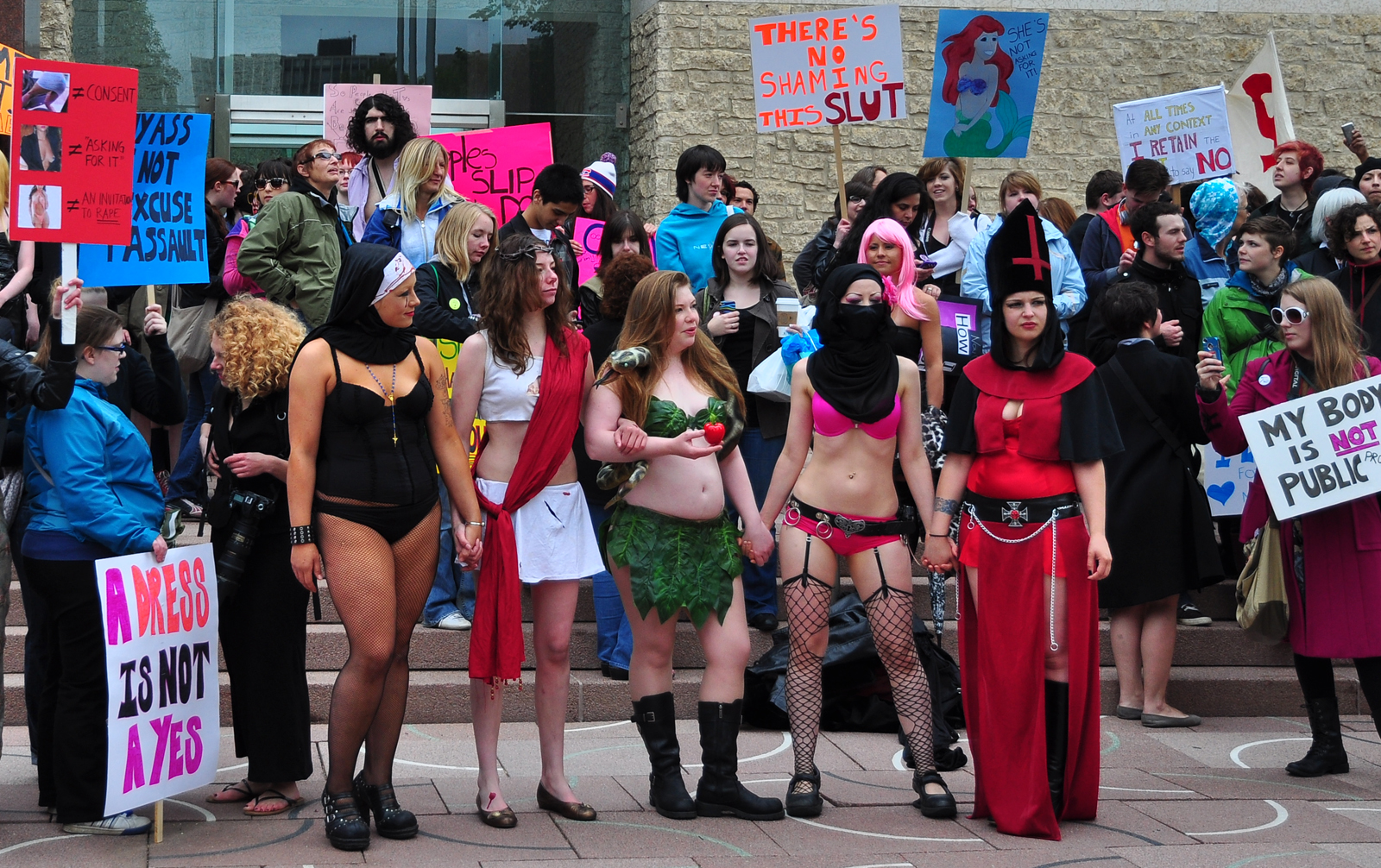|
Frontier Justice
Frontier justice is extrajudicial punishment that is motivated by the nonexistence of law and order or dissatisfaction with judicial punishment. The phrase can also be used to describe a prejudiced judge. Lynching, vigilantism and gunfighting are considered forms of frontier justice. Examples United States * March 20 to April 15, 1882: Wyatt Earp and Doc Holliday tracked and killed 4 cowboys said to be responsible for Morgan Earp's death, which would later become known as the Earp Vendetta Ride. * Late 1800s: A group of self-appointed lawmen called "stranglers" lynched around sixty horse rustlers and cattle rustlers along southwest North Dakota's Little Missouri River. Brazil * April 1991: José Vicente Anunciação murdered a co-worker during a drunken knife-fight in Salvador, Bahia. Witnesses to the crime were not able to provide evidence in court. Anunciação was set free and then dragged from his bed at night by a mob of forty people who beat him to death with br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrajudicial Punishment
Extrajudicial punishment is a punishment for an alleged crime or offense which is carried out without legal process or supervision by a court or tribunal through a legal proceeding. Politically motivated Extrajudicial punishment is often a feature of politically repressive regimes, but even self-proclaimed or internationally recognized democracies have been known to use extrajudicial punishment under certain circumstances. Although the legal use of capital punishment is generally decreasing around the world, individuals or groups deemed threatening—or even simply "undesirable"—to a government may nevertheless be targeted for punishment by a regime or its representatives. Such actions typically happen quickly, with security forces acting on a covert basis, performed in such a way as to avoid a massive public outcry and/or international criticism that would reflect badly on the state. Sometimes, the killers are agents outside the government. Criminal organizations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvador, Bahia
Salvador () is a Municipalities of Brazil, Brazilian municipality and capital city of the Federative units of Brazil, state of Bahia. Situated in the Zona da Mata in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region of Brazil, Salvador is recognized throughout the country and internationally for its #Cuisine, cuisine, #Music, music, and #Pelourinho, architecture. The African influence in many cultural aspects of the city makes it a center of Afro-Brazilian culture. As the Capitals of Brazil, first capital of Colonial Brazil, the city is List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, one of the oldest in the Americas. Its foundation in 1549 by Tomé de Sousa took place on account of the implementation of the List of governors-general of Brazil, General Government of Brazil by the Portuguese Empire. Centralization as a capital, along with Portuguese colonization, were important factors in shaping the profile of the municipality, as were certain geographic characteristics. The construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victimization
Victimisation ( or victimization) is the state or process of being victimised or becoming a victim. The field that studies the process, rates, incidence, effects, and prevalence of victimisation is called victimology. Peer victimisation Peer victimisation is the experience among children of being a target of the aggressive behaviour of other children, who are not siblings and not necessarily age-mates. Peer victimisation is correlated with an increased risk of depression and decreased well-being in adulthood. Secondary victimisation Secondary victimization (also known as post crime victimization"post-crime victimization or secondary victimization". Comprehensive Criminal Justice Terminology. Prentice Hall. Archived from the original on 10 March 2013. Retrieved 9 January 2008. or double victimization) refers to further victim-blaming from criminal justice authorities following a report of an original victimization. Revictimisation The term revictimisation refers to a pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victim Blaming
