|
Forests Department, Haryana
Forests Department, Haryana is a department of the Government of Haryana, a States and union territories of India, state in India, that runs and maintains many protected nature areas in the state of Haryana. It has two administrative divisions: Forest and Wildlife. The department is responsible for maintaining National park, National Parks, Nature reserve, Wildlife Sanctuaries and Reserved forests and protected forests of India, Conservation Reserves in Haryana. It also provides a special emphasis on Soil and Moisture Conservation works in the hills to conserve water and deliver it to adjacent farmlands. Two National Parks, eight Wildlife Sanctuaries, two Conservation Reserves, four Animal & Bird Breeding Centres, one Deer Park, Hisar, Deer park, and 49 herbal parks. Kanwar Pal Gujjar has been the cabinet minister responsible for this department since October 2019. constitute the Protected Area network of the department, covering 0.75% of the Haryana, state. It also maintains a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Of Government Of Haryana
Seal may refer to any of the following: Common uses * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** Earless seal, also called "true seal" ** Fur seal ** Eared seal * Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of authentication, on paper, wax, clay or another medium (the impression is also called a seal) * Seal (mechanical), a device which helps prevent leakage, contain pressure, or exclude contamination where two systems join ** Hermetic seal, an airtight mechanical seal * Security seals such as labels, tapes, bands, or ties affixed onto a container in order to prevent and detect tampering Arts, entertainment and media * ''Seal'' (1991 album), by Seal * ''Seal'' (1994 album), sometimes referred to as ''Seal II'', by Seal * '' Seal IV'', a 2003 album by Seal * ''Seal Online'', a 2003 massively multiplayer online role-playing game Law * Seal (contract law), a legal formality for contracts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural or cultural values. Protected areas are those areas in which human presence or the exploitation of natural resources (e.g. firewood, non-timber forest products, water, ...) is limited. The term "protected area" also includes marine protected areas and transboundary protected areas across multiple borders. As of 2016, there are over 161,000 protected areas representing about 17 percent of the world's land surface area (excluding Antarctica). For waters under national jurisdiction beyond inland waters, there are 14,688 Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), covering approximately 10.2% of coastal and marine areas and 4.12% of global ocean areas. In contrast, only 0.25% of the world's oceans beyond national jurisdiction are covered by MPAs. In recent years, the 30 by 30 initiative has targeted to protect 30% of ocean territory and 30% of land territory worldwide by 2030; this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Mountains
Sacred mountains are central to certain religions, and are usually the subjects of many legends. For many, the most symbolic aspect of a mountain is the peak because it is believed that it is closest to heaven or other religious realms. Many religions have traditions centered on sacred mountains, which either are or were considered holy (such as Mount Olympus in Greek mythology) or are related to famous events (like Mount Sinai in Judaism and descendant religions or Mount Kailash, Mount Meru in Hinduism). In some cases, the sacred mountain is purely mythical, like the Hara Berezaiti in Zoroastrianism. Mount Kailash is believed to be the abode of the deities Shiva and Parvati, and is considered sacred in four religions: Hinduism, Bon, Buddhism, and Jainism. Volcanoes, such as Mount Etna in Italy, were also considered sacred, Mount Etna being believed to have been the home of Vulcan (mythology), Vulcan, the Roman mythology, Roman god of fire and the forge. Themes of sacrality Edwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the Runoff (hydrology), runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their Bank (geography), banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghaggar-Hakra River
The Ghaggar-Hakra River () is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season. The river is known as Ghaggar before the Ottu barrage at , and as Hakra downstream of the barrage in the Thar Desert. In pre-Harappan times the Ghaggar was a tributary of the Sutlej. It is still connected to this paleochannel of the Sutlej, and possibly the Yamuna, which ended in the Nara River (Sindh), Nara River, presently a Distributary, delta channel of the Indus River joining the sea via Sir Creek. The Sutlej changed its course about 8,000–10,000 years ago, leaving the Ghaggar-Hakra as a system of monsoon-fed rivers terminating in the Thar Desert. The Indus Valley Civilisation prospered when the monsoons that fed the rivers diminished around 5,000 years ago, and a large number of sites from the Mature Indus Valley Civilisation (2600–1900 BCE) are found along the middle course of the (dried-up) Hakra in Pakistan. Around 4,000 years ago, the Indus Valley Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarasvati River
The Sarasvati River () is a Apotheosis, deified myth, mythological Rigvedic rivers, river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedas, Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda. As a physical river, in the oldest texts of the Rigveda it is described as a "great and holy river in north-western Indian subcontinent, India," but in the middle and late Rigvedic books it is described as a small river ending in "a terminal lake (samudra)." As the goddess Saraswati, Sarasvati, the other referent for the term "Sarasvati" which developed into an independent identity in post-Vedic times, the river is also described as a powerful river and mighty flood. The Sarasvati is also considered by Hindus to exist in a Metaphysics, metaphysical form, in which it formed a confluence with the sacred rivers Ganges, Ganga and Yamuna, at the Triveni Sangam. According to Michael Witzel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Lower Himalaya in Uttarakhand, it travels and has a drainage system of , 40.2% of the entire Ganges Basin. It merges with the Ganges at Triveni Sangam, Prayagraj, which is a site of the Kumbh Mela, a Hindu festival held every 12 years. Like the Ganges, the Yamuna is highly venerated in Hinduism and worshipped as the goddess Yamuna. In Hinduism, she is believed to be the daughter of the sun god, Surya, and the sister of Yama, the god of death, and so she is also known as Yami. According to popular Hindu legends, bathing in Yamuna's sacred waters frees one from the torments of death. The river crosses several states such as Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Delhi. It also meets several tributaries along the way, including Ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Grove
Sacred groves, sacred woods, or sacred forests are groves of trees that have special religious importance within a particular culture. Sacred groves feature in various cultures throughout the world. These are forest areas that are, for the most part, untouched by local people and often protected by local communities. They often play a critical role in protecting water sources and biodiversity, including essential resources for the groups that protect them. They were important features of the mythological landscape and cult practice of Celtic, Estonian, Baltic, Germanic, ancient Greek, Near Eastern, Roman, and Slavic polytheism. They are also found in locations such as India (Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu), Japan ( sacred shrine forests), China ( Fengshui woodland), West Africa and Ethiopia ( church forests). Examples of sacred groves include the Greco-Roman '' temenos'', various Germanic words for sacred groves, and the Celtic '' nemeton'', which was la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangar Bani
Mangar Bani is a Paleolithic archaeological site and sacred grove hill forest next to the Mangar village on Delhi-Haryana border. It lies in the South Delhi Ridge of Aravalli mountain range in Faridabad tehsil of Faridabad district in the Indian state of Haryana.Mangar Census of India 2011. It is to the immediate south of India's national capital , within the NCR. Mangar Bani is the Indian subcontinent's largest neolithic tool making site dating back to 100,000 years |
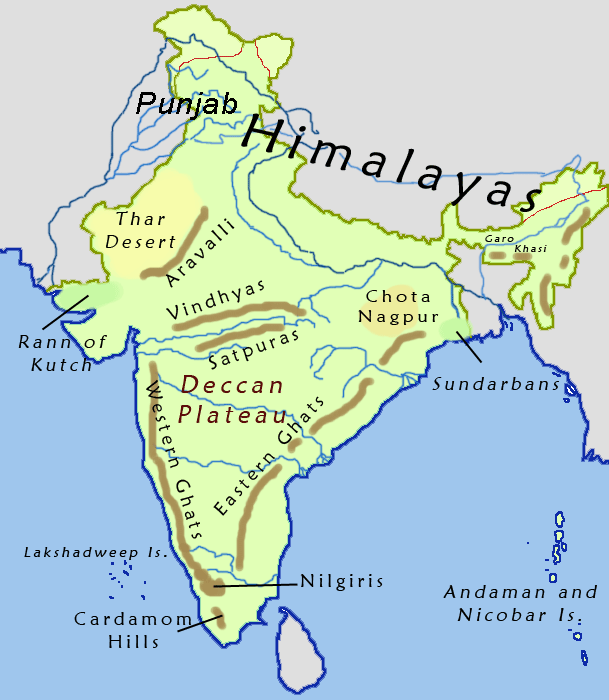
Aravalli Range
The Aravalli Range (also spelled ''Aravali'') is a mountain range in North India, Northern-Western India, running approximately in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana and Rajasthan, and ending in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. The highest peak is Guru Shikhar on Mount Abu at . The Aravalli Range is one of the oldest geological features on Earth, dating to the Proterozoic era. The Aravalli Range is rich in natural resources and serves to check the growth of the western desert. Etymology Aravalli, a composite Sanskrit word from the roots ''"ara"'' and ''"vali"'', literally means the ''"line of peaks"''. Natural history Geology The Aravalli Range, an eroded stub of ancient mountains, is believed to be the oldest range of fold mountains in India.Roy, A. B. (1990). Evolution of the Precambrian crust of the Aravalli Range. Developments in Precambrian Geology, 8, 327–347. The natural history of the Aravalli Range dates back to times when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivalik Hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas. The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and are also home to the Soanian Middle Paleolithic archaeological culture. Geography The Sivalik Hills are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. It is wide with an average elevation of . Between the Teesta and Raidāk Rivers in Assam is a gap of about . They are well known for their Neogene and Pleistocene aged vertebrate fossils. Geology Geologically, the Sivalik Hills belong to the Tertiary deposits of the outer Himalayas. They are chiefly composed of sandstone and conglomerate rock formations, which are the solidified detritus of the Himalayas to their north; they are poorly consolidated. The sedimentary rocks comprising the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Cover
Forest cover is the amount of trees that covers a particular area of land. It may be measured as relative (in percent) or absolute (in square kilometres/ square miles). Nearly a third of the world's land surface is covered with forest, with closed-canopy forest accounting for 4 - 5 billion hectares of land. Forests provide many ecosystem services that humans and animals cannot survive without, but anthropogenic actions and climate change are threatening global forest cover in potentially irreversible ways. Global patterns Forest cover by the numbers According to the FAO's Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, the world has a total forest area of 4.06 billion hectares (10.0 billion acres), which is 31% of the total land area. More than one-third of the world's forest cover is primary forest: naturally regenerated forests with native species and no visible indication of human activity. More than half (54%) of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |