|
Fazao Malfakassa National Park
Fazao Malfakassa National Park is the largest of three national parks in Togo, the others being Kéran National Park, Kéran and Fosse aux Lions National Park, Fosse aux Lions. It is situated between the Kara Region and Centrale Region, Togo, Centrale Region in semi-mountainous wetland, and forms part of the border with Ghana. The Fondation Franz Weber (activist), Franz Weber was authorized by the government to manage the park for 25 years, beginning in 1990 and ending in 2015. It was established in 1975 by the merger of two reserve forests created in 1951: Fazao () and Malfakassa (). The Forest Classée Du Fazao contains most of the biodiversity of the forest, while visitors go hiking in the rocky hills of the Malfacassa Zone de Chasse. The terrain consists of "savanna woodland ... good stands of gallery forest ... , submontane forest and grass-covered hilltops." The site is currently being considered for inclusion in the World Heritage Site, World Heritage list of sites with "out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kara Region
Kara is one of Togo's five regions. Kara is the regional capital. Other major cities in the Kara region include Bafilo, Bassar, and Niamtougou. Kara is divided into the prefectures of Assoli, Bassar, Bimah, Dankpen, Doufelgou, Kéran, and Kozah. Kara is located north of Centrale Region and south of Savanes Region. To the west lies the Northern Region of Ghana, and to the east lie the Atakora (further north) and Donga (further south) Departments of Benin Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the nort .... See also * Regions of Togo References Kara Region {{Togo-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulletin Of The African Bird Club
Bulletin or The Bulletin may refer to: Periodicals (newspapers, magazines, journals) * Bulletin (online newspaper), a Swedish online newspaper * ''The Bulletin'' (Australian periodical), an Australian magazine (1880–2008) ** Bulletin Debate, a famous dispute from 1892 to 1893 between Henry Lawson and Banjo Paterson * ''The Bulletin'' (alternative weekly), an alternative weekly published in Montgomery County, Texas, U.S. * ''The Bulletin'' (Bend), a daily newspaper in Bend, Oregon, U.S. * ''The Bulletin'' (Belgian magazine), a weekly English-language magazine published in Brussels, Belgium * ''The Bulletin'' (Philadelphia newspaper), a newspaper in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S. (2004–2009) * ''The Bulletin'' (Norwich) * ''The Bulletin'' (Pittsburgh), a monthly community newspaper in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, U.S. * ''London Bulletin'', surrealist monthly magazine (1938–1940) * ''The Morning Bulletin'', a daily newspaper published in Rockhampton, Queensland, Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oribi
The oribi (; ''Ourebia ourebi'') is a small antelope found in eastern, southern and western Africa. The sole member of its genus, it was described by the German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm von Zimmermann in 1783. While this is the only member in the genus ''Ourebia'', eight subspecies are identified. The oribi reaches nearly at the shoulder and weighs . It possesses a slightly raised back, and long neck and limbs. The glossy, yellowish to rufous brown coat contrasts with the white chin, throat, underparts and rump. Only males possess horns; the thin, straight horns, long, are smooth at the tips and ringed at the base. Typically diurnal, the oribi is active mainly during the day. Small herds of up to four members are common; males defend their group's territory, large. It is primarily a grazer, and prefers fresh grasses but also browses occasionally. A seasonal breeder, the time when mating occurs varies geographically. Unlike all other small antelopes, oribi can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Hartebeest
The western hartebeest (''Alcelaphus buselaphus major'') is an antelope native to the medium to tall grassland plains of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, and Togo. It is possibly extirpated from Gambia. Average adults stand tall at the shoulder and weigh . A western hartebeest's coat is fawn-colored, ranging from tan to dark brown. It has a small hump at the front shoulders. It has slim legs and a very narrow face. Both sexes are horned. Horns may be long. Considerable variation in horn growth occurs, but they generally grow sideways out from the head, before curving forward, then inward and backward. The horns are terminated by sharp tips. The western hartebeest is mainly active during the day. A herbivore, it grazes during the cooler morning and afternoon periods, resting in shaded areas during the hot daytime. Females form herds of five to 12 members, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterbuck
The waterbuck (''Kobus ellipsiprymnus'') is a large antelope found widely in sub-Saharan Africa. It is placed in the genus '' Kobus'' of the family Bovidae. It was first described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1833. Its 13 subspecies are grouped under two varieties: the common or ellipsiprymnus waterbuck and the defassa waterbuck. The head-and-body length is typically between and the typical height is between . In this sexually dimorphic antelope, males are taller and heavier than females. Males reach roughly at the shoulder, while females reach . Males typically weigh and females . Their coat colour varies from brown to grey. The long, spiral horns, present only on males, curve backward, then forward, and are long. Waterbucks are rather sedentary in nature. As gregarious animals, they may form herds consisting of six to 30 individuals. These groups are either nursery herds with females and their offspring or bachelor herds. Males start showing territorial behavio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Duiker
The common duiker (''Sylvicapra grimmia''), also known as the grey or bush duiker, is a small antelope and the only member of the genus ''Sylvicapra''. This species is found everywhere in Africa south of the Sahara, excluding the Horn of Africa and the rainforests of the central and western parts of the continent. Generally, they are found in habitats with sufficient vegetation cover to allow them to hide—savanna and hilly areas, including the fringes of human settlements. Description Colouration of this species varies widely over its vast geographic range. There are 14 subspecies described, ranging from chestnut in forested areas of Angola to grizzled gray in northern savannas and light brown shades in arid regions. It grows to about in height and generally weighs ; although females are generally larger and heavier than the males. Only the male has horns and these can grow to long. Behavior Breeding is year round and the female gives birth to one fawn after a gestation per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow-backed Duiker
The yellow-backed duiker (''Cephalophus silvicultor'') is a forest dwelling antelope in the order Artiodactyla from the family Bovidae. Yellow-backed duikers are the most widely distributed of all duikers. They are found mainly in Central and Western Africa, ranging from Senegal to Western Uganda with possibly a few in Gambia. Their range also extends southward into Rwanda, Burundi, Zaire, and most of Zambia. Taxonomy and etymology The scientific name of the yellow-backed duiker is ''Cephalophus silvicultor''. It is the type species of ''Cephalophus'', and placed in the subfamily Cephalophinae and family Bovidae. The species was first described by English botanist Adam Afzelius in the journal ''Nova Acta Regiæ Societatis Scientiarum Upsaliensis'' in 1815. The generic name has possibly originated from the combination of the New Latin word ''cephal'', meaning head, and the Greek word ''lophos'', meaning crest. The specific name ''silvicultor'' is composed by two Latin words: '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Duiker
The bay duiker (''Cephalophus dorsalis''), also known as the black-striped duiker and the black-backed duiker, is a forest-dwelling duiker native to western and southern Africa. It was first described by British zoologist John Edward Gray in 1846. Two subspecies are identified. The bay duiker is reddish-brown and has a moderate size. Both sexes reach at the shoulder. The sexes do not vary considerably in their weights, either; the typical weight range for this duiker is . Both sexes have a pair of spiky horns, measuring . A notable feature of this duiker is the well-pronounced solid stripe of black extending from the back of the head to the tail. The bay duiker is a nocturnal animal. It tends to remain solitary, but pairs can also be observed. The leopard is the main predator of this duiker. It mainly prefers fruits, but may also feed on animal matter such as bird eggs. Females may conceive by the age of 18 months. Breeding occurs throughout the year. Gestation lasts about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red-flanked Duiker
The red-flanked duiker (''Cephalophus rufilatus'') is a species of small antelope found in western and central Africa in countries as far apart as Senegal and Sudan. Red-flanked duikers grow to almost 15 in (35 cm) in height and weigh up to 31 lb (14 kg). They have russet coats, with greyish-black legs and backs, and white underbellies. They feed on leaves, fallen fruits, seeds and flowers, and sometimes twigs and shoots. The adults are territorial, living in savannah and lightly wooded habitats, and the females usually produce a single offspring each year. They have lifespans of ten to fifteen years in captivity. Description The red-flanked duiker is one of the smallest species of antelope, growing to a height of about with a weight of around . The head and body are blackish-grey near the spine gradually blending into a reddish-brown colour on the neck and flanks. There are small white markings on the ears and snout and a dark streak runs along the centre of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Duiker
The Maxwell's duiker (''Philantomba maxwellii'') is a small antelope found in western Africa. Taxonomy The scientific name of Maxwell's duiker is ''Philantomba maxwelli''. It is classified in the genus ''Philantomba'' along with the blue duiker (''P. monticola'') and Walter's duiker (''P. walteri''). It was first described by English naturalist Charles Hamilton Smith in 1827. The species is sometimes treated as a species of ''Cephalophus'', another genus of duikers, although ''Philantomba'' has been recognised as a genus by zoologists such as Peter Grubb and Colin Groves. Theodor Haltenorth has considered this species to be a race of the blue duiker due to their identical features. In 2012, Anne R. Johnston (of the University of Orleans) and colleagues constructed a cladogram of the subfamily Cephalophinae (duiker), that includes the three genera ''Cephalophus'', ''Philantomba'' and '' Sylvicapra'', based on mitochondrial analysis. ''Philantomba'' was shown to be monophylet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushbuck
The Cape bushbuck (''Tragelaphus sylvaticus'') is a common and a widespread species of antelope in sub-Saharan Africa.Wronski T, Moodley Y. (2009)Bushbuck, harnessed antelope or both? ''Gnusletter'', 28(1):18-19. Bushbuck are found in a wide range of habitats, such as rain forests, montane forests, forest-savanna mosaic, savanna, bushveld, and woodland. Bushbuck stand about at the shoulder and weigh from . They are generally solitary, territorial browsers. Taxonomy The taxonomy of bushbuck, and of the Tragelaphini tribe in general, has been contested. Bushbuck have been fractured into over 40 subspecies in the past. mtDNA profiles of a large number of samples were resolved in 2009 as belonging to 19 groups, some corresponding to previously described subspecies, while others were previously unrecognised and remained unnamed. These groups were then organised into two taxa - a nominate northern subspecies (''T. s. scriptus'') and a southern subspecies ''T. s. sylvaticus''. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Ourebia_nigricaudata.png)

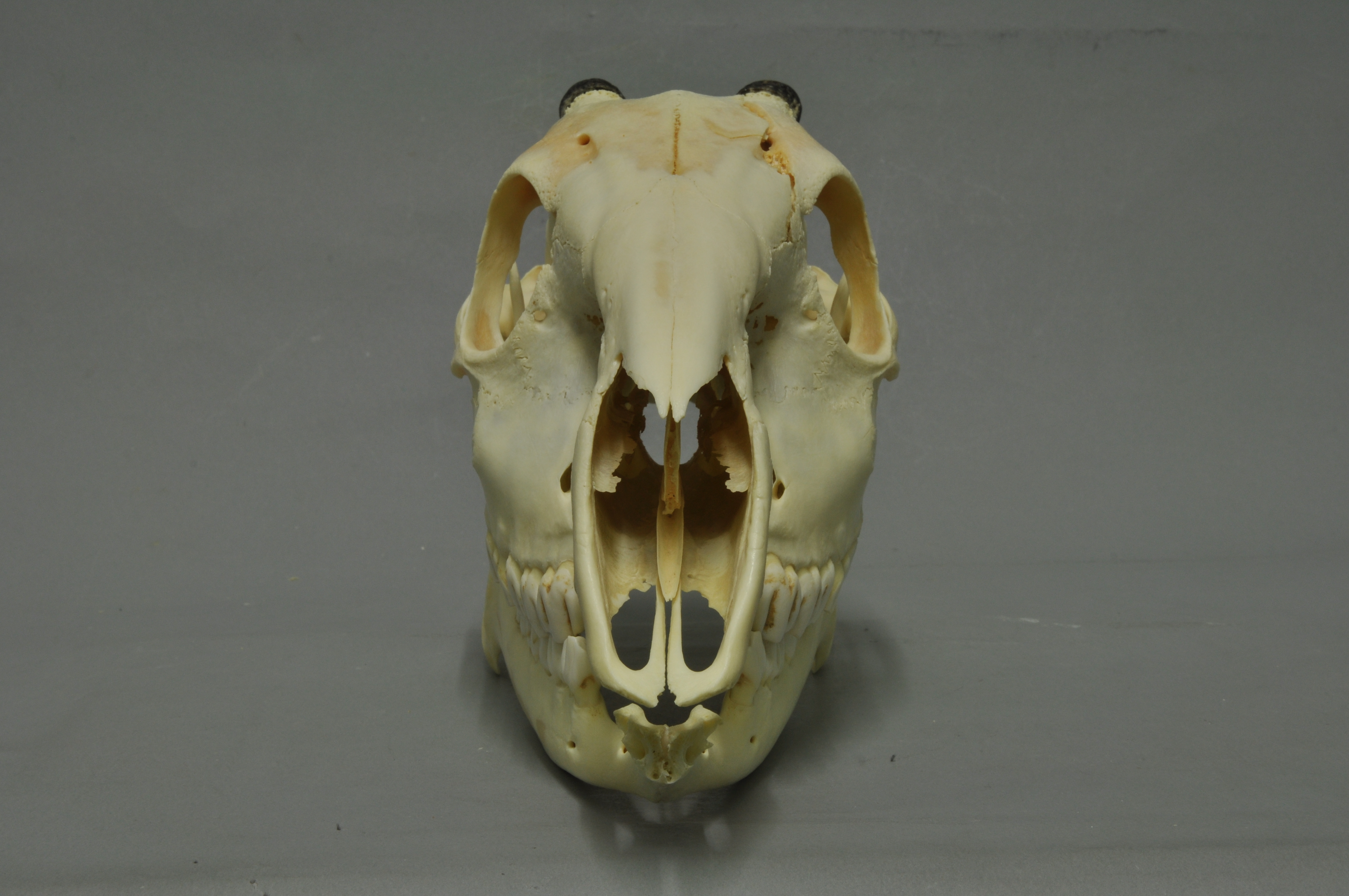
_Cephalophus_dorsalis.png)
_Cephalophus_maxwelli.png)
_Tragelaphus_scriptus_decula.png)