|
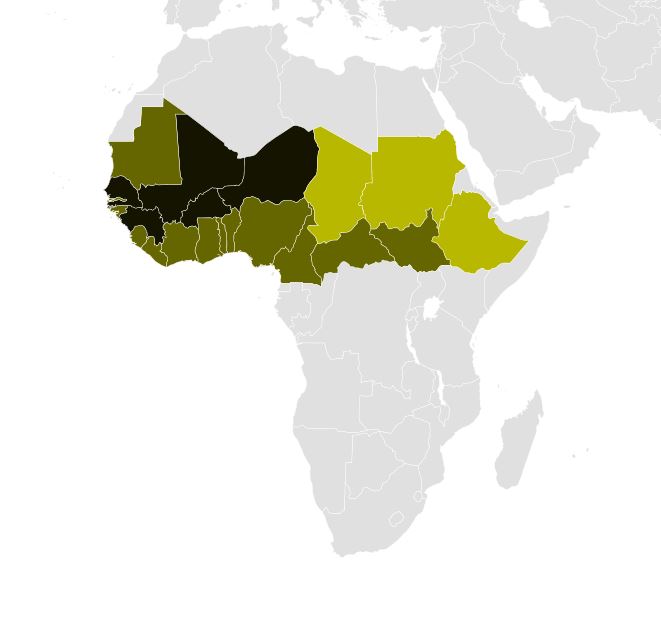
Fulfulde
Fula ( ),Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student's Handbook'', Edinburgh also known as Fulani ( ) or Fulah (, , ; Adlam: , , ; Ajami: , , ), is a Senegambian language spoken by around 36.8 million people as a set of various dialects in a continuum that stretches across some 18 countries in West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer and Wolof, it belongs to the Atlantic geographic group within Niger–Congo, and more specifically to the Senegambian branch. Unlike most Niger-Congo languages, Fula does not have tones. It is spoken as a first language by the Fula people ("Fulani", ) from the Senegambia region and Guinea to Cameroon, Nigeria, and Sudan and by related groups such as the Toucouleur people in the Senegal River Valley. It is also spoken as a second language by various peoples in the region, such as the Kirdi of northern Cameroon and northeastern Nigeria. Nomenclature Several names are applied to the language, just a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adamawa Fulfulde
Adamawa Fulfulde is a variety of the Fula language. It is spoken mainly in Cameroon but also by significant communities residing in Nigeria, Chad, and Sudan by Fulani pastoralists across the Sahel. It is also known as Eastern Fulfulde and by various other names including Boulbe, Dzemay, Fula, Fulfulde, Mbororo, Palata, Peul etc. Adamawa Fulfulde was originally brought to Cameroon in the early parts of the 19th century during a religious war (Jihad) that was launched by Usman dan Fodio from Northern Nigeria. It was originally used as a trade language, however since the arrival of Christian missionaries in the latter half of the 19th century in 1885 to the area in what is now Northern Cameroon and Northern Nigeria, Adamawa Fulfulde became a language widely used in churches and is now used as a Language Of Wider Communication (LWC) in 3 regions of Cameroon. It is an Atlantic language that belongs to the Niger–Congo language family. The speakers of the language are the Fulani peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula People
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown, due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 7 to 10 million – are pastoralism, pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary Fulani – Fulbe Laddi – who also farm, although they argue that they do so out of necessity, not choice. The major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigerian Fulfulde
Nigerian Fulfulde, also known as Hausa States Fulfulde, Fula, or Fulani is a variety of the Fula language spoken by the Fulani people in Nigeria, particularly in the Northern region of Nigeria. It belongs to the West Atlantic branch of the Niger-Congo language family. Phonologically, Nigerian Fulfulde exhibits a system of vowel harmony and a relatively simple consonant inventory, including stops, fricatives, and nasal sounds. The syntax of Nigerian Fulfulde is characterized by a subject-verb-object (SVO) word order, but it is flexible due to the use of extensive nominal and verbal agreement markers. These markers convey information about gender, number, and person, playing a crucial role in indicating grammatical relationships within sentences. The language employs a complex system of noun classes, which impacts both nominal and verbal concord. Word order in Nigerian Fulfulde is subject to pragmatic and contextual factors, allowing for variations in emphasis and focus. It ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maasina Fulfulde
Maasina Fulfulde is a variety of the Fula language. It is spoken mainly in Mali, Ivory Coast, and Ghana by 1.6 million people. The language has several mutually intelligible dialects albeit with some differences. The variety is named after the Macina region in Mali. Maasinankoore is the most widely spoken dialect of Fula spoken in Mali and is a national language of the country. According to Ethnologue there are two dialects - Western and Eastern - and "There are some dialect differences, but popular opinion is that all dialects in Mali are inherently intelligible." Maasina Fulfulde is grammatically basically the same as other varieties of Fula, with some particularities. For instance there are some slight differences in some verb endings. The counting system retains a recapitulation of older systems historically used by other groups in what is now Mali. Tens from 60-90 have alternative versions not used in other varieties of Fula. In the table the general form, which wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagirmi Fulfulde
Bagirmi Fulfulde also known as Baghirmi Peul or Bagirmi Fula is a variety of the Fula language spoken primarily in the Chari-Baguirmi region of Chad as well as in the Central African Republic. Bagirmi Fulfulde, like other Fula varieties, has a consonant inventory with sounds such as stops, fricatives, and nasals. It typically includes a set of oral and nasalized vowels.Gaden, Henry. 1908. Notes on the Foul dialect spoken by the Foulbé of Baguirmi. Asian Journal 11. 5-70. The lexicon of Bagirmi Fulfulde shares many common words with other Fula varieties. Bagirmi Fulfulde, like other Fula varieties, is generally classified as a member of the Atlantic branch of the Niger–Congo language family. It exhibits agglutinative features, where affixes are added to a root to convey grammatical meaning. Fula languages, including Bagirmi Fulfulde, often have a complex noun class system, which is reflected in the agreement patterns with verbs and modifiers. Verbs in Bagirmi Fulfulde typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Niger Fulfulde
Western Niger Fulfulde, also known as Gorgal Niiser Fulfulde ( Ajami: ) is a variety of the Fula language, spoken mainly in Niger, and Burkina Faso, as well as by a small number of speakers in Benin Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its po ... by 3 million people. It has SOV word order and is closely related to other varieties of Fula spoken in Niger.https://www.sil.org/system/files/reapdata/28/92/20/28922087092038854933212051748501873382/silesr2003_009.pdf Western Niger Fulfulde, a member of the Niger-Congo language family, exhibits a range of grammatical features, syntax, and phonology. In terms of phonology, the language is characterized by a system of vowels and consonants, and it employs a tonal system, where pitch variations play a crucial role in distinguishing lexica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central-Eastern Niger Fulfulde
Central-Eastern Niger Fulfulde, also known as Lettugal Niiser Fulfulde ( Ajami: ) is a variety of the Fula language, a Niger–Congo language predominantly spoken in the Central and Eastern regions of Niger, particularly among the Fulani people The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, .... The linguistic structure of this language exhibits distinct features, including a Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) word order. Prepositions and postpositions are utilized in the language to convey spatial relationships. Genitives, articles, adjectives, numerals, and relatives follow noun heads, contributing to the overall complexity of sentence structures. The language employs a question-word-final pattern, placing question words at the end of interrogative sentences. Additionally, there is a spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borgu Fulfulde
Borgu Fulfulde, also known as Borgu Fulani, Benin-Togo Fulfulde, Fulbe-Borgu, or Peul is a variety of the Fula language a West Atlantic language part of the Niger-Congo language family, it is spoken primarily in the Borgou Department of Benin, spanning Nigeria, other parts of Benin, as well as Togo and parts of Burkina Faso. Phonologically, Borgu Fulfulde exhibits a system of vowel and consonant sounds, with a notable presence of glottalized and nasalized consonants. Morphologically, the language is agglutinative, forming words through the addition of prefixes and suffixes to root morphemes. The grammatical structure is characterized by a system of noun class agreement, where various affixes indicate the gender and number of nouns. Word order in Borgu Fulfulde typically follows a subject-object-verb (SOV) pattern, and the language employs postpositions rather than prepositions for expressing spatial and temporal relationships. Syntactically, it features a system of verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Atlantic Languages
The West Atlantic languages (also the Atlantic languages"West Atlantic" is the traditional term, following Diedrich Hermann Westermann; "Atlantic" is more typical in recent work, particularly since Bendor-Samuel (1989), but is also used specifically for the northern branch of West Atlantic. or North Atlantic languages) of West Africa are a major subgroup of the Niger–Congo languages. The Atlantic languages are spoken along the Atlantic coast from Senegal to Liberia, though transhumant Fula speakers have spread eastward and are found in large numbers across the Sahel, from Senegal to Nigeria, Cameroon and Sudan. Wolof of Senegal and several of the Fula languages are the most populous Atlantic languages, with several million speakers each. Other significant members include Serer and the Jola dialect cluster of Senegal. Temne, a major language of Sierra Leone, was included in the Atlantic subgroup in earlier classifications but in modern proposals, it is no longer grouped with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Languages
The West Atlantic languages (also the Atlantic languages"West Atlantic" is the traditional term, following Diedrich Hermann Westermann; "Atlantic" is more typical in recent work, particularly since Bendor-Samuel (1989), but is also used specifically for the northern branch of West Atlantic. or North Atlantic languages) of West Africa are a major subgroup of the Niger–Congo languages. The Atlantic languages are spoken along the Atlantic coast from Senegal to Liberia, though transhumant Fula speakers have spread eastward and are found in large numbers across the Sahel, from Senegal to Nigeria, Cameroon and Sudan. Wolof of Senegal and several of the Fula languages are the most populous Atlantic languages, with several million speakers each. Other significant members include Serer and the Jola dialect cluster of Senegal. Temne, a major language of Sierra Leone, was included in the Atlantic subgroup in earlier classifications but in modern proposals, it is no longer grouped wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajami Script
Ajami (, ) or Ajamiyya (, ), which comes from the Arabic root for 'foreign' or 'stranger', is an Arabic script, Arabic-derived script used for writing Languages of Africa, African languages, particularly Songhai languages, Songhai, Mandé languages, Mandé, Hausa language, Hausa and Swahili language, Swahili, although many other languages are also written using the script, including Mooré language, Mooré, Pulaar language, Pulaar, Wolof language, Wolof, and Yoruba language, Yoruba. It is an adaptation of the Arabic script to write sounds not found in Standard Arabic. Rather than adding new letters, modifications usually consist of additional dots or lines added to pre-existing letters. History The script was first used between the 10th and the 16th centuries. It was likely originally created with the intent of promoting Islam in West Africa. The first languages written in the script were likely old Shilha language, Taseelhit or medieval Berber languages, Amazigh, Kanuri language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic (Arabic alphabet) and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world (after the Latin script), the second-most widely used List of writing systems by adoption, writing system in the world by number of countries using it, and the third-most by number of users (after the Latin and Chinese characters, Chinese scripts). The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Quran, the holy book of Islam. With Spread of Islam, the religion's spread, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols. Such languages still using it are Arabic language, Arabic, Persian language, Persian (Western Persian, Farsi and Dari), Urdu, Uyghur language, Uyghur, Kurdish languages, Kurdish, Pashto, Punjabi language, Punjabi (Shahmukhi), Sindhi language, Sindhi, South Azerbaijani, Azerb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |