , , , , 10/28Blue Ice , - valign=top , Petrel Skiway , , SA47 , , Dundee Island , , 08/26Ice , - valign=top , Phoenix Airfield(serving McMurdo Station and Scott Base) , , NZFX , , Ross Island , , 15/33Compacted Snow , - valign=top , Plateau Station Skiway , , AT20 , , Queen Maud Land , , 18/36Ice , - valign=top , Plog Island Skiway(serving Davis) , , , , Plog Island , , (variable)Ice , - valign=top , Princess Elisabeth Skiway , , QAP , AT99 , Utsteinen Nunatak , , Blue Ice , - valign=top , Progress Skiway , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Field Camps
Many Antarctic research stations support satellite field camps which are, in general, seasonal camps. The type of field camp can vary – some are permanent structures used during the annual Antarctic summer, whereas others are little more than tents used to support short term activities. Field camps are used for many things, from logistics (Sky Blu) to dedicated scientific research (WAIS Divide Field Camp). List of field camps See also *Research stations in Antarctica *Demographics of Antarctica *List of Antarctic expeditions This list of Antarctic expeditions is a chronological list of expeditions involving Antarctica. Although the existence of a southern continent had been hypothesized as early as the writings of Ptolemy in the 1st century AD, the South Pole was no ... * Transport in Antarctica References External links COMNAP Antarctic Facilities() COMNAP Antarctic Facilities Map() Antarctic Digital Database Map ViewerSCAR {{Polar exploration Field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
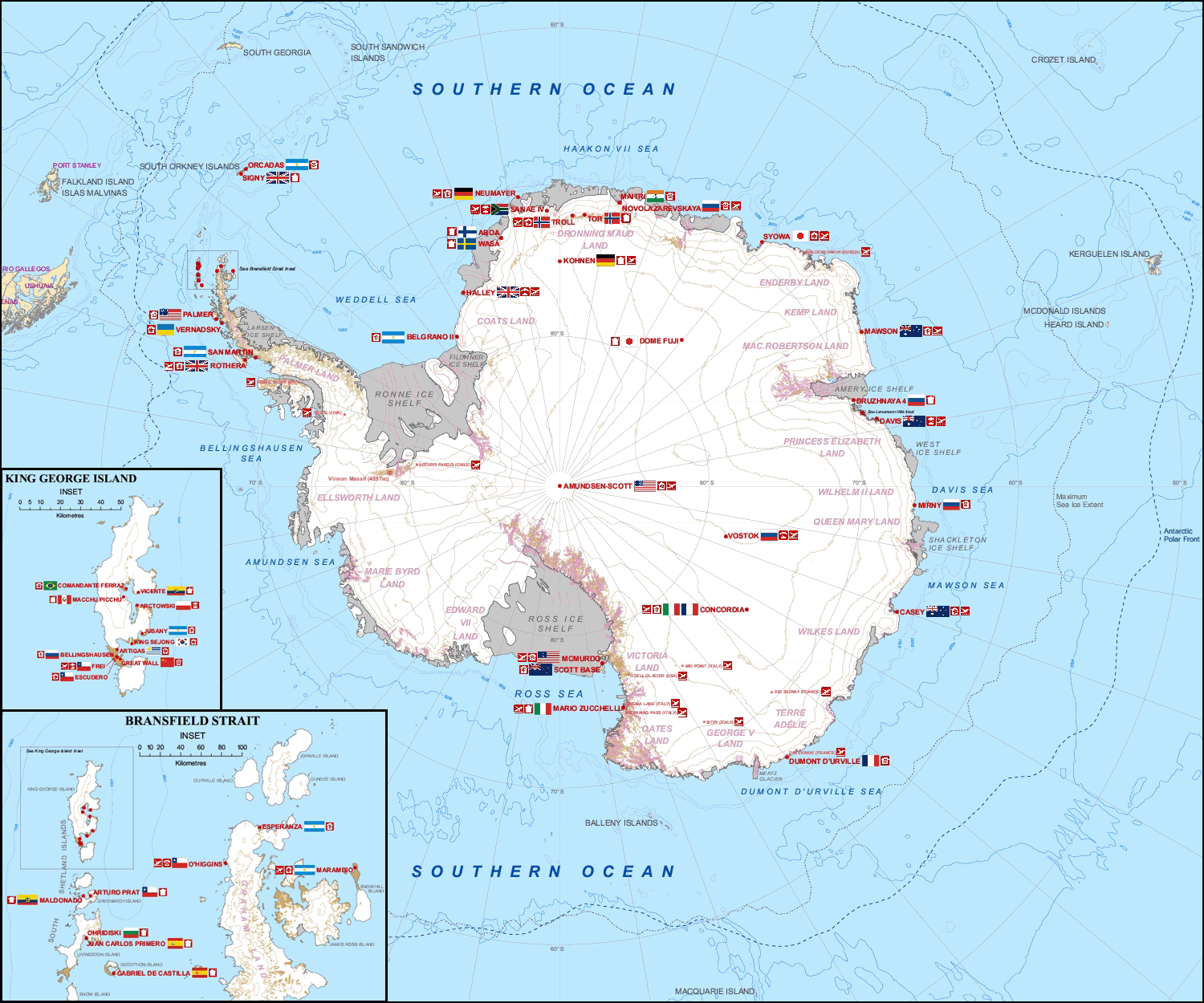
Research Stations In Antarctica
Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rock or on ice that is (for practical purposes) fixed in place. Many of the stations are demographics of Antarctica, staffed throughout the year. A total of 42 countries (as of October 2006), all signatories to the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, operate seasonal (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent. The population of people performing and supporting scientific research on the continent and nearby islands varies from approximately 4,000 during the summer season to 1,000 during winter (June). In addition to these permanent stations, approximately Antarctic field camps, 30 field camps are established each summer to support specific projects. History First bases During the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sky Blu
Sky Blu is a forward operating station for the British Antarctic Survey located in southern Palmer Land, Antarctica. It is in an area of blue ice, an extremely hard and dense ice which has lost the air bubbles that normally cloud the ice. It provides a runway able to accommodate wheeled aircraft that are larger than can be handled by other types of runways in the area. The facility is used to store fuel drums and field equipment for onward transport by the Twin Otter aircraft. The camp is staffed by a minimum of 2, but usually 3 people, including a mechanic. Staff eat and sleep in a Melon hut, but there is also a garage and other tents. History It was first located by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) in 1993-94 and rapidly became an essential tool in BAS's ability to operate further south. This is mainly because the Blue Ice runway is able to accommodate wheeled aircraft. BAS can therefore fly its Dash-7 4-engined plane from Rothera directly to Sky Blu. The Dash has a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter
The de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter is a Canadian STOL (Short Takeoff and Landing) utility aircraft developed by de Havilland Canada, which produced the aircraft from 1965 to 1988; Viking Air purchased the type certificate, then restarted production in 2008 before re-adopting the DHC name in 2022. The aircraft's fixed tricycle undercarriage, STOL capabilities, twin turboprop engines and high rate of Climb (aeronautics), climb have made it a successful commuter airliner, typically seating 18-20 passengers, as well as a cargo and medical evacuation aircraft. In addition, the Twin Otter has been popular with commercial skydiving operations, and is used by the United States Army Parachute Team and the United States Air Force's 98th Flying Training Squadron. Design and development Development of the aircraft began in 1964, with the first flight on May 20, 1965. A twin-engine replacement for the single-engine de Havilland Canada DHC-3 Otter, DHC-3 Otter retaining DHC's STOL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, grass, soil, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or road salt, salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and Airport apron, ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using Tarmacadam, tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now International Civil Aviation Organization#Use of the International System of Units, commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rothera Research Station
The Rothera Research Station is a British Antarctic Survey (BAS) base on the Antarctic Peninsula, located at Rothera Point, Adelaide Island. Rothera also serves as the capital of the British Antarctic Territory, a British Overseas Territory. History and current activities Rothera station was established in 1975 to replace Adelaide station (1961-1977) where the skiway had deteriorated. The opening of the Bonner Laboratory in 1996/1997 marked the start of new activities in biological sciences in the Antarctic peninsula. These included scuba diving and experiments conducted in the Bonner Laboratory throughout the year. The first Bonner Lab burned down in the winter of 2001 after an electrical fault; it was rebuilt and opened in December 2003. Meteorological research using satellite data intercepted at the Rothera ground station also continues year round. In January 2017, it was announced that the Rothera Research Station will receive £100m in funding from the government. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Science
''Antarctic Science'' is a bimonthly peer reviewed scientific journal published by Cambridge University Press, focusing on all aspects of scientific research in the Antarctic. The editors-in-chief are David W. H. Walton (British Antarctic Survey), Walker O. Smith (Virginia Institute of Marine Sciences), Laurie Padman (Earth & Space Research), Alan Rodger (University of Aberystwyth), and John Smellie (University of Leicester). This journal is a continuation of the "British Antarctic Survey Bulletin" published from 1963 to 1988. Under this former title the journal was indexed in Biological abstracts, Chemical abstracts, and GeoRef.Library Catalog. "British Antarctic Survey Bulletin".Harvard University - Hollis Classic. 2014. This journal's name was changed to "Antarctic Science" in 1989. Abstracting and indexing This journal is indexed by the following services: * Science Citation Index * Current Contents/ Agriculture, Biology & Environmental Sciences * Current Contents/ Physical, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