Victim blaming occurs when the victim of a crime or any wrongful act is held entirely or partially at fault for the harm that befell them. There is historical and current prejudice against the victims of domestic violence and sex crimes, such as the greater tendency to blame victims of rape than victims of robbery if victims and perpetrators knew each other prior to the commission of the crime. The Gay Panic Defense has been characterized as a form of victim blaming. Coining of the phrase Psychologist William Ryan (psychologist), William Ryan coined the phrase "blaming the victim" in his 1971 book of that title. In the book, Ryan described victim blaming as an ideology used to justify racism and social injustice against African American, black people Racism in the United States, in the United States. Ryan wrote the book to refute Daniel Patrick Moynihan's 1965 work ''The Negro Family: The Case for National Action'' (usually simply referred to as the Moynihan Report). Moynihan had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rough Music
Charivari (, , , alternatively spelled shivaree or chivaree and also called a skimmington) was a European and North American folk custom designed to shame a member of the community, in which a mock parade was staged through the settlement accompanied by a discordant mock serenade. Since the crowd aimed to make as much noise as possible by beating on pots and pans or anything that came to hand, these parades were often referred to as rough music. Parades were of three types. In the first and generally most violent form, an alleged wrongdoer (or wrongdoers) might be dragged from his or her home or place of work and paraded by force through a community. In the process, the victim was subject to the derision of the crowd and might be pelted and was frequently dunked at the end of the proceedings. A safer form involved a neighbour of the wrongdoer impersonating the victim while being carried through the streets. The impersonator was obviously not themselves punished and often cried out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Range War
A range war, also known as range conflict or cattle war, is a type of usually violent conflict, most commonly in the 19th and early 20th centuries in the American West. The subject of these conflicts was control of " open range", or range land freely used for cattle grazing, or as sheep pasture, which gave these conflicts its name. Typically they were disputes over water rights, grazing rights, or cattle ownership. Range wars occurred prior to the Taylor Grazing Act of 1934, which regulated grazing allotments on public land. Range wars included the Pleasant Valley War, Colfax County War, Castaic Range War, San Elizario Salt War, Mason County War, Porum Range War, Johnson County War, Pecos War, Fence Cutting Wars, Sheep Wars, Barber–Mizell feud, Stuart's Stranglers conflict, and others. While in previous centuries violence may have been involved, the term is now applied to nonviolent competition for scarce resources, such as between ranchers and environmentalists, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochlocracy
Mob rule or ochlocracy or mobocracy is a pejorative term describing an oppressive majoritarianism, majoritarian form of government controlled by the common people through the intimidation of authorities. Ochlocracy is distinguished from democracy or similarly legitimate and representative governments by the absence or impairment of a procedurally civil process reflective of the entire polity. Names Ochlocracy comes from Latin , from Ancient Greek, Greek (''okhlokratía''), from (''ókhlos'', "mass", "mob", or "common people") and (''krátos'', "rule"). An ochlocrat is one who is an advocate or partisan of ochlocracy. The adjective may be either ochlocratic or ochlocratical. Ochlocracy is synonymous in meaning and usage to mob rule or wikt:mobocracy, mobocracy, which neologism, was coined in the 18th century from the sense of "mob" meaning the common rabble that arose from the Latin phrase ("the fickle crowd") in the 1680s during disputes over the United Kingdom's Glori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Cause Corruption
Noble cause corruption is corruption caused by the adherence to a teleological ethical system, suggesting that people will use unethical or illegal means to attain desirable goals, a result which appears to benefit the greater good. Where traditional corruption is defined by personal gain, noble cause corruption forms when someone is convinced of their righteousness, and will do anything within their powers to achieve the desired result. An example of noble cause corruption is police misconduct "committed in the name of good ends", or neglect of due process through "a moral commitment to make the world a safer place to live". The knowing misconduct by a law enforcement officer or prosecutor with the goal of attaining what the officer believes is a "just" result. Conditions for such corruption usually occur where individuals feel no administrative accountability and lose faith in the criminal justice system. These conditions can be compounded by arrogance and weak supervision. Orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jungle Law
"The law of the jungle" (also called jungle law) is an expression that has come to describe a scenario where "anything goes". The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' defines the Law of the Jungle as "''the code of survival in jungle life'', now usually with reference to the superiority of brute force or self-interest in the struggle for survival". The phrase was introduced in Rudyard Kipling's 1894 work ''The Jungle Book'', where it described the behaviour of wolves in a pack. ''The Jungle Book'' In his 1894 novel ''The Jungle Book'', Rudyard Kipling uses the term to describe an actual set of legal codes used by wolves and other animals in the jungles of India. Chapter Two of '' The Second Jungle Book'' (1895) includes a poem featuring the Law of the Jungle, as known to the wolves and taught to their offspring. It begins: In the 1994 film ''The Jungle Book'', the jungle law is portrayed as a decree forbidding the killing of animals for reasons outside of one's own survival, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanging Of Patrick O'Connor
The hanging of Patrick O'Connor happened on June 20, 1834, in Dubuque, Michigan Territory, to a man convicted in Iowa's first murder trial. He was an immigrant from Ireland to the United States. The hanging occurred after his attempted lynching on May 19, 1834. The case and others like it showed a need for formal laws in the territory. Murder of George O'Keaf O'Connor was born in Ireland in 1797 and immigrated to Galena, Illinois, in 1826. Two years later, he broke his leg, requiring amputation. This helped make him a quarrelsome trouble maker. He shot a merchant, who survived. Some men considered lynching him, then decided otherwise when he promised them he would leave Galena. After leaving Galena, O'Connor traveled to Dubuque, Michigan Territory, to work in the lead mines. In 1833, he met fellow Irishman George O'Keaf. They built a cabin two miles south of Dubuque. On May 19, 1834, O'Keaf traveled to Dubuque to gather supplies and returned with one of his friends near 2pm. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjakmarrja
In traditional Albanian culture, ( English: "blood-taking", i.e. "blood feud") or ("revenge") is the social obligation to kill an offender or a member of their family in order to salvage one's honor. This practice is generally seen as in line with the social code known as the Canon of Lekë Dukagjini () or simply the '' Kanun'' (consisting of 12 books and 1,262 articles). The code was originally a "a non-religious code that was used by Muslims and Christians alike." Protecting one's honor is an essential component to Albanian culture because it is the core of social respectability. Honor is held in very high regard because it carries over generations. Legacies and history are carried in the family names of Albanians and must be held in high priority, even at the cost of one's life. Therefore, when a personal attack of a formidable magnitude is unleashed on a member of any family, an equal punishment is to be expected by the laws of the Kanun. Some of the actions that initiate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divine Retribution
Divine retribution is supernatural punishment of a person, a group of people, or everyone by a deity in response to some action. Many cultures have a story about how a deity imposed punishment on previous inhabitants of their land, causing their doom. An example of divine retribution is the story found in many religions about a great flood destroying all of humanity, as described in the Epic of Gilgamesh, the Hindu Vedas, or the Book of Genesis (6:9–8:22), leaving one principal 'chosen' survivor. In the first example, the survivor is Utnapishtim, in the Hindu Vedas, it is Manu, and in the last example, it is Noah. References in the Old Testament and the Quran to a man named Nuh (Noah) who was commanded by God to build an ark also suggest that one man and his followers were saved in a great flood. Other examples in Bible history include the dispersion of the builders of the Tower of Babel (Genesis 11:1–9), the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah (Genesis 18:20–21, 19: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |