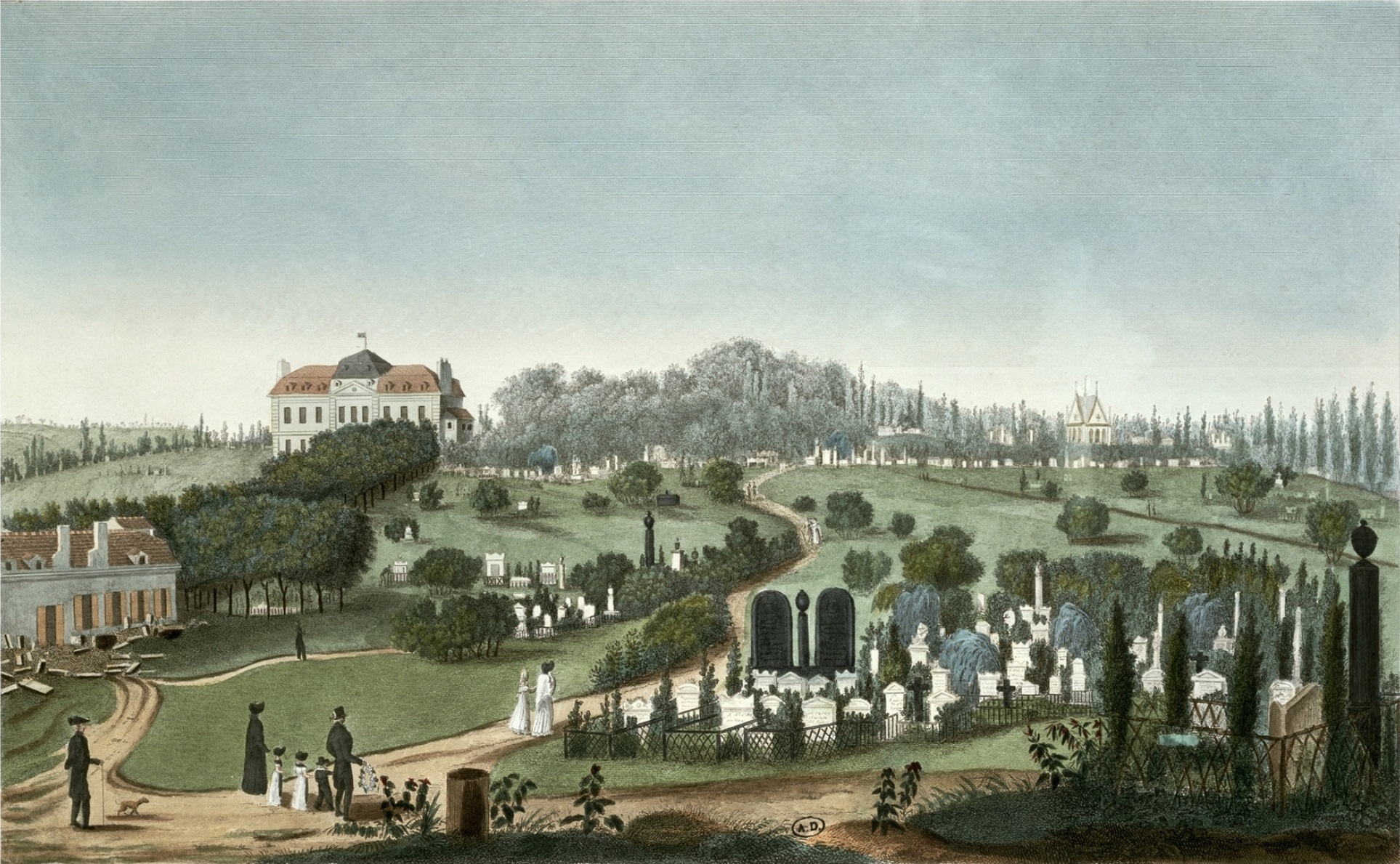|
François De La Chaise
François de la Chaise (; 25 August 1624 – 20 January 1709), also known as Père Lachaise (Father Lachaise), was a French Jesuit priest, the father confessor of King Louis XIV of France. Biography François de la Chaise was born at the Château of Aix in Aix-la-Fayette, Puy-de-Dôme, Auvergne, being the son of Georges d'Aix, seigneur de La Chaise, and of Renée de Rochefort. On his mother's side he was a grandnephew of Pierre Coton, the confessor of Henry IV. He became a novice of the Society of Jesus before completing his studies at Lyon, where, after taking final vows, he lectured on philosophy to students attracted by his fame from all parts of France. Through the influence of Camille de Villeroy, Archbishop of Lyon, Père de la Chaise was in 1674 nominated confessor of Louis XIV, who entrusted him during the lifetime of Harlay de Champvallon, archbishop of Paris, with the administration of the ecclesiastical patronage of the crown. The confessor united his influence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Father Lachaise
A father is the male parent of a child. Besides the paternal bonds of a father to his children, the father may have a parental, legal, and social relationship with the child that carries with it certain rights and obligations. A biological father is the male genetic contributor to the creation of the infant, through sexual intercourse or sperm donation. A biological father may have legal obligations to a child not raised by him, such as an obligation of monetary support. An adoptive father is a man who has become the child's parent through the legal process of adoption. A putative father is a man whose biological relationship to a child is alleged but has not been established. A stepfather is a non-biological male parent married to a child's preexisting parent and may form a family unit but generally does not have the legal rights and responsibilities of a parent in relation to the child. The adjective "paternal" refers to a father and comparatively to "maternal" for a mother. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pere Lachaise
Pere may refer to: *Pere, Hungary, a village in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county *Pärtel-Peeter Pere (born 1985), Estonian entrepreneur, urban strategist, and politician * Rangimārie Te Turuki Arikirangi Rose Pere (1937–2020), Māori New Zealand educationalist and spiritual leader *Wi Pere (1837–1915), a Māori Member of Parliament in New Zealand *Pere Wihongi Pere Te Ruru o te Ramana Wihongi (born ), sometimes known mononymously as PERE, is a New Zealand musician, voice actor, choreographer, and kapa haka performer. She is part of the award-winning music groups Maimoa and Te Kākano. Early life Wiho ... (born 1993), New Zealand musician, voice actor, choreographer, and kapa haka performer See also * Péré (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Régis Chantelauze
Regis or Régis may refer to: People * Regis (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name) * Regis (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * Regis (musician), full name Karl O'Connor, an English electronic music and techno DJ * Régis (footballer, born 1965), full name Reginaldo Paes Leme Ferreira, Brazilian football goalkeeper * Régis (footballer, born 1976), full name Régis Amarante Lima de Quadros, Brazilian football manager and former centre-back * Régis (footballer, born June 1989), full name Régis Ribeiro de Souza, Brazilian football right-back * Régis (footballer, born November 1989), full name Régis dos Santos Silva, Brazilian football defensive midfielder * Régis (footballer, born 1992), full name Régis Augusto Salmazzo, Brazilian football attacking midfielder * Régis (footballer, born 1998), full name Régis Tosatti Giacomin, Brazilian football forward Education * Regis College (Massachusetts) (town of Weston) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The King's Daughter (2022 Film)
''The King's Daughter'' is a 2022 action-adventure fantasy film directed by Sean McNamara from a screenplay by Barry Berman and James Schamus. It is based on the 1997 novel '' The Moon and the Sun'' by Vonda N. McIntyre. It stars Pierce Brosnan as King Louis XIV, Kaya Scodelario as Marie-Josèphe, and Benjamin Walker as Yves De La Croix. It was William Hurt's final screen performance to be released before his death in March 2022, though it had been filmed eight years prior. Principal photography began in early April 2014 in Versailles, France. After the two-week shoot in France, production then began on April 23 in Melbourne, Australia. Shooting wrapped up at the end of May. Originally intended to be released in April 2015, the film was delayed just three weeks prior in order to complete post-production effects. It then sat in development hell for over five years, until the distribution rights were acquired by Gravitas Ventures, which released it theatrically on January 21 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hurt
William McChord Hurt (March 20, 1950 – March 13, 2022) was an American actor. For his performances on stage and screen, he received various awards including an Academy Award, a British Academy Film Award, and a Cannes Film Festival Award for Best Actor, in addition to nominations for five Golden Globe Awards, two Primetime Emmy Awards, and a Tony Award. Hurt studied at the Juilliard School before his film debut, in Ken Russell's science-fiction feature ''Altered States'' (1980), for which he received a nomination for the Golden Globe Award for New Star of the Year. He went on to receive the Academy Award for Best Actor playing a gay prisoner in '' Kiss of the Spider Woman'' (1985). Hurt was Oscar-nominated for '' Children of a Lesser God'' (1986), and '' Broadcast News'' (1987), and ''A History of Violence'' (2005). He starred in films such as ''Body Heat'' (1981), '' The Big Chill'' (1983), '' The Accidental Tourist'' (1988), ''Alice'' (1990), '' One True Thing'' (1998), ''Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philibert-Joseph Le Roux
Philibert-Joseph Le Roux (? – before 1735 Brussels) was an 18th-century French lexicographer. Le Roux is remembered for hi''Dictionaire comique, satyrique, critique, burlesque, libre & proverbial''published in 1718. Le Roux was forced to leave France in 1693 after he published a pamphlet against François de la Chaise. He fled to Brussels where he died before 1735 while serving Marie-Elisabeth of Austria.Monica Barsi, « Le « Dictionnaire burlesque » de Richelet et sa continuation per Philibert Joseph Le Roux », ''Lingua, cultura e testo : miscellanea di studi francesi in onore di Sergio Cigada'', Milan, Vita e Pensiero, 2003, 762 p., (), (p. 63–79). Works ''Histoire du père La Chaize, jésuite et confesseur du roi Louis XIV où l'on verra les intrigues secrettes qu'il a eues à la cour de France et dans toutes les cours de l'Europe''pour l'avancement des grands desseins du roi son maître, Köln 1693; *''Dictionaire comique, satyrique, critique, burlesque, libre et p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Père Lachaise Cemetery
Père Lachaise Cemetery (, , formerly , ) is the largest cemetery in Paris, France, at . With more than 3.5 million visitors annually, it is the most visited necropolis in the world. Buried at Père Lachaise are many famous figures in the arts, including Miguel Ángel Asturias, Honoré de Balzac, Sarah Bernhardt, Georges Bizet, Frédéric Chopin, Colette, George Enescu, Max Ernst, Olivia de Havilland, Marcel Marceau, Georges Méliès, Amedeo Modigliani, Molière, Édith Piaf, Camille Pissarro, Marcel Proust, Gertrude Stein, Oscar Wilde, Richard Wright (author), Richard Wright, Sadegh Hedayat, Jim Morrison, and Michel Petrucciani. Many famous philosophers, scientists, and historical figures are buried there as well, including Peter Abelard, Pierre Bourdieu, Jean-François Champollion, Auguste Comte, Georges Cuvier, Joseph Fourier, Manuel Godoy, Georges-Eugène Haussmann, Jean-François Lyotard, Nestor Makhno, Maurice Merleau-Ponty, Jean Moulin, Henri de Saint-Simon, Jean-Bap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon, a series of military campaigns across Europe during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars from 1796 to 1815. He led the French First Republic, French Republic as French Consulate, First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then ruled the First French Empire, French Empire as Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814, and briefly again in 1815. He was King of Italy, King of Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Italy from 1805 to 1814 and Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine, Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine from 1806 to 1813. Born on the island of Corsica to a family of Italian origin, Napoleon moved to mainland France in 1779 and was commissioned as an officer in the French Royal Army in 1785. He supported the French Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Fénelon
François de Salignac de la Mothe-Fénelon, PSS (), more commonly known as François Fénelon (6 August 1651 – 7 January 1715), was a French Catholic archbishop, theologian, poet and writer. Today, he is remembered mostly as the author of ''Les Aventures de Télémaque, The Adventures of Telemachus'', first published in 1699. He was a member of the Society of the Priests of Saint Sulpice, Sulpician Fathers. Childhood and education, 1651–75 Fénelon was born on 6 August 1651 at the Château de Fénelon, in Sainte-Mondane, Périgord, Aquitaine, in the Dordogne river valley, the second of the three children of Pons de Salignac, Comte de La Mothe-Fénelon by his wife Louise de La Cropte. Reduced to the status of "impecunious old nobility" by François' time, the La Mothe-Fénelons had produced leaders in both Church and state. At the time of Fénelon's birth, his uncle Francois served as bishop of nearby Sarlat, a see in which fifteen generations of the Fénelon family had fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis De Rouvroy, Duc De Saint-Simon
Louis de Rouvroy, duc de Saint-Simon, Grandee of Spain, GE (; 16 January 16752 March 1755), was a French soldier, diplomat, and memoirist. He was born in Paris at the Hôtel Selvois, 6 rue Taranne (demolished in 1876 to make way for the Boulevard Saint-Germain). The family's ducal peerage (''duché-pairie''), granted in 1635 to his father Claude de Rouvroy, duc de Saint-Simon, Claude de Rouvroy (1608–1693), served as both perspective and theme in Saint-Simon's life and writings. He was the second and last Duke of Saint-Simon. His enormous memoirs are a classic of French literature, giving the fullest and most lively account of the court at Palace of Versailles, Versailles of Louis XIV and the ''Régence'' at the start of Louis XV's reign. Peerage of France Men of the nobility, noblest blood (in Saint-Simon's view) might not be, and in most cases were not, peers in France. Derived at least traditionally and imaginatively from the ''douze pairs'' (twelve peers) of Charlemagne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jansenism
Jansenism was a 17th- and 18th-century Christian theology, theological movement within Roman Catholicism, primarily active in Kingdom of France, France, which arose as an attempt to reconcile the theological concepts of Free will in theology, free will and Grace in Christianity, divine grace in response to certain developments in the Catholic Church, but later developed political and philosophical aspects in opposition to Absolutism (European history), royal absolutism. It was based on the ideas of Cornelius Jansen, (1585-1638), a Dutch bishop, and his book ''Augustinus (Jansenist book), Augustinus''. Jansenists believed that God’s grace was the only way to salvation and that human free will had no role. Jansenists provoked lively debates, particularly in France, where five propositions, including the doctrines of limited atonement and irresistible grace, were extracted from the work and declared heretical by theologians hostile to Jansen. In 1653, Pope Innocent X condemned f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edict Of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was an edict signed in April 1598 by Henry IV of France, King Henry IV and granted the minority Calvinism, Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was predominantly Catholic Church, Catholic. While upholding Catholicism as the State_religion, established religion, and requiring the re-establishment of Catholic worship in places it had lapsed, it granted certain religious toleration to the Protestant Huguenots, who had been waging a long and bloody struggle for their rights in France. The Edict of Nantes helped to end the Wars of Religion in France, which had been raging for decades. It also ensured that the Protestant minority in France would have a measure of religious and political freedom, and helped to establish France as a more tolerant and pluralistic society. However, the Edict was eventually revoked by King Louis XIV in 1685, leading to a mass exodus of Huguenots from France and a loss of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |