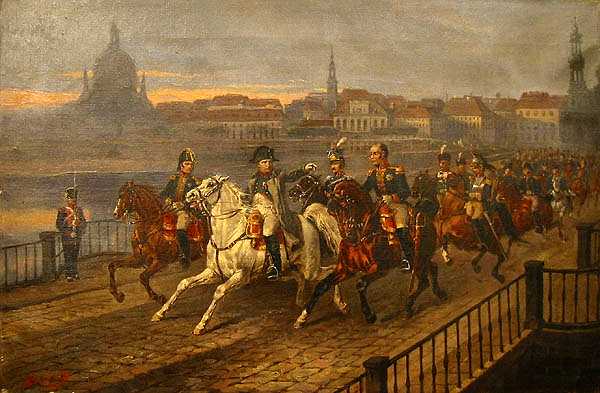|
Fürstenzug
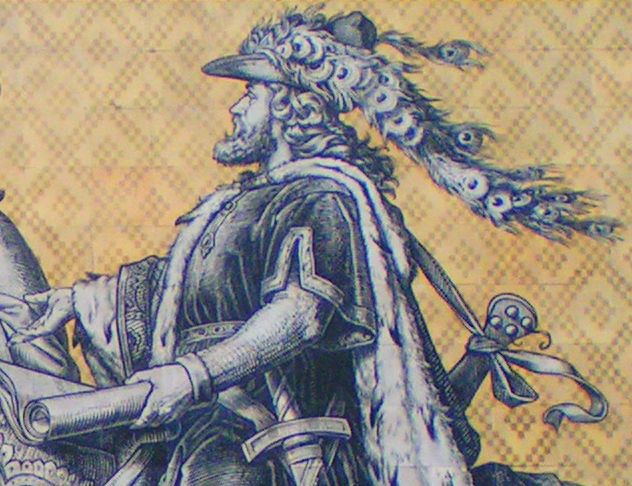
The Fürstenzug (English: Procession of Princes) in Dresden, Germany, is a large mural of a mounted procession of the rulers of Saxony. It was originally painted between 1871 and 1876 to celebrate the 800th anniversary of the House of Wettin, Wettin Dynasty, Saxony's ruling family. In order to make the work weatherproof, it was replaced with approximately 23,000 Meissen porcelain tiles between 1904 and 1907. With a length of , it is known as the largest porcelain artwork in the world. The mural displays the ancestral portraits of the 35 margraves, electors, dukes and kings of the House of Wettin between 1127 and 1904. The Fürstenzug is located on the outer wall of the ''Stallhof'' (Stables Courtyard) of Dresden Castle. History By 1589, the outer wall of the recently built ''Stallhof'' (Stables Courtyard) of the Dresden Castle was already decorated with a fresco.Fritz Löffler: ''Das alte Dresden - Geschichte seiner Bauten''. 16th ed. Leipzig: Seemann, 2006, Reinhard Delau: '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden Fuerstenzug Augustusstr C
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Saxony, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Dresden Basin, Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden Fuerstenzug Konrad Der Grosse
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. Many boroughs west of the Elbe lie in the Ore Mountain Foreland, as well as in the valleys of the rivers ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Saxony, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Dresden Basin, Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert III, Duke Of Saxony
Albert III () (27 January 144312 September 1500) was a Duke of Saxony. He was nicknamed Albert the Bold or Albert the Courageous and founded the ''Albertine line'' of the House of Wettin. Biography Albert was born in Grimma as the third and youngest son (but fifth child in order of birth) of Frederick II the Gentle, Elector of Saxony, and Margarete of Austria, sister of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor. Later, he was a member of the Order of the Golden Fleece. After escaping from the hands of Kunz von Kaufungen, who had abducted him together with his brother Ernest, he spent some time at the court of the emperor Frederick III in Vienna. Endnote: See *F. A. von Langenn, ''Herzog Albrecht der Beherzte, Stammvater des königlichen Hauses Sachsen'' (Leipzig, 1838) *O. Sperling, ''Herzog Albrecht der Beherzte von Sachsen als Gubernator Frieslands'' (Leipzig, 1892). In Eger (Cheb) on 11 November 1464 Albert married Zdenka (Sidonie), daughter of George of Podebrady, King of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest, Elector Of Saxony
Ernest (24 March 144126 August 1486), known as Ernst in German, was Elector of Saxony from 1464 to 1486. Ernst was the founder and progenitor of the ''Ernestine line'' of Saxon princes. Biography Ernst was born in Meissen, the second son (but fourth in order of birth) of the eight children of Frederick II, Elector of Saxony and Margaret of Austria, sister of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor. The death of his older brother Frederick (1451) made him the new heir apparent to the position of Elector of Saxony. In 1455 Ernst was briefly kidnapped, along with his brother Albert, by the knight Kunz von Kaufungen an episode famous in German history as the (''i.e.'' The Stealing of the Princes). In 1464, he succeeded his father as Elector of Saxony, and annexed Thuringia in 1482, and three years later (Treaty of Leipzig, 1485) shared his territory with his brother Albert, until he arranged the division of the common possession. According to the Treaty of Leipzig he received an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick II, Elector Of Saxony
Frederick II, The Gentle (''Friedrich, der Sanftmütige''; Frederick the Gentle; 22 August 1412 – 7 September 1464) was Elector of Saxony (1428–1464) and was Landgrave of Thuringia (1440–1445). Biography Frederick was born in Leipzig, the eldest of the seven children of Frederick I, Elector of Saxony, and Catherine of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Catherine of Brunswick and Lunenburg. After the death of his father in 1428 he took over the government together with his younger brothers William III, Duke of Saxony, William III, Henry and Sigismund. In 1433 the Wettin (dynasty), Wettins finally concluded peace with the Hussites and in 1438 Frederick led Saxon forces to victory in the Battle of Sellnitz. That same year it was considered the first federal state parliament of Saxony. The parliament received the right to find together in case of innovations in fiscal matters also without summoning by the ruler. Also in 1438 it was decided that Frederick, and not his rival Bernard IV, duk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick I, Elector Of Saxony
Frederick I, the Belligerent or the Warlike (; 11 April 1370 – 4 January 1428), a member of the House of Wettin, ruled as List of margraves of Meissen, Margrave of Meissen from 1407 and List of rulers of Saxony, Elector of Saxony (as Frederick I) from 1423 until his death. He is not to be confused with his cousin Landgrave Frederick IV, Landgrave of Thuringia, Frederick IV of Thuringia, the son of Landgrave Balthasar, Landgrave of Thuringia, Balthasar. Biography He was the eldest son of Frederick III, Landgrave of Thuringia, and Catherine of Henneberg. After the death of his uncle William I, Margrave of Meissen in 1407, he was made governor of the Margraviate of Meissen together with his brother William II, Margrave of Meissen, William II as well as with his cousin Frederick IV, Landgrave of Thuringia, Frederick IV (son of Balthasar, Landgrave of Thuringia, Balthasar), until their possessions were divided in 1410 and 1415. In the German town war of 1388, he assisted Fred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert II, Margrave Of Meissen
Albert II, the Degenerate (de: ''Albrecht II der Entartete'') (1240 – 20 November 1314) was a Margrave of Meissen, Landgrave of Thuringia and Count Palatine of Saxony. He was a member of the House of Wettin. He was the eldest son of Henry III, Margrave of Meissen by his first wife, Constantia of Austria. Life In 1265 Margrave Henry III granted the Landgraviate of Thuringia and the Palatinate to Albert and the Margraviate of Landsberg in the Osterland to his younger brother Dietrich. Henry III kept for himself the Margraviates of Meissen and Lusatia as a formal power over his sons. In June 1255 Albert married Margaret of Sicily, the daughter of Emperor Frederick II, who was also King of Sicily, and Isabella of England. Margaret, also known as Margaret of Schwaben was a sister of Henry Otto, also known as ''Carlotto''. As a dowry the Pleissnerland was pledged to the House of Wettin The House of Wettin () was a dynasty which included Saxon monarch, kings, Prince Elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert I, Margrave Of Meissen
Albert I (1158 – 24 June 1195), called the Proud (), a member of the House of Wettin, was the Margrave of Meissen from 1190 until his death. Life Albert was the eldest son of Margrave Otto the Rich (1156–1190) with his consort Hedwig of Brandenburg, a daughter of the Ascanian margrave Albert the Bear. In 1186 in Ústí nad Labem he married the Přemyslid princess Sophia, a daughter of Duke Frederick of Bohemia. His father did not intend to let Albert succeed him in Meissen, openly preferring his younger brother Theodoric. Albert did not accept this and started a war against his father and brother. In 1188, he even took his father prisoner. Under the orders of the Hohenstaufen emperor Frederick Barbarossa, he had to set him free but in 1190 he was able to obtain the margravial title upon Otto's death. Albert accompanied Barbarossa's son Henry VI on his campaign to Sicily; nevertheless, he quickly abandoned the Imperial forces and returned to Meissen when his brother trie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto II, Margrave Of Meissen
Otto II, the Rich (; 1125 – 18 February 1190), a member of the House of Wettin, was Margrave of Meissen from 1156 until his death. Life He was the eldest surviving son of Conrad, Margrave of Meissen and Lusatia. When his father, under pressure from Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, retired and entered the Augustinian convent of Lauterberg in 1156, Otto succeeded him in Meissen while his younger brothers Theodoric and Dedi received the March of Lusatia and the County of Groitzsch with Rochlitz. The partition meant a weakening of the Wettin rule, and Otto's Imperial politics remained rather ineffective. He had to stand by and watch the emperor's extension of power in the Pleissnerland territory around Altenburg, Chemnitz and Zwickau; moreover he picked an unsuccessful quarrel with the rising burgraves of Dohna in the Eastern Ore Mountains. Together with Archbishop Wichmann of Magdeburg he joined Emperor Frederick's expedition against the rebellious Saxon duke Henry the Lion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietrich I, Margrave Of Meissen
Theodoric I (11 March 1162 – 18 February 1221), called the Oppressed (''Dietrich der Bedrängte''), was the Margrave of Meissen from 1198 until his death. He was the second son of Otto II, Margrave of Meissen and Hedwig of Brandenburg. Biography Theodoric, called in German Dietrich, the younger son of Otto II, Margrave of Meissen, fell out with his brother, Albert the Proud, after his mother persuaded his father to change the succession so that Theodoric was given the Margraviate of Meissen and Albrecht (although the older son) the margraviate of Weissenfels. Albert took his father prisoner to try to make him return the succession to the way it had been. After Otto obtained his release by an order of the emperor Frederick I, he had only just renewed the war when he died in 1190. Albert then took back the Meissen margraviate from his brother. Theodoric attempted to regain the margraviate, supported by ''Landgraf'' Hermann I of Thuringia, his father-in-law. In 1195, howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry III, Margrave Of Meissen
Henry III, called Henry the Illustrious (''Heinrich der Erlauchte'') (c. 1215 – 15 February 1288) from the House of Wettin was Margrave of Meissen and last Margrave of Lusatia (as Henry IV) from 1221 until his death; from 1242 also Landgrave of Thuringia. Life Born probably at the Albrechtsburg residence in Meissen, Henry was the youngest son of Margrave Theodoric I, Margrave of Meissen and his wife Jutta, daughter of Landgrave Hermann I of Thuringia. In 1221 he succeeded his father as Margrave of Meissen and Lusatia, at first under guardianship of his maternal uncle, Landgrave Louis IV of Thuringia, and after his death in 1227, under that of Duke Albert I of Saxony. In 1230 he was legally proclaimed an adult. Henry had his first combat experience in sometime around 1234, while on crusade in Prussia, fighting against the Pomesanians. His pilgrimage and company is well-documented by Peter of Dusburg, and it resulted in the construction of Balga castle, an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |