|
Frise Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in Flight dynamics, roll (or movement around the aircraft's Flight control surfaces#Longitudinal axis, longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the Lift (force), lift vector. Movement around this axis is called rolling or banking. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long Wright brothers patent war, legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the World War I, First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually air or water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or afterend. Often rudders are shaped to minimize hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may link rudders to steering wheels. In typical aircraft, the rudder is operated by pedals via mechanical linkages or hydraulics. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
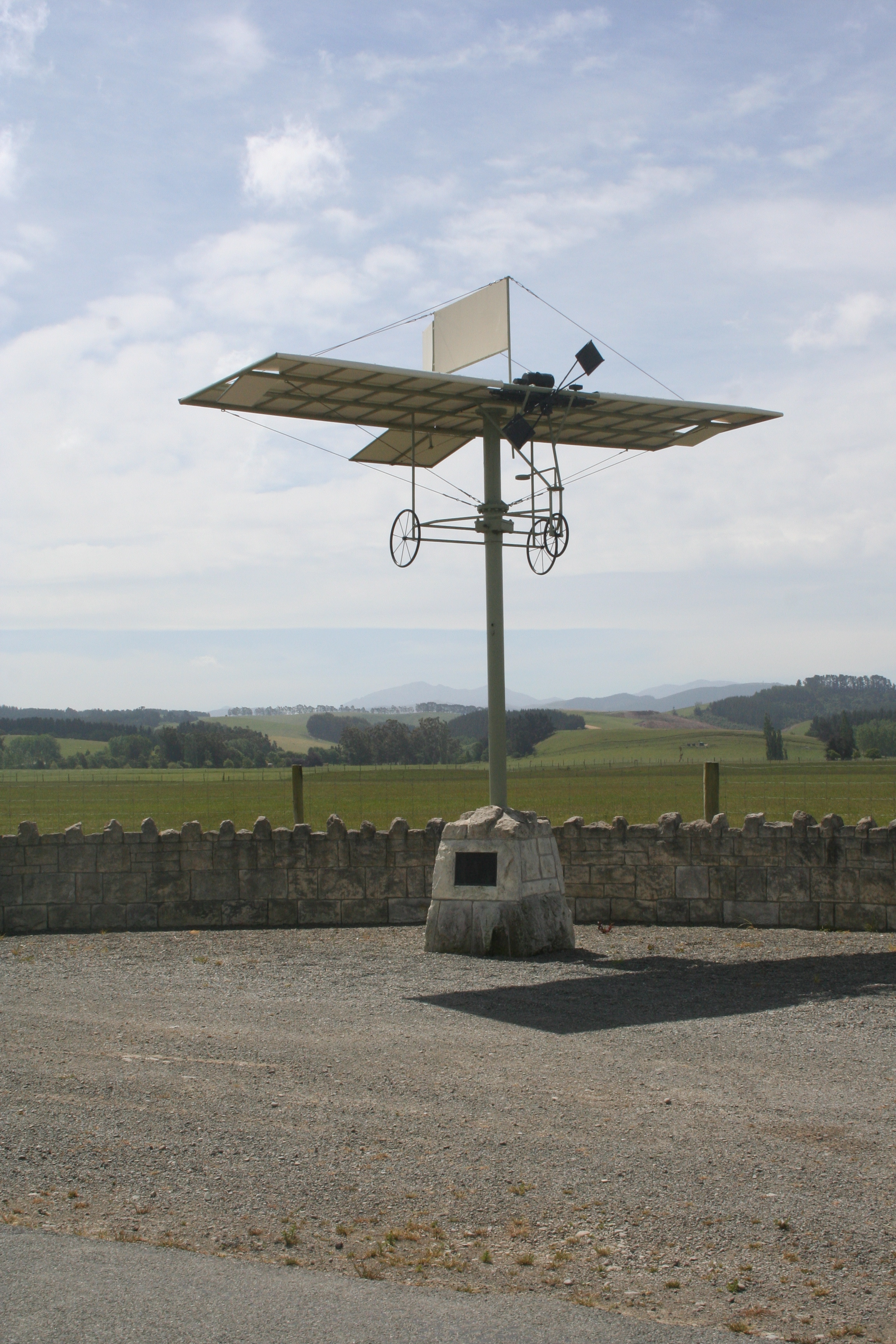
Richard Pearse
Richard William Pearse (3 December 1877 – 29 July 1953) was a New Zealand farmer and inventor who performed pioneering aviation experiments. Witnesses interviewed many years afterwards describe observing Pearse flying and landing a powered heavier-than-air machine on 31 March 1903, nine months before the Wright brothers flew. Ambiguous statements made by Pearse himself make it difficult to date the aviation experiments with certainty. In a newspaper interview in 1909, with respect to inventing a flying machine, he said "I did not attempt anything practical with the idea until 1904". Biographer Gordon Ogilvie credits Pearse with "several far-sighted concepts: a monoplane configuration, wing flaps and rear elevator, tricycle undercarriage with steerable nosewheel, and a propeller with variable-pitch blades." Pearse largely ended his early flying experiments about 1911 but pioneered novel aircraft and aero-engine invention from 1933 with the development of his "private plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John J
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent Pool
In patent law, a patent pool is a consortium of two or more companies agreeing to cross-license patents relating to a particular technology. The creation of a patent pool can save patentees and licensees time and money, and, in case of blocking patents, it may also be the only reasonable method for making the invention available to the public. Competition law issues are usually important when a large consortium is formed. History In 1856, sewing machine manufacturers Grover & Baker, Singer, and Wheeler & Wilson, all accusing each other of patent infringement, met in Albany, New York to pursue their suits. Orlando B. Potter, a lawyer and president of Grover & Baker, proposed that, rather than squander their profits on litigation, they pool their patents. This was the first patent pool, a process which enables the production of complicated machines without legal battles over patent rights. In 1917, the two major patent holders for airplanes, the Wright Company and the Curtiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
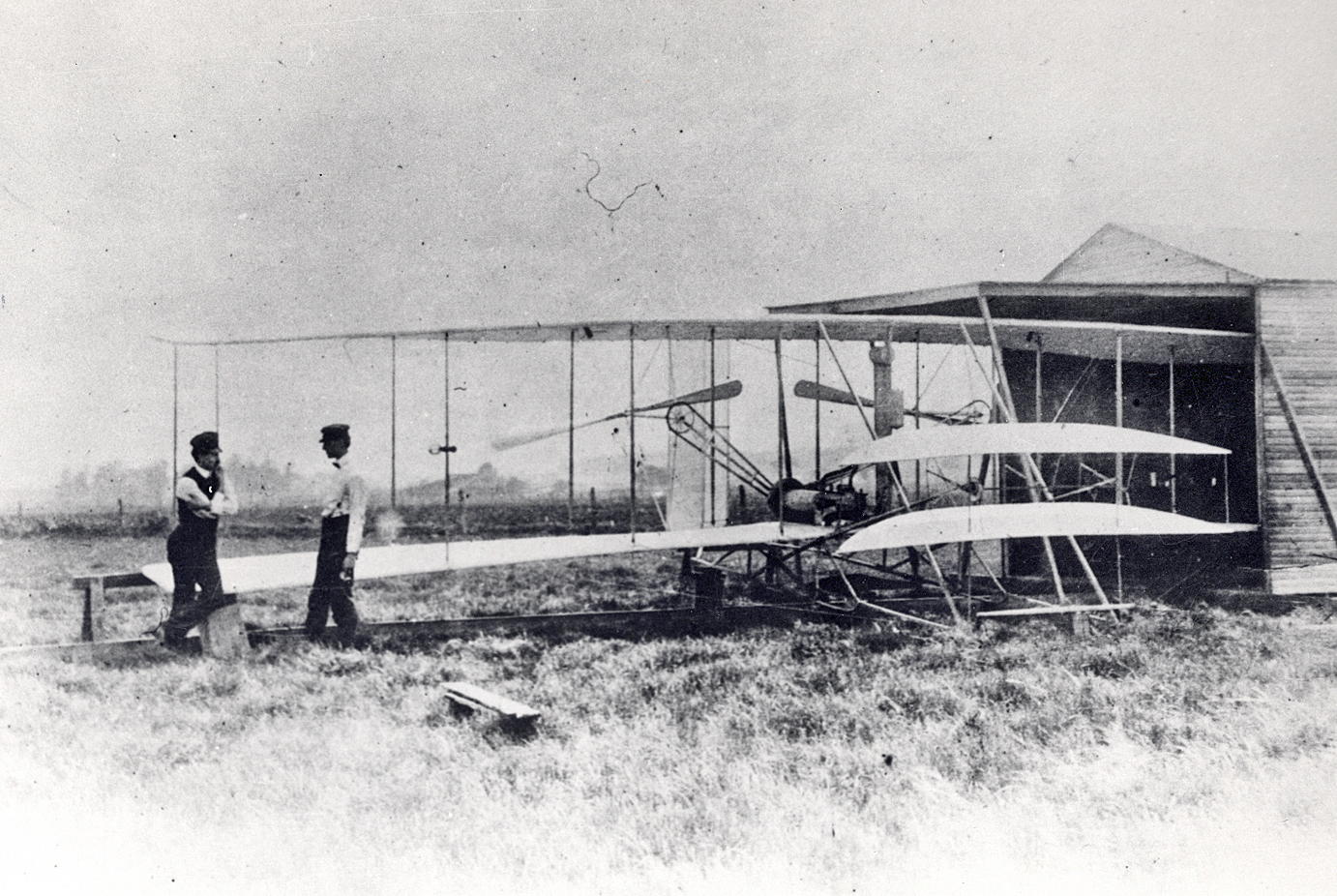
Wright Flyer II
The ''Wright Flyer II'' was the second powered aircraft built by Wilbur and Orville Wright. During 1904 they used it to make a total of 105 flights, ultimately achieving flights lasting five minutes and also making full circles, which was accomplished by Wilbur for the first time on September 20. Design and development The design of the Flyer II was very similar to the original 1903 ''Wright Flyer'', but with a slightly more powerful engine and construction using white pine instead of the spruce they used in the 1903 machine and the gliders of 1900–1902. An important change was reducing the wing camber to 1-in-25 from the 1-in-20 used in 1903. The brothers thought that reducing the camber would reduce drag, though less lift was actually achieved. With these alterations Flyer II was heavier by some than the 1903 machine. Operational history The Wrights tested the new aircraft at Huffman Prairie, a cow pasture outside of Dayton, Ohio, which is now part of Dayton Aviati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Glider
The Wright brothers designed, built and flew a series of three manned Glider (aircraft), gliders in 1900–1902 as they worked towards achieving powered flight. They also made preliminary tests with a kite in 1899. In 1911 Orville conducted tests with a much more sophisticated glider. Neither the kite nor any of the gliders were preserved, but replicas of all have been built. 1899 kite The 1899 kite, which Wilbur flew near his home in Dayton, Ohio had a wingspan of only 5 feet (1.5 m). This pine wood and shellacked craft, although too small to carry a pilot, tested the concept of wing-warping for flight dynamics, roll control that would prove essential to the brothers' solving the problem of controlled flight. The Wrights burned the craft along with other trash in 1905. 1900 glider The 1900 Wright Glider was the brothers' first to be capable of carrying a human. Its overall structure was based on Octave Chanute's two-surface glider of 1896. Its wing airfoil was derived from Otto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octave Chanute
Octave Chanute (February 18, 1832 – November 23, 1910) was a French-American civil engineer and aviation pioneer. He advised and publicized many aviation enthusiasts, including the Wright brothers. At his death, he was hailed as the father of aviation and the initial concepts of the heavier-than-air flying machine. Early life Octave Chanute was born in Paris to Elise and Joseph Chanut, professor at the Collège de France. Octave and Joseph emigrated to the United States of America in 1838, when Joseph was named Vice President of Jefferson College in Louisiana. Octave attended private schools in New York. He added the "e" to his last name in his adult life. In 1857, he married Anne Riddell James, with whom he had a son and three daughters. Career Railroad civil engineer Chanute began his training as a civil engineer in 1848. He was widely considered brilliant and innovative in the engineering profession. He designed and constructed the two biggest stockyards in the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Renard
Charles Renard (1847–1905) born in Damblain, Vosges, was a French military engineer. Airships After the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-1871 he started work on the design of airships at the French army aeronautical department. Together with Arthur C. Krebs and his brother Paul, in 1884 he constructed '' La France'', which made its maiden flight on 9 August 1884 at Chalais-Meudon, making a 23-minute circular flight. This was the first time that a flying machine made a flight which returned to the place of take-off. It was later exhibited at the Paris Exposition Universelle (1889). Preferred numbers Ca. 1877 he proposed a now widely used system of preferred numbers known as Renard numbers that was later reportedly published in an 1886 instruction for captive balloon troops, named after him in the 1920s and finally became international standard ISO 3. It helped the French army to reduce the number of different balloon ropes kept on inventory Inventory (British English) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Esnault-Pelterie
Robert Albert Charles Esnault-Pelterie (8 November 1881 – 6 December 1957) was a French aircraft designer and spaceflight theorist. He is referred to as being one of the founders of modern rocketry and astronautics, along with the Russian Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, the Germans Hermann Oberth, Wernher von Braun and the American Robert H. Goddard. Biography He was born on 8 November 1881 in Paris to a textile industrialist. He was educated at the ''Faculté des Sciences'', studying engineering at the University of Paris, Sorbonne. He served in World War I and was made an ''Officier de la Légion d'Honneur''. In November 1928, on board the ''SS Ile de France, Ile de France'' while sailing to New York City, he was married to Carmen Bernaldo de Quirós, the daughter of Don Antonio and Yvonne Cabarrus, and granddaughter of General Marquis of Santiago, Grandee of Spain, Head of the Military Household of Queen Isabella II of Spain, Isabella II. He died on 6 December 1957 in Nice, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles M
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (James (wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/ǵerh₂-">ĝer-, where the ĝ is a palatal consonant, meaning "to rub; to be old; grain." An old man has been worn away and is now grey with age. In some Slavic languages, the name ''Drago (given name), Drago'' (and variants: ''Drago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |