|
Funeral Ale
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect the dead, from interment, to various monuments, prayers, and rituals undertaken in their honour. Customs vary between cultures and religious groups. Funerals have both normative and legal components. Common secular motivations for funerals include mourning the deceased, celebrating their life, and offering support and sympathy to the bereaved; additionally, funerals may have religious aspects that are intended to help the soul of the deceased reach the afterlife, resurrection or reincarnation. The funeral usually includes a ritual through which the corpse receives a final disposition. Depending on culture and religion, these can involve either the destruction of the body (for example, by cremation, sky burial, decomposition, disintegration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funeral Rites (novel)
''Funeral Rites'' (''Pompes funèbres'') is a 1948 novel by Jean Genet. It is a story of love and betrayal across political divides, written this time for the narrator's lover, Jean Decarnin, killed by the Germans in World War II. The first edition was limited to 1,500 copies; in 1953 the text was revised by Gallimard, excising some possibly offensive passages, which became the basis for the 1953 English translation by Bernard Frechtman, Frechtman. References 1948 French novels Novels by Jean Genet Novels about gay topics 1940s LGBTQ novels {{1940s-LGBT-novel-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disposal Of Human Corpses
The disposal of human corpses, also called final disposition, is the practice and process of dealing with the remains of a deceased human being. Disposal methods may need to account for the fact that soft tissue will decompose relatively rapidly, while the skeleton will remain intact for thousands of years under certain conditions. Several methods for disposal are practiced. A funeral is a ceremony that may accompany the final disposition. Regardless, the manner of disposal is often dominated by spirituality with a desire to hold vigil for the dead and may be highly ritualized. In cases of mass death, such as war and natural disaster, or in which the means of disposal are limited, practical concerns may be of greater priority. Ancient methods of disposing of dead bodies include cremation practiced by the Romans, Greeks, Hindus, and some Mayans; burial practiced by the Chinese, Japanese, Bali, Jews, Christians, and Muslims, as well as some Mayans; mummification, a type of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reincarnation
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the Philosophy, philosophical or Religion, religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new lifespan (other), lifespan in a different physical form or physical body, body after biological death. In most beliefs involving reincarnation, the soul of a human being is immortality, immortal and does not disperse after the physical body has perished. Upon death, the soul merely becomes transmigrated into a newborn baby or into an animal to continue its immortality. (The term "transmigration" means the passing of a soul from one body to another after death.) Reincarnation (''punarjanman'') is a central tenet of Indian religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. In various forms, it occurs as an esoteric belief in many streams of Judaism, in certain Paganism, pagan religions (including Wicca), and in some beliefs of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas and of Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
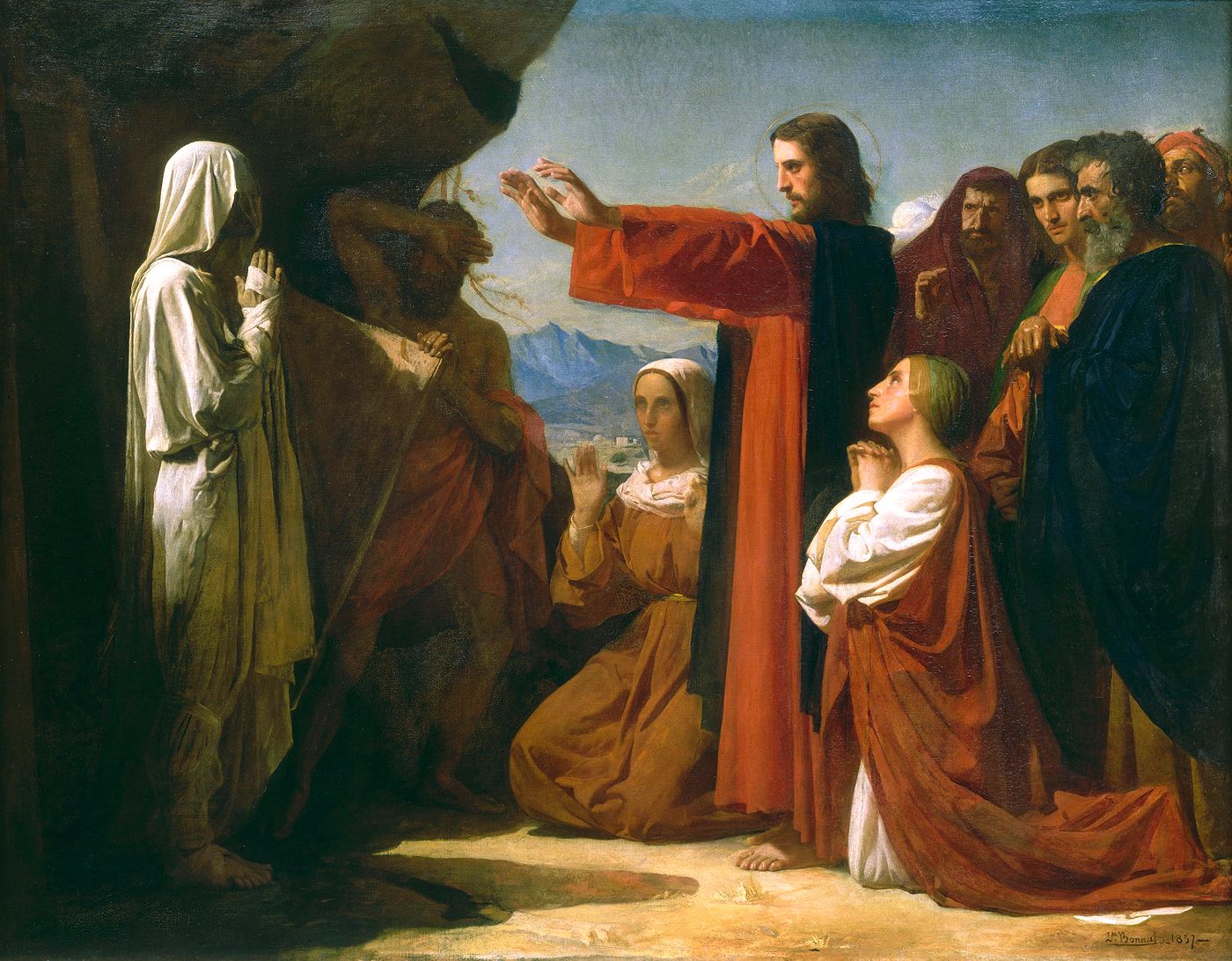
Resurrection
Resurrection or anastasis is the concept of coming back to life after death. Reincarnation is a similar process hypothesized by other religions involving the same person or deity returning to another body. The disappearance of a body is another similar but distinct belief in some religions. With the advent of written records, the earliest known recurrent theme of resurrection was in Egyptian and Canaanite religions, which had cults of dying-and-rising gods such as Osiris and Baal. Ancient Greek religion generally emphasised immortality, but in the mythos, a number of individuals were made physically immortal as they were resurrected from the dead. The universal resurrection of the dead at the end of the world is a standard eschatological belief in the Abrahamic religions. As a religious concept, resurrection is used in two distinct respects: # a belief in the ''individual resurrections'' of individual souls that is current and ongoing (e.g., Christian idealism, realized e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterlife
The afterlife or life after death is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's Stream of consciousness (psychology), stream of consciousness or Personal identity, identity continues to exist after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit, which carries with it one's personal identity. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a Supernatural, spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into World#Religion, this world and begin the life cycle over again in a process referred to as reincarnation, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, Western esotericism, esotericism, and metaphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that describe the relationship between the soul and the body are Interactionism (philosophy of mind), interactionism, Psychophysical parallelism, parallelism, and epiphenomenalism. Anthropology, Anthropologists and Psychology, psychologists have found that most humans are naturally inclined to believe in the existence of the soul and that they have interculturally distinguished between souls and bodies. The soul has been the central area of interest in philosophy since Ancient history, ancient times. Socrates envisioned the soul to possess a rational faculty, its practice being man's most godlike activity. Plato believed the soul to be the person's real self, an immaterial and immortal dweller of our lives that continues and thinks even after d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mourning
Mourning is the emotional expression in response to a major life event causing grief, especially loss. It typically occurs as a result of someone's death, especially a loved one. The word is used to describe a complex of behaviors in which the bereaved participate or are expected to participate, the expression of which varies by culture. Wearing black clothes is one practice followed in many countries, though other forms of dress are seen. Those most affected by the loss of a loved one often observe a period of mourning, marked by withdrawal from social events and quiet, respectful behavior in some cultures, though in others mourning is a collective experience. People may follow religious traditions for such occasions. Mourning may apply to the death of, or anniversary of the death of, an important individual such as a local leader, monarch, religious figure, or member of family. State mourning may occur on such an occasion. In recent years, some traditions have given way to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normative
Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good, desirable, or permissible, and others as bad, undesirable, or impermissible. A Norm (philosophy), norm in this sense means a standard for evaluating or making judgments about behavior or outcomes. "Normative" is sometimes also used, somewhat confusingly, to mean relating to a descriptive standard: doing what is normally done or what most others are expected to do in practice. In this sense a norm is not evaluative, a basis for judging behavior or outcomes; it is simply a fact or observation about behavior or outcomes, without judgment. Many researchers in science, law, and philosophy try to restrict the use of the term "normative" to the evaluative sense and refer to the description of behavior and outcomes as positive, descriptive, predictive, or empirical. ''Normative'' has specialized meanings in different academic disciplines such as philosophy, social sciences, and law. In most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or religious organization, organizations, that generally relate humanity to supernatural, transcendence (religion), transcendental, and spirituality, spiritual elements—although there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. It is an essentially contested concept. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacredness, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). and a supernatural being or beings. The origin of religious belief is an open question, with possible explanations including awareness of individual death, a sense of community, and dreams. Religions have sacred histories, narratives, and mythologies, preserved in oral traditions, sac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ritual
A ritual is a repeated, structured sequence of actions or behaviors that alters the internal or external state of an individual, group, or environment, regardless of conscious understanding, emotional context, or symbolic meaning. Traditionally associated with gestures, words, or revered objects, rituals also occur in non-human species, such as elephant mourning or corvid object-leaving. They may be prescribed by tradition, including religious practices, and are often characterized by formalism, traditionalism, rule-governance, and performance. Rituals are a feature of all known human societies. They include not only the worship rites and sacraments of organized religions and cults, but also rites of passage, atonement and ritual purification, purification rites, oaths of allegiance, dedication ceremonies, coronations and presidential inaugurations, marriages, funerals and more. Even common actions like handshake, hand-shaking and saying "hello" may be termed as ''rituals''. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prayer
File:Prayers-collage.png, 300px, alt=Collage of various religionists praying – Clickable Image, Collage of various religionists praying ''(Clickable image – use cursor to identify.)'' rect 0 0 1000 1000 Shinto festivalgoer praying in front of the Tagata fertility shrine rect 1000 0 2000 1000 Balinese Hindu bride praying during a traditional wedding ceremony rect 2000 0 3000 1000 Muslim pilgrim praying at the Masjid al-Haram rect 0 1000 1000 2000 Catholic Trappist monk praying before a crucifix rect 1000 1000 2000 2000 Ethiopian priest praying in Lalibela rect 2000 1000 3000 2000 Buddhists praying in Leh rect 0 2000 1000 3000 Sikh praying in Front of the Golden Temple in Amritsar rect 1000 2000 2000 3000 Members of the Mengjia Longshan Temple Association gather for a traditional Chinese prayer service rect 2000 2000 3000 3000 Jewish people praying at the Western Wall Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monument
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, historical, political, technical or architectural importance. Examples of monuments include statues, (war) memorials, historical buildings, archaeological sites, and cultural assets. If there is a public interest in its preservation, a monument can for example be listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The ''Palgrave Macmillan, Palgrave Encyclopedia of Cultural Heritage and Conflict'' gives the next definition of monument:Monuments result from social practices of construction or conservation of material artifacts through which the ideology of their promoters is manifested. The concept of the modern monument emerged with the development of capital and the nation-state in the fifteenth century when the ruling classes began to build and conserve what w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |