|
François-Guillaume Ménageot
François-Guillaume Ménageot (1744–1816) was a French painter of religious and French historical scenes. A pupil of François Boucher (1703–1770), he went on to win the Grand Prix de Rome and become a director of the French Academy in Rome, an academician and a member of the Institute. Biography Ménageot was born in London, the son of Augustin Ménageot (d 1784), an art dealer and adviser to Denis Diderot. François-Guillaume trained under first Jean-Baptiste-Henri Deshays, then Joseph-Marie Vien, and finally François Boucher (1703–1770), in his early works adopting the latter's style and use of warm, light colours. His 1766 ''Tomyris Plunging the Head of Cyrus into a Bowl of Blood'' (Paris, Ecole Normale Supérieure des Beaux-Arts) won the Prix de Rome and a stay at the French Academy in Rome from 1769 to 1774. The Académie Royale in Paris approved François-Guillaume as a history painter in 1777, and he then exhibited ''The Farewells of Polyxena to Hecuba'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis I Of France
Francis I (; ; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law Louis XII, who died without a legitimate son. A prodigious patron of the arts, Francis promoted the emergent French Renaissance by attracting many Italian artists to work for him, including Leonardo da Vinci, who brought the ''Mona Lisa'', which Francis had acquired. Francis's reign saw important cultural changes with the growth of central power in France, the spread of humanism and Protestantism, and the beginning of French exploration of the New World. Jacques Cartier and others claimed lands in the Americas for France and paved the way for the expansion of the first French colonial empire. For his role in the development and promotion of the French language, Francis became known as (the 'Father and Restorer of Letters'). He was also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1744 Births
Events January–March * January 6 – The Royal Navy ship ''Bacchus'' engages the Spanish Navy privateer ''Begona'', and sinks it; 90 of the 120 Spanish sailors die, but 30 of the crew are rescued. * January 24 – The Dagohoy rebellion in the Philippines begins, with the killing of Father Giuseppe Lamberti. * February 22–February 23, 23 – Battle of Toulon (1744), Battle of Toulon: The British fleet is defeated by a joint Franco-Spanish fleet. * February 27 – Violent storms frustrate a Planned French invasion of Britain (1744), planned French invasion of Britain. * March 1 (approximately) – The Great Comet of 1744, one of the brightest ever seen, reaches perihelion. * March 13 – The British ship ''Betty'' capsizes and sinks off of the Gold Coast (modern-day Ghana) near Anomabu. More than 200 people on board die, although there are a few survivors. * March 15 – France declares war on Great Britain. April–June * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tullia Driving Her Chariot Over The Body Of Her Father
''Tullia Driving her Chariot over the Body of her Father'' is a 1765 painting by François-Guillaume Ménageot which depicts the Roman princess Tullia driving her chariot over the dead body of her father, the king Servius Tullius. The painting won second prize at the Prix de Rome The Prix de Rome () or Grand Prix de Rome was a French scholarship for arts students, initially for painters and sculptors, that was established in 1663 during the reign of Louis XIV of France. Winners were awarded a bursary that allowed them t .... See also * '' Tullia Drives over the Corpse of her Father'', by Jean Bardin * '' Tullia driving her Chariot over her Father'', by Giuseppe Bartolomeo Chiari * '' Tullia Running Her Chariot over the Body of Her Father'', by Michel-François Dandré-Bardon References Further reading * Women in Livy: Tullia Minor' 1765 paintings Cultural depictions of Tullia Minor Cultural depictions of Servius Tullius {{1760s-painting-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Eustache, Paris
The Church of St. Eustache, Paris (, ), is a church in the 1st arrondissement of Paris. The present building was built between 1532 and 1633. Situated near the site of Paris' medieval marketplace ( Les Halles) and rue Montorgueil, Saint-Eustache exemplifies a mixture of multiple architectural styles: its structure is Flamboyant Gothic while its interior decoration and other details are Renaissance and classical. It is the second largest church in the city, just behind Notre-Dame. The 2019 Easter Mass at Notre-Dame cathedral in Paris was relocated to Saint-Eustache after the Notre-Dame de Paris fire. History Situated in Les Halles, an area of Paris once home to the country's largest food market, the origins of Saint Eustache date back to the 13th century. A modest chapel was built in 1213, dedicated to Saint Agnes, a Roman martyr. The small chapel was funded by Jean Alais, a merchant at Les Halles who was granted the rights to collect a tax on the sale of fish baskets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villeneuve-sur-Yonne
Villeneuve-sur-Yonne () is a commune in the Yonne department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in north-central France. It is surrounded by a partly intact wall, built during the 12th century, which was one of the 8 residences of the French kings. Geography The city lies on the bank of the river Yonne, between the cities of Sens and Joigny. History The city was founded in 1163 by Louis VII of France to protect the kingdom of France at the boundary of the Champagne. In 1204 King Philip II Augustus held parliament in the city, and Louis IX resided in the city before departing for the Eighth Crusade. In 1594 the city was burnt down. During the French Revolution the name was changed from ''le-Roi'' (the king) to ''sur-Yonne'' (on the Yonne). In 1870 a memorial for the dead was designed by the sculptor Émile Peynot. The city was governed from 1927 till 1931 by the infamous mayor Marcel Pétiot, who was guillotined in 1946, convicted of 26 killings. Demography The inhabitants are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meleager
In Greek mythology, Meleager (, ) was a hero venerated in his '' temenos'' at Calydon in Aetolia. He was already famed as the host of the Calydonian boar hunt in the epic tradition that was reworked by Homer. Meleager is also mentioned as one of the Argonauts. Biography Meleager was a Calydonian prince as the son of Althaea and the vintner King Oeneus or according to some, of the god Ares. He was the brother of Deianeira, Toxeus, Clymenus, Periphas, Agelaus (or Ageleus), Thyreus (or Phereus or Pheres), Gorge, Eurymede and Melanippe. Antoninus Liberalis2as cited in Nicander's ''Metamorphoses'' Meleager was the father of Parthenopeus by Atalanta but he married Cleopatra, daughter of Idas and Marpessa. They had a daughter, Polydora, who became the bride of Protesilaus, who left her bed on their wedding-night to join the expedition to Troy. Mythology Calydonian boar hunt When Meleager was born, the Moirai (the Fates) predicted he would only live u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
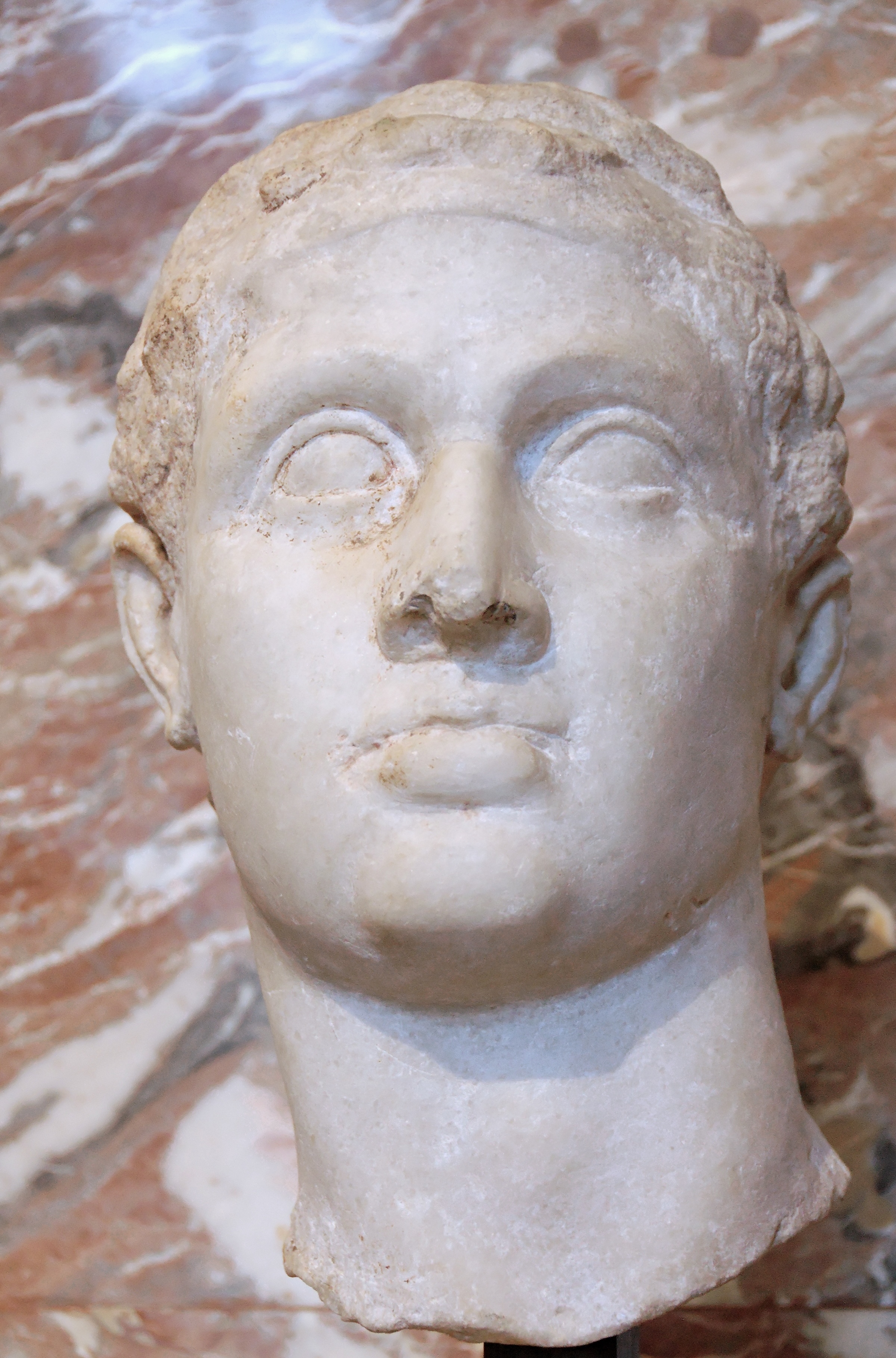
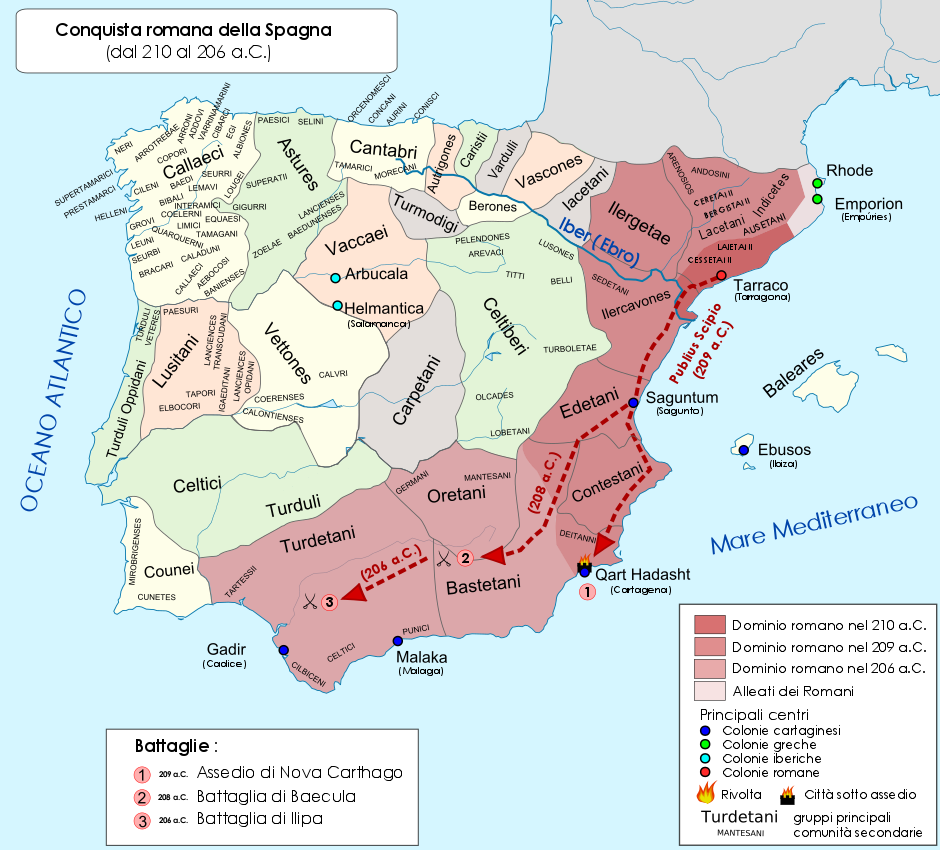
Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet ''Africanus'', literally meaning 'the African', but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa (Roman province), Africa. Scipio's conquest of Carthaginian Iberia culminated in the Battle of Ilipa in 206 BC against Hannibal's brother Mago Barca. Although considered a hero by the Roman people, primarily for his victories against Carthage, Scipio had many opponents, especially Cato the Elder, who hated him deeply. In 187 BC, he was tried in a show trial alongside his brother for bribes they supposedly received from the Seleucid king Antiochus III ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra Paying Her Last Respects To Anthony
Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator (; The name Cleopatra is pronounced , or sometimes in both British and American English, see and respectively. Her name was pronounced in the Greek dialect of Egypt (see Koine Greek phonology). She was also styled as Thea Neotera () and Philopatris (); see 70/69 BC10 or 12 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and the last active Hellenistic pharaoh.She was also a diplomat, Ancient navies and vessels, naval commander, linguist, and Ancient Greek medicine, medical author; see and . A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Government of Macedonia (ancient kingdom)#Companions, friends, councils, and assemblies, companion of Alexander the Great. writes about Ptolemy I Soter: "The Ptolemaic dynasty, of which Cleopatra was the last representative, was founded at the end of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |