|
Free Miner
''Freeminer'' is an ancient title given to coal or iron miners in the Forest of Dean, Gloucestershire, England, who have earned the right to mine personal plots, known as ''gales''. History of Freemining For hundreds of years, mining of the Forest of Dean Coalfield and iron reserves has been regulated through a system of Freemining, with the Free Miner's Mine Law Court sitting at the Speech House from 1682. The earliest known existing copy of ''Dean Miners’ Laws and Privileges'', known locally as the ''Book of Dennis'', dates from 1610 but the copy itself contains references to much earlier origins. It also claims that Freemining rights were granted to Foresters by Edward I who, in so doing, also confirmed that such 'customes and franchises' had existed since 'tyme out of mynde'. Freeminers had been instrumental in recapturing Berwick-upon-Tweed several times (1296, 1305 and 1315) and it is thought that these privileges were granted as a reward for their endeavours. A plaque be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abenhall
Abenhall is a small village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Mitcheldean, in the Forest of Dean district, in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It lies on the road between Mitcheldean and Flaxley in the Forest of Dean. The parish included the settlement of Plump Hill, which is actually more populous than Abenhall itself, and was once part of the Hundred of St Briavels (known as Dene at the time of the Domesday Book in 1086). Originally a mining and iron-making centre like much of the surrounding area, the village is notable for its 14th century Church of St Michael, which is built of local red sandstone and has ornate contemporary carvings relating to the Forest of Dean's principal industries. These include a shield bearing the arms of the Freeminer ''Freeminer'' is an ancient title given to coal or iron miners in the Forest of Dean, Gloucestershire, England, who have earned the right to mine personal plots, known as ''gales''. History of Freemining For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), iron ochre, or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as red ochre (or, in some dialects, ruddle). The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper. Earth pigments Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known as limonite, which gives them a yellow colour. A range of other minerals may also be included in the mixture:Krivovichev V. G. Mineralogical glossary. Scientific editor :uk:Булах Андрій Глібович, A. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
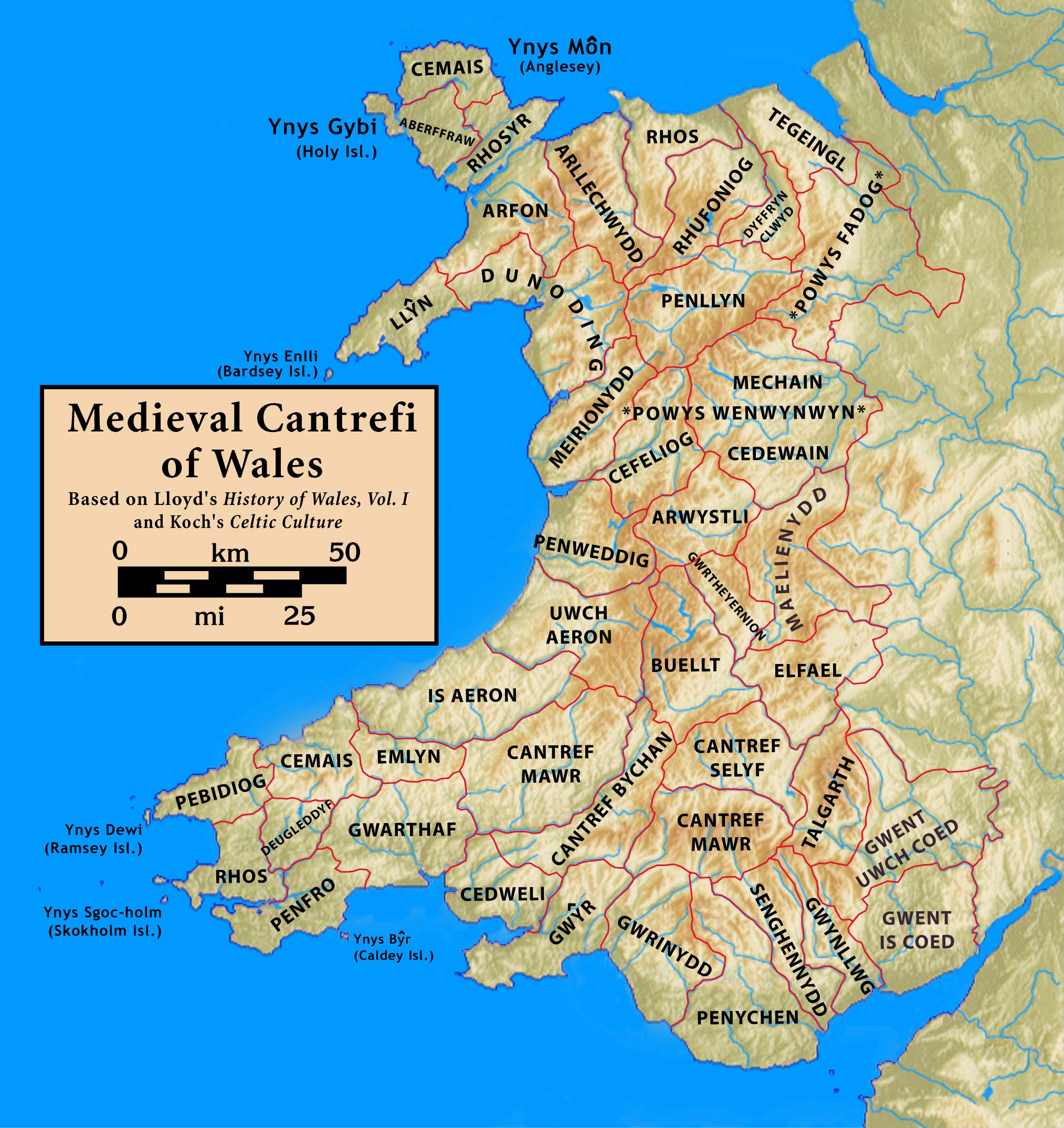
Hundred (country Subdivision)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County, New South Wales, Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''#wapentake, wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål, Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' (Nynorsk, Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' (North Frisian language, North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and ''cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a Barony (Ireland), barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
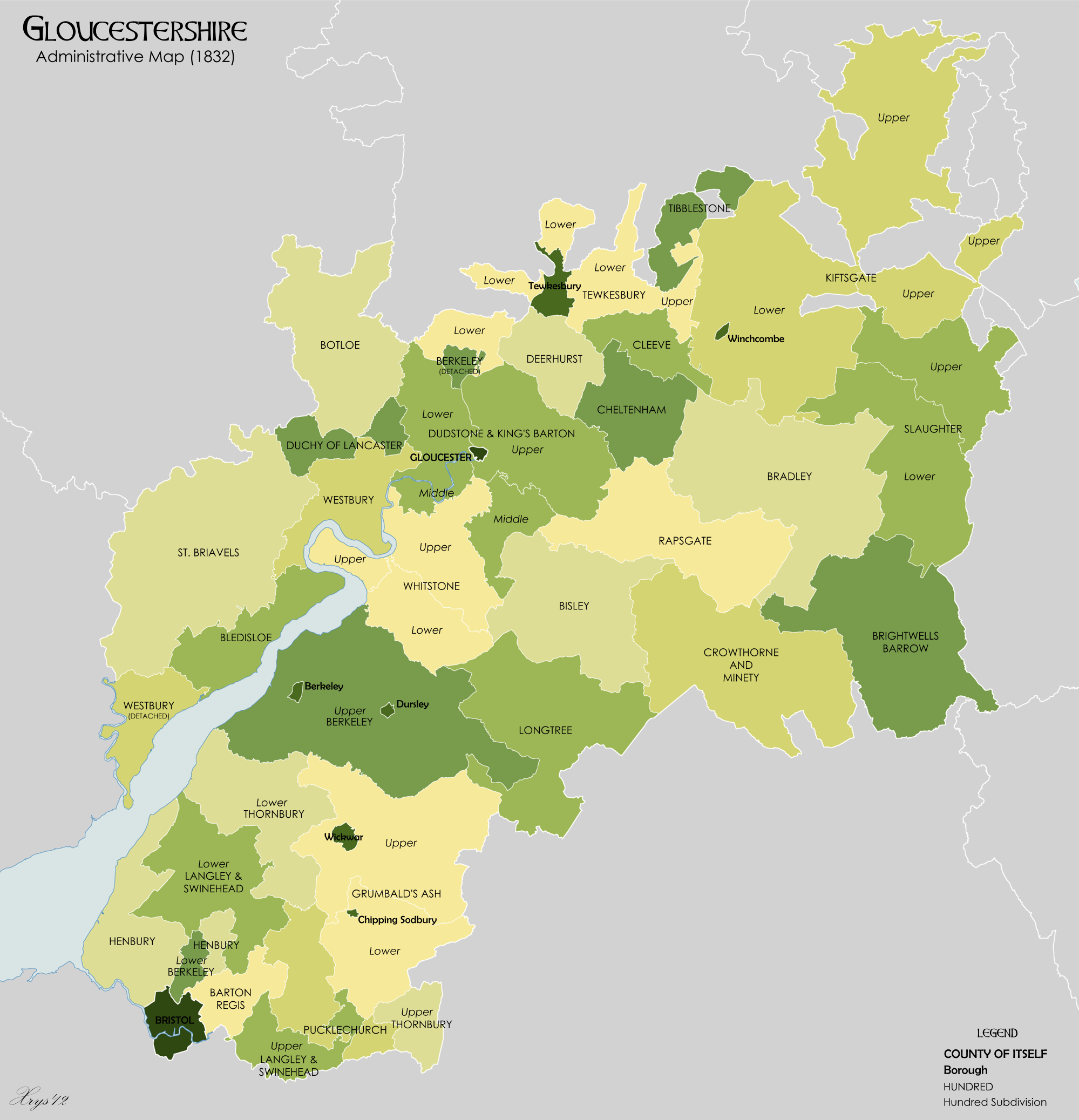
Hundred Of St Briavels
St Briavels was an ancient hundred of Gloucestershire, England. It comprised the extra-parochial area of the Forest of Dean, and the ancient parishes of *Abenhall *English Bicknor *St Briavels * Littledean * Flaxley *Hewelsfield *Mitcheldean * Newland *Ruardean * Staunton * Lea (part) The hundred was created at some time between 1086 and 1220 to provide a structure for the administration of the Forest of Dean. The meeting place was St Briavels Castle St Briavels Castle (most likely named after Saint Brioc) is a moated Norman architecture, Norman castle at St Briavels in the England, English county of Gloucestershire. The castle is noted for its huge Edward I of England, Edwardian gatehouse t .... References External links The National Gazetteer of Great Britain and Ireland (1868) Hundreds of Gloucestershire Forest of Dean {{Gloucestershire-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Coal Board
The National Coal Board (NCB) was the statutory corporation created to run the nationalised coal mining industry in the United Kingdom. Set up under the Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946, it took over the United Kingdom's collieries on "vesting day", 1 January 1947. In 1987, the NCB was renamed the British Coal Corporation, and its assets were subsequently privatised. Background Collieries were taken under government control during the World War I, First and World War II, Second World Wars. The Sankey Commission in 1919 gave R. H. Tawney, Sidney Webb and Sir Leo Chiozza Money the opportunity to advocate nationalisation, but it was rejected. Coal reserves were nationalised during the war in 1942 and placed under the control of the Coal Commission (United Kingdom), Coal Commission, but the mining industry remained in private hands. At the time, many coal companies were small, although some consolidation had taken place in the years before the war. Formation and organisat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946
The Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946 (9 & 10 Geo. 6. c. 59) was an Act of Parliament (United Kingdom), Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which nationalised, or brought into state control, the coal industry in the United Kingdom. It established the National Coal Board as the managing authority for coal mining and coal processing activities. It also initially provided for the establishment of consumers' councils. The Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946 was the first of a number of Acts promulgated by the post-war Labour government to nationalise elements of the UK's industrial infrastructure; other Acts include the Electricity Act 1947; the Transport Act 1947 (railways and long-distance road haulage); the Gas Act 1948; and the Iron and Steel Act 1949. Background The Coal Industry Nationalisation Bill was published in December 1945 by the Minister of Fuel and Power, Emanuel Shinwell, and got passed through the House of Commons by his Parliamentary Secretary Hugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statute Law (Repeals) Act 1969
The Statute Law (Repeals) Act 1969 (c. 52) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The act implemented recommendations contained in the first report on statute law revision made by the Law Commission. The enactments which were repealed (whether for the whole or any part of the United Kingdom) by the act were repealed so far as they extended to the Isle of Man on 25 July 1991.The Interpretation Act 1978, section 4(b) Section 1 - Repeal of enactments Refers to the schedules for the complete list of repealed laws and the extent of repeals. Section 1 of the act was repealed by Group 2 oPart IXof schedule 1 to the Statute Law (Repeals) Act 1998. Section 2 - Advowsons Section 2 of the act amends the Statute of Westminster 1285 ( 13 Edw. 1. St. 1) to clarify the proceedings of Advowsons in case of Quare impedit. Section 2(3) of the act was repealed by Group 2 oPart IXof schedule 1 to the Statute Law (Repeals) Act 1998. Section 3 - Rentcharges, etc., under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 & 2 Vict
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive government specifically or only to the monarch and their Viceroy, direct representatives. The term can be used to refer to the rule of law; or to the functions of executive (government), executive (the Crown-King-in-Council, in-council), legislative (the Crown-in-parliament), and judicial (the Crown on the bench) governance and the civil service. The concept of the Crown as a corporation sole developed first in the Kingdom of England as a separation of the physical crown and property of the kingdom from the person and personal property of the monarch. It spread through English and later British colonisation and developed into an imperial crown, which rooted it in the legal lexicon of all 15 Commonwealth realms, their various dependencies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succeeding the Second Agricultural Revolution. Beginning in Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain around 1760, the Industrial Revolution had spread to continental Europe and the United States by about 1840. This transition included going from craft production, hand production methods to machines; new Chemical industry, chemical manufacturing and Puddling (metallurgy), iron production processes; the increasing use of Hydropower, water power and Steam engine, steam power; the development of machine tools; and rise of the mechanisation, mechanised factory system. Output greatly increased, and the result was an unprecedented rise in population and population growth. The textile industry was the first to use modern production methods, and textiles b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newland, Gloucestershire
Newland is a village and civil parish in the Forest of Dean in Gloucestershire, England. situated on the east side of the River Wye, south-east of Monmouth. It is notable for its parish church of All Saints, known as the 'Cathedral of the Forest'. It was the centre of a large parish with complex boundaries and scattered settlements. The church The church, dedicated to All Saints, was founded shortly before 1216. It was sited on a low, flat-topped hill, sheltered by higher hills except to the south where the land descends to the River Wye. The church comprises a chancel with side chapels, an aisled nave with south chapel and south porch, and a west tower. The tower was begun in the late 13th century, although the upper stages are of the late 14th or early 15th century. The chancel, the chapel south of it, the arcades and aisles, and the south porch are mainly 14th century features, and the north and east chapels were added in the 15th century. The church was thoroughly restored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |