|
Freud
Sigmund Freud ( ; ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies seen as originating from conflicts in the psyche, through dialogue between patient and psychoanalyst, and the distinctive theory of mind and human agency derived from it. Freud was born to Galician Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire. He qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1881 at the University of Vienna. Upon completing his habilitation in 1885, he was appointed a docent in neuropathology and became an affiliated professor in 1902. Freud lived and worked in Vienna having set up his clinical practice there in 1886. Following the German annexation of Austria in March 1938, Freud left Austria to escape Nazi persecution. He died in exile in the United Kingdom in 1939. In founding psychoanalysis, Freud developed therapeutic techniques su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoanalysis
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek language, Greek: and is a set of theories and techniques of research to discover unconscious mind, unconscious processes and their influence on conscious mind, conscious thought, emotion and behaviour. Based on The Interpretation of Dreams, dream interpretation, psychoanalysis is also a talk therapy method for treating of mental disorders."All psychoanalytic theories include the idea that unconscious thoughts and feelings are central in mental functioning." Milton, Jane, Caroline Polmear, and Julia Fabricius. 2011. ''A Short Introduction to Psychoanalysis''. Sage Group, SAGE. p. 27."What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a body of knowledge. In what might be considered an unfortunately abbreviated description, Freud said that anyone who recognizes transference and resistance is a psychoanalyst, even if he comes to conclusions other than his own. … I prefer to think ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Freud
Anna Freud CBE ( ; ; 3 December 1895 – 9 October 1982) was a British psychoanalyst of Austrian Jewish descent. She was born in Vienna, the sixth and youngest child of Sigmund Freud and Martha Bernays. She followed the path of her father and contributed to the field of psychoanalysis. Alongside Hermine Hug-Hellmuth and Melanie Klein, she may be considered the founder of psychoanalytic child psychology. Compared to her father, her work emphasized the importance of the ego and its normal "developmental lines" as well as incorporating a distinctive emphasis on collaborative work across a range of analytical and observational contexts. After the Freud family were forced to leave Vienna in 1938 with the advent of the Nazi regime in Austria, she resumed her psychoanalytic practice and her pioneering work in child psychoanalysis in London, establishing the Hampstead Child Therapy Course and Clinic in 1952 (later renamed the Anna Freud National Centre for Children and Familie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
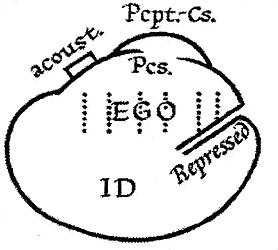
Id, Ego And Super-ego
In psychoanalytic theory, the id, ego, and superego are three distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus, outlined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The three agents are theoretical constructs that Freud employed to describe the basic structure of mental life as it was encountered in psychoanalytic practice. Freud himself used the German terms ''das Es'', ''Ich'', and ''Über-Ich'', which literally translate as "the it", "I", and "over-I". The Latin terms id, ego and superego were chosen by his original translators and have remained in use. The structural model was introduced in Freud's essay '' Beyond the Pleasure Principle'' (1920) and further refined and formalised in later essays such as '' The Ego and the Id'' (1923). Freud developed the model in response to the perceived ambiguity of the terms "conscious" and "unconscious" in his earlier ''topographical'' model. Broadly speaking, the id is the organism's unconscious array of uncoordinated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oedipus Complex
In classical psychoanalytic theory, the Oedipus complex is a son's sexual attitude towards his mother and concomitant hostility toward his father, first formed during the phallic stage of psychosexual development. A daughter's attitude of desire for her father and hostility toward her mother is referred to as the feminine (or female) Oedipus complex. The general concept was considered by Sigmund Freud in '' The Interpretation of Dreams'' (1899), although the term itself was introduced in his paper "A Special Type of Choice of Object Made by Men" (1910). Freud's ideas of castration anxiety and penis envy refer to the differences of the sexes in their experience of the Oedipus complex. The complex is thought to persist into adulthood as an unconscious psychic structure which can assist in social adaptation but also be the cause of neurosis. According to sexual difference, a ''positive'' Oedipus complex refers to the child's sexual desire for the opposite-sex parent and aversion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freud's Psychoanalytic Theories
Sigmund Freud (6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) is considered to be the founder of the psychodynamic approach to psychology, which looks to unconscious drives to explain human behavior. Freud believed that the mind is responsible for both conscious and unconscious decisions that it makes on the basis of psychological drives. The id, ego, and super-ego are three aspects of the mind Freud believed to comprise a person's personality. Freud believed people are "simply actors in the drama of heirown minds, pushed by desire, pulled by coincidence. Underneath the surface, our personalities represent the power struggle going on deep within us". Views on religion Freud did not believe in the existence of a supernatural force that has pre-programmed us to behave in a certain way. His idea of the Id explains why people act out in certain ways when it is not in line with the ego or superego. "Religion is an illusion and it derives its strength from the fact that it falls in with our ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freud Corner (Golders Green Crematorium)
Freud Corner is the name used for the place within Golders Green Crematorium in North London, where the funerary urns of Sigmund Freud and many other members of the Freud family are deposited. History When writing his will in 1919, Sigmund Freud stated that he wanted to be cremation, cremated as it was a cheaper and easier process than conventional burial. Freud died around 3 A.M on September 23, 1939. Three days later, his body was cremated at Golders Green Crematorium. His son Ernst L. Freud, Ernst Freud had organised the funeral arrangements, and Harrods, Harrods of Knightsbridge acted as funeral directors.Michael Turner: After the funeral, Freud's ashes were deposited in an Pottery of ancient Greece, ancient Greek bell krater from the 4th century BC which came from his large collection of over 2000 antiquities (see below). The ancient bell krater, now serving as a funerary urn, was later placed atop a black marble Pedestal, plinth, designed by Ernst Freud and erected in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martha Bernays
Martha Bernays ( ; ; 26 July 1861 – 2 November 1951) was the wife of Austrian psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud. Bernays was the second daughter of Emmeline and Berman Bernays. Her paternal grandfather Isaac Bernays was a Chief Rabbi of Hamburg. Background Martha Bernays was raised in an observant Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jewish family, the daughter of Berman Bernays (1826–1879) and Emmeline Philipp (1830–1910). Her grandfather, Isaac Bernays, was the chief rabbi of Hamburg and a distant relative of the German Romantic poetry, Romantic poet Heinrich Heine, who frequently mentioned Isaac in his letters. Isaac's son, Michael Bernays (1834–1897), Martha's uncle, converted to Christianity at an early age and was professor of German at the University of Munich. Although the Bernays and Freud families were well-acquainted – her elder brother Eli married Freud's younger sister, for example – the latter were more liberal Jews, and Freud in particular had no time for ritual observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychosexual Development
In psychoanalysis, psychosexual development is a central element of the sexual drive theory. According to Freud, personality develops through a series of childhood stages in which pleasure-seeking energies from the child become focused on certain erogenous areas. An erogenous zone is characterized as an area of the body that is particularly sensitive to stimulation. The five psychosexual stages are the oral, the anal, the phallic, the latent, and the genital. The erogenous zone associated with each stage serves as a source of pleasure. Being unsatisfied at any particular stage can result in fixation. On the other hand, being satisfied can result in a healthy personality. Sigmund Freud proposed that if the child experienced frustration at any of the psychosexual developmental stages, they would experience anxiety that would persist into adulthood as a neurosis, a functional mental disorder. Background Sigmund Freud (1856–1939) observed that during the predictable stages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amalia Freud
Amalia Malka Nathansohn Freud ( Nathansohn; 18 August 1835 – 12 September 1930) was the mother of Sigmund Freud. She was born in Brody in the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria to Jakob Nathanson and Sara Wilenz and later grew up in Odesa, where her mother came from (both cities are located in modern-day Ukraine). She was married to Jacob Freud in 1855. Amalia Freud died of tuberculosis in Vienna at the age of 95. Children On 6 May 1856, when Amalia Freud was still 20 years old, she gave birth to her first child by her husband Jacob Freud, Sigmund Schlomo, who became a famous neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis. Amalia was almost always pregnant in the decade following Sigmund's birth, giving birth to seven more children in just nine years, of which six lived to adulthood. However, none of her other children became as renowned as their eldest brother. They are enumerated below in the consecutive order of their births: *Julius (October 1857 – 15 April 1858), died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repression (psychology)
Repression is a key concept of psychoanalysis, where it is understood as a defense mechanism that "ensures that what is unacceptable to the conscious mind, and would if recalled arouse anxiety, is prevented from entering into it." According to psychoanalytic theory, repression plays a major role in many mental illnesses, and in the psyche of the average person.Laplanche pp. 390, 392 American psychologists began to attempt to study repression in the experimental laboratory around 1930. However, psychoanalysts were at first uninterested in attempts to study repression in laboratory settings, and later came to reject them. Most psychoanalysts concluded that such attempts misrepresented the psychoanalytic concept of repression. Sigmund Freud's theory The founder of psychoanalysis, Sigmund Freud, in seeking to move away from hypnosis and towards encouraging patients to remember their past in a conscious state, observed that the process was strikingly difficult, and he began to suspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Freud
Jacob Kolloman Freud (; 1 April 1815 – 23 October 1896) was the father of Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis. Born in town of Tysmenytsia in the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria (now in Ukraine), and from a Hasidic background though himself an enlightened Jew of the Haskalah, he mainly earned his living as a wool merchant. Families Jacob Freud was the son of Schlomo Freud and Pepi, née Hoffmann. Jacob Freud married three times, with two children coming from his first marriage, and eight children from his third marriage to Amalia Freud, twenty years his junior. His first wife was Sally, and his second wife was Rebecca. Jacob's eldest son from his first marriage became a father a year before Sigmund - the first son of Jacob's third marriage - was born; so that Sigmund was an uncle at birth, with his nephew John a constant (and older) playmate in his early years. Ernest Jones speculates that the unusual family background may have prompted Sigmund - the eldest but thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |