|
Fishing Bank
An ocean bank, sometimes referred to as a fishing bank or simply bank, is a part of the seabed that is shallow compared to its surrounding area, such as a shoal or the top of an underwater hill. Somewhat like continental slopes, ocean bank slopes can upwell as tidal and other flows intercept them, sometimes resulting in nutrient-rich currents. Because of this, some large banks, such as Dogger Bank and the Grand Banks of Newfoundland, are among the richest fishing grounds in the world. There are some banks that were reported in the 19th century by navigators, such as Wachusett Reef, whose existence is doubtful. Types Ocean banks may be of volcanic nature. Banks may be carbonate or terrigenous. In tropical areas some banks are submerged atolls. As they are not associated with any landmass, banks have no outside source of sediments. Carbonate banks are typically platforms, rising from the ocean depths, whereas terrigenous banks are elevated sedimentary deposits. Seamounts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Bank
Georges Bank (formerly known as St. Georges Bank) is a large elevated area of the sea floor between Cape Cod, Massachusetts (United States), and Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia (Canada). It separates the Gulf of Maine from the Atlantic Ocean. The origin of its name is obscure. The 1610 Velasco map, prepared for King James I of England, used the name "S. Georges Banck", a common practice when the name of the English patron saint, St. George, was sprinkled around the English-colonized world. By the 1850s, it was known simply as Georges Bank. Physical environment Georges Bank is the most westward of the great Atlantic fishing banks. The now-submerged portions of the North American mainland are comprised in the continental shelf running from the Grand Banks of Newfoundland to Georges. Georges Bank was part of the North American mainland as recently as 12,000 years ago. Roughly oval in shape, Georges Bank measures about 149 miles (240 kilometres) in length by 75 miles (120 kilome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seamount
A seamount is a large geologic landform that rises from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form.IHO, 2008. Standardization of Undersea Feature Names: Guidelines Proposal form Terminology, 4th ed. International Hydrographic Organization and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, Monaco. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spratly Islands
The Spratly Islands ( fil, Kapuluan ng Kalayaan; zh, c=南沙群島/南沙群岛, s=, t=, p=Nánshā Qúndǎo; Malay, id, Kepulauan Spratly; vi, Quần đảo Trường Sa) are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea. Composed of islands, islets, cays, and more than 100 reefs, sometimes grouped in submerged old atolls, the archipelago lies off the coasts of the Philippines, Malaysia, and southern Vietnam. Named after the 19th-century British whaling captain Richard Spratly who sighted Spratly Island in 1843, the islands contain less than of naturally occurring land area, which is spread over an area of more than . The Spratly Islands are one of the major archipelagos in the South China Sea which complicate governance and economics in this part of Southeast Asia due to their location in strategic shipping lanes. The islands are largely uninhabited, but offer rich fishing grounds and may contain significant oil and natural gas reserves,Owen, N. A. and C. H. Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reed Bank
Reed Tablemount (also referred to as Reed Bank, Recto Bank and several other names) is a large tablemount or guyot in the South China Sea north-east of Dangerous Ground and north-east of the Spratly Islands. It covers an area of , but with depths between 9 and only 45 meters. The submerged but hydrocarbon-rich area includes Nares Bank and Marie Louise Bank. Although the Permanent Court of Arbitration ruled in 2016 that the area is within the Philippine Exclusive Economic Zone, economic rights to the area continue to be disputed – mainly by the People's Republic of China – and exploitation of the hydrocarbon reserves by the Philippines were suspended in 2015. The tablemount is in the northeast quadrant of the Philippine's Kalayaan claimed territory, which also includes most of the north and east portions of the Spratly Islands. The area is located off the northwest coast of Palawan, north of Iroquois reef, Pennsylvania reef and the Southern reefs, and east of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Chagos Bank
The Great Chagos Bank, in the Chagos Archipelago, about south of Maldives, is the largest atoll structure in the world, with a total area of . The atoll is administered by the United Kingdom through the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT). Islands Despite its enormous size, the Great Chagos Bank is largely a submarine structure. There are only four emerging reefs, mostly located on the western rim of the atoll, except for lonely Nelson Island, which lies wholly isolated in the middle of the northern fringe. These reefs have eight individual low and sandy islands, with a total land area of about . All islands and their surrounding waters are a Strict Nature Reserve since 1998. The total length of the eastern and southern expanses of the bank, as well as the reefs in its central area are wholly submerged. The islands of the Great Chagos Bank, starting clockwise from the south, are: * Danger Island (slightly more than long from North to South, by wide, land area , veget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Bahama Bank
The Bahama Banks are the submerged carbonate platforms that make up much of the Bahama Archipelago. The term is usually applied in referring to either the Great Bahama Bank around Andros Island, or the Little Bahama Bank of Grand Bahama Island and Great Abaco, which are the largest of the platforms, and the Cay Sal Bank north of Cuba. The islands of these banks are politically part of the Bahamas. Other banks are the three banks of the Turks and Caicos Islands, namely the Caicos Bank of the Caicos Islands, the bank of the Turks Islands, and wholly submerged Mouchoir Bank. Farther southeast are the equally wholly submerged Silver Bank and Navidad Bank north of the Dominican Republic. Geologic history and structure The limestone that comprises the Banks has been accumulating since at least the Cretaceous period, and perhaps as early as the Jurassic; today the total thickness under the Great Bahama Bank is over 4.5 kilometres (2.8 miles). As the limestone was deposited in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Caledonia
) , anthem = "" , image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg , map_alt = Location of New Caledonia , map_caption = Location of New Caledonia , mapsize = 290px , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = Annexed by France , established_date = 24 September 1853 , established_title2 = Overseas territory , established_date2 = 1946 , established_title3 = Nouméa Accord , established_date3 = 5 May 1998 , official_languages = French , regional_languages = , capital = Nouméa , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , demonym = New Caledonian , government_type = Devolved parliamentary dependency , leader_title1 = President of France , leader_name1 = Emmanuel Macron , leader_title2 = President of the Government , leader_name2 = Louis Mapou , leader_title3 = President of the Congress , leader_name3 = Roch Wamytan , leader_title4 = High Commissioner , leader_name4 = Patr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lansdowne Bank
Lansdowne Bank, sometimes called Landsdowne Bank, is an extensive submerged bank located between the main island of New Caledonia and the Chesterfield Islands, in the easternmost part of the Coral Sea. It covers an area of , p. 26 making it one of the largest banks of the world, has general depths of , and a largely sandy bottom. Two reefs mark the shallowest spots of the bank, but they are still submerged at low tide. Fairway Ridge, also called Fairway Plateau, is a submarine feature shown on some maps in that area. The Lansdowne Bank area marked is far larger than Fairway Plateau, but there are smaller, unnamed plateaus nearby. The Lansdowne Bank area, shown at the northeastern end of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seychelles Bank
The Mascarene Plateau is a submarine plateau in the Indian Ocean, north and east of Madagascar. The plateau extends approximately , from Seychelles in the north to Réunion in the south. The plateau covers an area of over of shallow water, with depths ranging from , plunging to to the abyssal plain at its edges. It is the second-largest oceanic plateau in the Indian Ocean after the Kerguelen Plateau. Geography The northern part of the Mascarene Plateau includes the Agaléga Islands and the Seychelles Islands. The southern part of the Mascarene Plateau includes Hawkins Bank, the Mascarene Islands, Nazareth Bank, the Saya de Malha Bank, and the Soudan Banks. The Mascarene Islands are the mountainous islands of the Cargados Carajos Shoals, Mauritius, Réunion, and Rodrigues. Geology The Indian subcontinent was at one time next to the east coast of Seychelles, but seafloor spreading has moved the landmass to its current position, where it has collided and fused wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saya De Malha
The Saya de Malha Bank (also the Sahia de Malha Bank, modern Portuguese: ''saia de malha'', English: ''mesh skirt'') or Mesh Skirt Bank, is one of the largest submerged ocean banks in the world, a part of the vast undersea Mascarene Plateau. Geography The Saya de Malha Bank lies northeast of Madagascar, southeast of Seychelles, and north of Nazareth Bank, the Cargados Carajos Shoals, and the island of Mauritius, and currently falls mostly under international waters. The closest land is tiny Agaléga (one of the Outer Islands of Mauritius), some further west, followed by the southern Seychellois island of Coëtivy, some northwest. Mauritius administers the whole Saya de Malha Bank as a portion of it lies within its exclusive economic zone. The bank covers an area of , and is composed of two separate structures, the smaller North Bank (also called Ritchie Bank), and the huge South Bank. If the South Bank were recognized as a submerged atoll structure, it would be the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bahama Bank
The Bahama Banks are the submerged carbonate platforms that make up much of the Bahama Archipelago. The term is usually applied in referring to either the Great Bahama Bank around Andros Island, or the Little Bahama Bank of Grand Bahama Island and Great Abaco, which are the largest of the platforms, and the Cay Sal Bank north of Cuba. The islands of these banks are politically part of the Bahamas. Other banks are the three banks of the Turks and Caicos Islands, namely the Caicos Bank of the Caicos Islands, the bank of the Turks Islands, and wholly submerged Mouchoir Bank. Farther southeast are the equally wholly submerged Silver Bank and Navidad Bank north of the Dominican Republic. Geologic history and structure The limestone that comprises the Banks has been accumulating since at least the Cretaceous period, and perhaps as early as the Jurassic; today the total thickness under the Great Bahama Bank is over 4.5 kilometres (2.8 miles). As the limestone was deposited in shal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
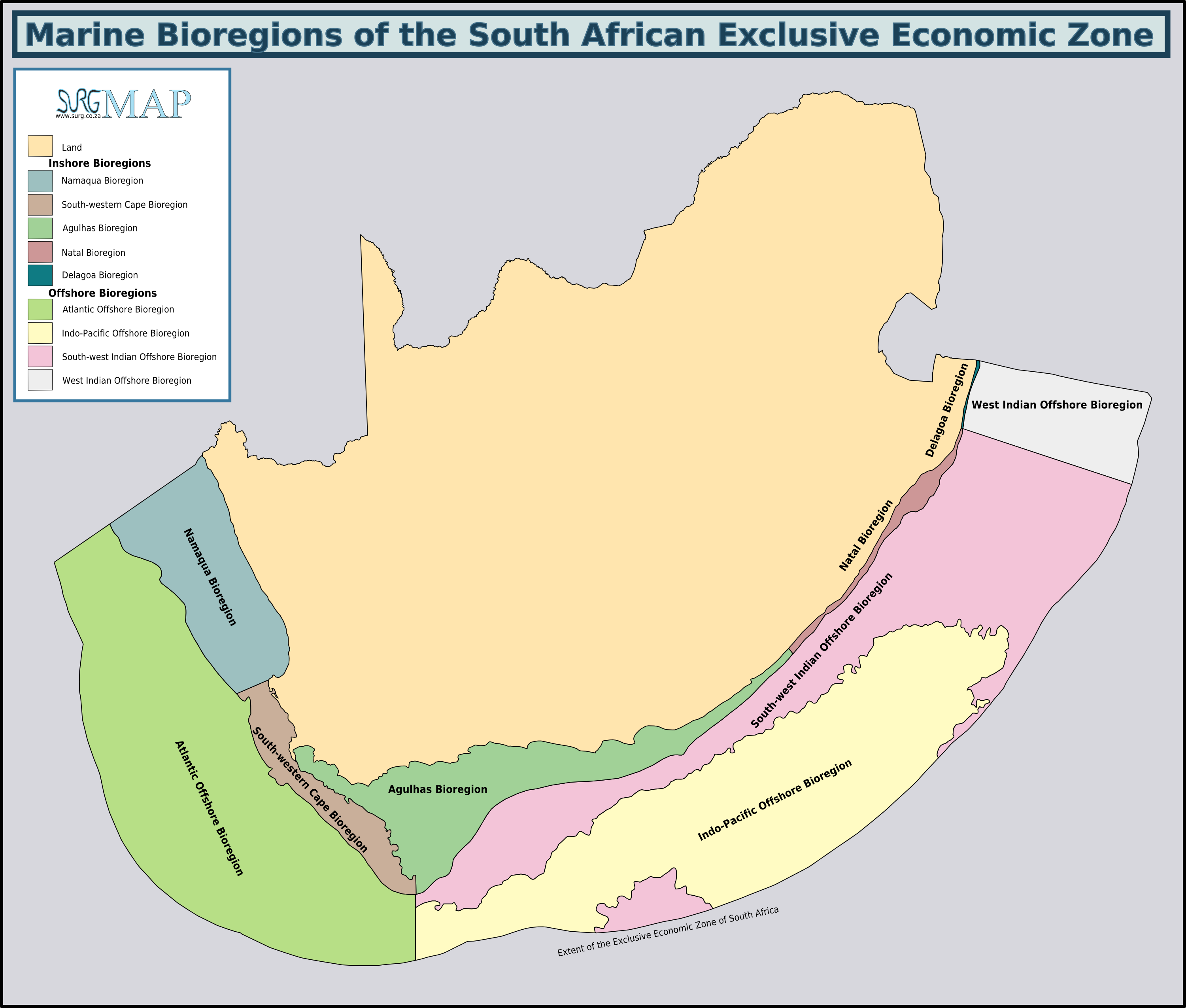
Agulhas Bank
The Agulhas Bank (, from Portuguese for Cape Agulhas, ''Cabo das Agulhas'', "Cape of Needles") is a broad, shallow part of the southern African continental shelf which extends up to south of Cape Agulhas before falling steeply to the abyssal plain. It is the ocean region where the warm Indian Ocean and the cold Atlantic Ocean meet. This convergence leads to treacherous sailing conditions, accounting for numerous wrecked ships in the area over the years. However, the meeting of the oceans here also fuels the nutrient cycle for marine life, making it one of the best fishing grounds in South Africa. Extent and characteristics South African marine ecoregions from the 2011 classification The Agulhas Bank stretches approximately along the African coast, from off Cape Peninsula (18°E) to Port Alfred (26°E), and up to from it. The bank slopes down relatively steeply from the coast to about deep and reaches before dropping steeply to on its southern edge. The shelf s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |