|
Former Zhao
The Han-Zhao ( zh, s=汉赵, t=漢趙, p=Hàn Zhào; 304–329 AD), or Former Zhao ( zh, s=前赵, t=前趙, p=Qián Zhào), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Liu ( Luandi) clan of Chuge-Xiongnu ethnicity during the Sixteen Kingdoms period of Chinese history. In Chinese historiography, it was given two conditional state titles, the Northern Han (; ) for the state proclaimed in 304 by Liu Yuan, and the Former Zhao (; ) for the state proclaimed in 319 by Liu Yao. The reference to them as separate states can be misleading, given that when Liu Yao changed the name of the state from "Han" to "Zhao" in 319, he treated the state as having been continuous from when Liu Yuan founded it in 304; instead, he de-established his imperial lineage from the Han dynasty and claimed ancestry directly from Modu Chanyu. The reason it is also referred to as "Former Zhao" in historiography is to distinguish it from the Later Zhao founded by Shi Le in 319, which was also known officially as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy), to fully autocratic (absolute monarchy), and may have Political representation, representational, Executive (government), executive, legislative, and judicial functions. The Order of succession, succession of monarchs has mostly been Hereditary monarchy, hereditary, often building dynasties; however, monarchies can also be elective monarchy, elective and Self-proclaimed monarchy, self-proclaimed. Aristocracy (class), Aristocrats, though not inherent to monarchies, often function as the pool of persons from which the monarch is chosen, and to fill the constituting institutions (e.g. Diet (assembly), diet and Royal court, court), giving many monarchies oligarchic elements. The Legitimacy (political)#Monarchy, political legitim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luandi
The Luandi (; alternatively written as Xulianti ) was the ruling clan of the Xiongnu that flourished from the 3rd century BCE to 4th century CE. The form Luandi comes from the '' Book of Han'', while the form Xulianti comes from the '' Book of Later Han''. Etymology Lanhai Wei and Hui Li reconstruct the Old Chinese pronunciation of 挛鞮 as *lyuan-tlïγ, evolving from an earlier 虚连题 (*Hala-yundluγ), as a result of a historical sound shift involving the initial dropping of *h- by demonstrating its occurrence in several historical sources. Furthermore, the conjugation of the roots *hala, meaning colorful; *yund meaning horse, *-luγ as the participle suffix would have resulted in the semantic meaning "tribe with skewbald horses" in an early Turkic dialect, allowing it to be further identified with the historical Ulayundluğ tribe. Moreover, the authors argue that the conquest of the same clan by the Xue in the 4th century CE eventually gave birth to the Xueyantuo. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (266–420)
The Jin dynasty or Jin Empire, sometimes distinguished as the or the , was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty in China that existed from 266 to 420. It was founded by Emperor Wu of Jin, Sima Yan, eldest son of Sima Zhao, who had previously been declared the King of Jin. There are two main divisions in the history of the dynasty. The (266–316) was established as the successor to Cao Wei after Sima Yan usurped the throne from Cao Huan. The capital of the Western Jin was initially in Luoyang, though it later moved to Chang'an (modern Xi'an). In 280, after conquering Eastern Wu, the Western Jin ended the Three Kingdoms period and reunited China proper for the first time since the end of the Han dynasty. From 291 to 306, a series of civil wars known as the War of the Eight Princes were fought over control of the Jin state which weakened it considerably. In 304, the dynasty experienced a wave of Invasion and rebellion of the Five Barbarians, rebellions by non-Han Chinese, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
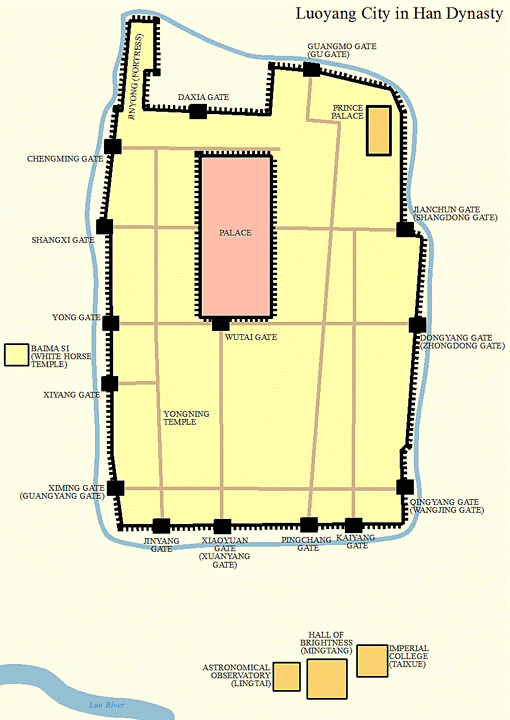
Disaster Of Yongjia
The Disaster of Yongjia (simplified Chinese: 永嘉之乱; traditional Chinese: 永嘉之亂) occurred in 311 CE, when forces of the Han-Zhao dynasty captured and sacked Luoyang, the capital of the Western Jin dynasty. The Han's army committed a massacre of the city's inhabitants, killing the Jin crown prince, a host of ministers, and over 30,000 civilians. They also burnt down the palaces and dug up the Jin dynasty's mausoleums. Though the Western Jin would survive for a few more years, this event is often seen as one of the worst disasters in Chinese history, as both the emperor and one of the ancient capitals fell to the hands of "barbarian" forces. Background Despite the War of the Eight Princes concluding in early 307, the Western Jin court, under the paramountcy of the Prince of Donghai, Sima Yue, had to deal subsequently with an assortment of rebellions throughout the empire. Most concerning was the Five Divisions in Bing province, descendants of the Southern Xiongnu wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upheaval Of The Five Barbarians
The Upheaval of the Five Barbarians also translated as the Uprising, Rebellion or the Revolt of the Five Barbarians () is a Chinese expression used to refer to a chaotic period of warfare from 304 to 316 during the fall of the Western Jin dynasty. Overlapping with the War of the Eight Princes, these conflicts which involved non- Han groups living within China eventually drove the Jin imperial court out of the northern and southwestern China. The "Five Barbarians" were the Xiongnu, Jie, Qiang, Di and Xianbei, many of whom had resettled within China during the preceding centuries. Despite the period's name, many Han Chinese and other tribal people like the Wuhuan were also involved, wavering their support between Jin and the separatist regimes. Years of poor administration and civil wars between the ruling princes left the empire open to its disaffected and opportunistic subjects. Ethnic tensions in the Guanzhong region between the Han and the tribes, primarily the Qiang and Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi and Datong. Its one-character abbreviation is (), after the Jin (Chinese state), state of Jin that existed there during the Spring and Autumn period (). The name ''Shanxi'' means 'west of the mountains', a reference to its location west of the Taihang Mountains. Shanxi borders Hebei to the east, Henan to the south, Shaanxi to the west and Inner Mongolia to the north. Shanxi's terrain is characterised by a plateau bounded partly by mountain ranges. Shanxi's culture is largely dominated by the ethnic Han Chinese, Han majority, who make up over 99% of its population. Jin Chinese is considered by some linguists to be a distinct language from Mandarin and its geographical range covers most of Shanxi. Both Jin and Mandarin are spoken in Shanxi. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Han
The Northern Han ( zh, t=北漢, s=北汉, p=Běi Hàn) was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was founded by Liu Min (Emperor Shizu) as a continuation of the Later Han dynasty founded by his brother Liu Zhiyuan (Emperor Gaozu). The Northern Han lasted from 951 to 979, when it was conquered by the Northern Song dynasty. Founding of the Northern Han The short-lived state of Later Han fell in 950 because of Guo Wei, a powerful military governor's ''de facto'' coup. Liu Min founded the Northern Han Kingdom, sometimes referred to as the Eastern Han, in 951 claiming that he was the legitimate heir to the imperial throne of Later Han. Liu Min immediately restored the traditional relationship with the Khitans, who had founded the Liao dynasty. Sources conflict as to the origin of the Later Han and Northern Han emperors; some indicate sinicized Shatuo ancestry while some traditional historical sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Zhao
Zhao, briefly known officially as Wei (衛) in 350 AD, known in historiography as the Later Zhao (; 319–351) or Shi Zhao (石趙), was a dynasty of China ruled by the Shi family of Jie ethnicity during the Sixteen Kingdoms period. Among the Sixteen Kingdoms, the Later Zhao was the second in territorial size to the Former Qin dynasty that once unified northern China under Fu Jian. In historiography, it is given the prefix of "Later" to distinguish it with the Han-Zhao or Former Zhao, which changed its name from "Han" to "Zhao" just before the Later Zhao was founded. When the Later Zhao was founded by former Han-Zhao general Shi Le, the capital was at Xiangguo (襄國, in modern Xingtai, Hebei), but in 335 Shi Hu moved the capital to Ye (Hebei), Yecheng (鄴城, in modern Handan, Hebei), where it would remain for the rest of the state's history (except for Shi Zhi's brief attempt to revive the state at Xiangguo). After defeating the Han-Zhao in 329, the Later Zhao ruled a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modu Chanyu
Modu () was the son of Touman and the founder of the empire of the Xiongnu. He came to power by ordering his men to kill his father in 209 BCE. Modu ruled from 209 to 174 BCE. He was a military leader under his father Touman and later ''chanyu'' of the Xiongnu Empire, based on the Mongolian Plateau. He secured the throne and established a powerful Xiongnu Empire by successfully unifying the tribes of the Mongolian–Manchurian grassland in response to the loss of Xiongnu pasture lands to invading Qin forces commanded by Meng Tian in 215 BCE. While Modu rode and then furthered the wave of militarization and effectively centralized Xiongnu power, the Qin quickly fell into disarray with the death of the first emperor in 210 BCE, leaving Modu a free hand to expand his empire into one of the largest of his time. The eastern border stretched as far as the Liao River, the western borders of the empire reached the Pamir Mountains, whilst the northern border reached Lake Baikal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Yuan (Han-Zhao)
Liu Yuan (劉淵, died 29 August 310), courtesy name Yuanhai (元海), also known by his posthumous name as the Emperor Guangwen of Han (Zhao) (漢(趙)光文帝) was the founding emperor of the Xiongnu-led Han-Zhao dynasty of China during the Sixteen Kingdoms period. Due to Tang dynasty naming taboo, he is referred to by his courtesy name as Liu Yuanhai (劉元海) in the ''Book of Jin''. With the dissolution of the Southern Xiongnu in 216, the last vestiges of their power were divided into Five Divisions in Bing province around modern-day Shanxi. Liu Yuan was born into the aristocracy of the Five Divisions and was sent to the Chinese capital, Luoyang as a hostage during his youth, where he became highly sinicized and later held several government offices under the Western Jin dynasty. As the War of the Eight Princes weakened Jin authority in northern China, Liu Yuan was called upon by the Five Divisions to lead their rebellion, and in 304, he declared independence from the Jin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |