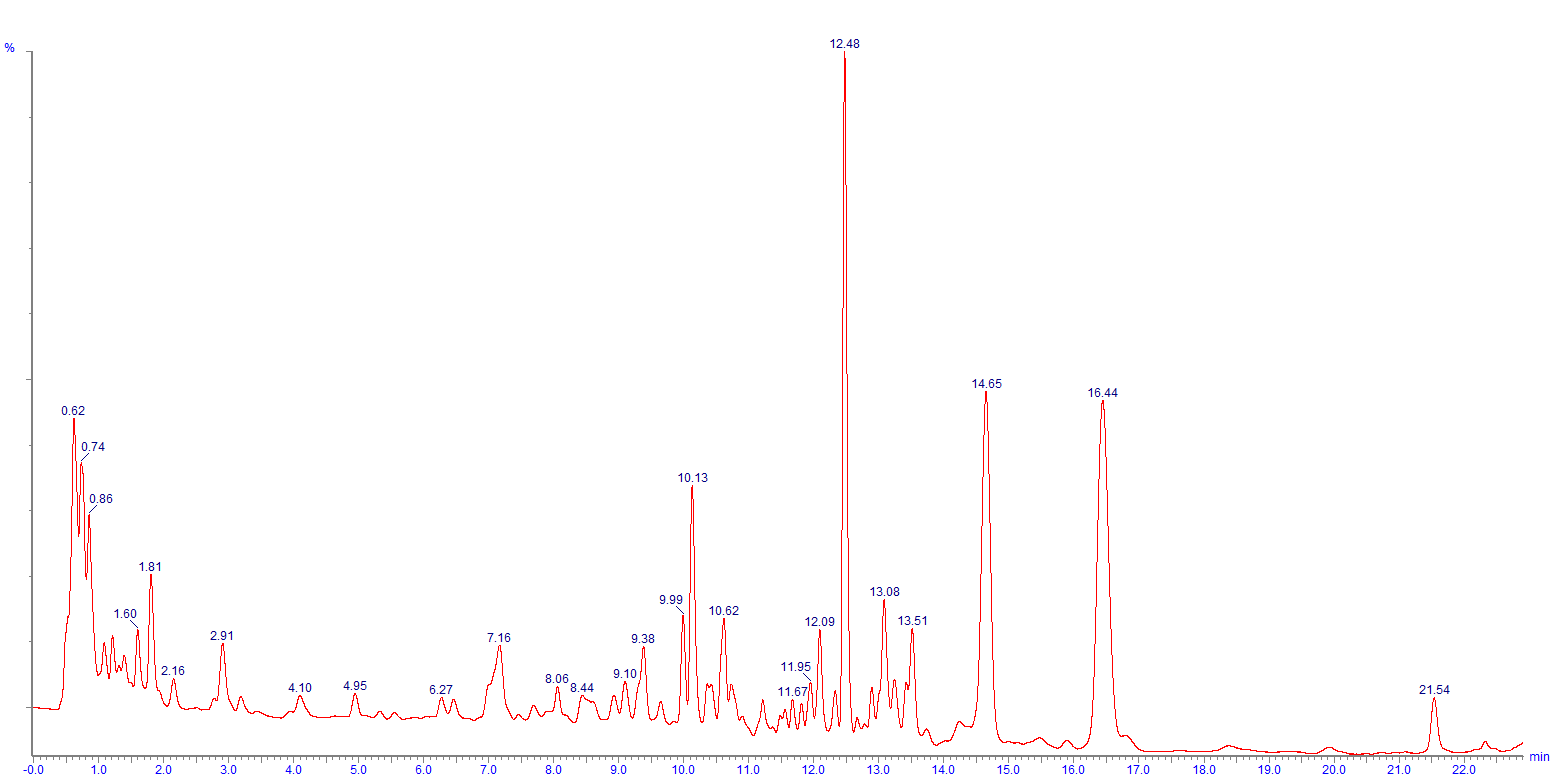
|
Flavonoid Rhamnosides
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into: *flavonoids or bioflavonoids *isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenyl chromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyrone) structure *neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarin (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyrone) structure The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavonoid have also been more loosely used to describe non-k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavon
Flavon is a ''frazione'' of the ''Communes of Trentino, comune'' (municipality) of Contà in Trentino in the northern Italy, Italian region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, located about north of Trento. It was an independent commune until 1 January 2016. References {{Authority control Frazioni of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' are methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, ''e.g.'', testosterone, and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered retained IUPAC names, although some introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonoids Biochemistry
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into: *flavonoids or bioflavonoids *isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenyl chromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyrone) structure *neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarin (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyrone) structure The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavonoid have also been more loosely used to describe non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalconoids
Chalconoids (Greek: χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper", due to its color), also known as chalcones, are natural phenols derived from chalcone. They form the central core for a variety of important biological compounds. They show antibacterial, antifungal, antitumor and anti-inflammatory properties. Some chalconoids demonstrated the ability to block voltage-dependent potassium channels. Chalcones are also natural aromatase inhibitors. Chalcones are aromatic ketones with two phenyl rings that are also intermediates in the synthesis of many biological compounds. The closure of hydroxy chalcones causes the formation of the flavonoid structure. Flavonoids are substances in the plant's secondary metabolism with an array of biological activities. Chalconoids are also intermediating in the Auwers synthesis of flavones. Biosynthesis and metabolism Chalcone synthase is an enzyme responsible for the production of chalconoids in plants. Chalcone isomerase is responsible for their c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neohesperidin
Neohesperidin is a flavanone glycoside found in citrus fruits. It is the 7-O- neohesperidose derivative of hesperetin, which in turn is the 4'-methoxy derivative of eriodictyol. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone has an intense sweet taste, and is listed as a generally recognized as safe Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) is a United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) designation that a chemical or substance added to food is considered safe by experts under the conditions of its intended use. An ingredient with a GRAS d ... flavour enhancer by the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association. References External links * {{Glycosides Flavanone glycosides Flavonoids found in Rutaceae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eriodictyol
Eriodictyol is a bitter-masking flavanone, a flavonoid extracted from yerba santa ('' Eriodictyon californicum''), a plant native to North America. Eriodictyol is one of the four flavanones identified in this plant as having taste-modifying properties, the other three being homoeriodictyol, its sodium salt, and sterubin. Eriodictyol has garnered scientific attention for its strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties. Structurally similar to other flavonoids, such as hesperidin and naringenin, eriodictyol scavenges free radicals and regulates inflammatory responses. Eriodictyol was also found in the twigs of '' Millettia duchesnei'', in '' Eupatorium arnottianum'', and its glycosides ( eriocitrin) in lemons and rose hips (''Rosa canina''). Eriodictyol belongs to the flavanone The flavanones, a type of flavonoids, are various aromatic, colorless ketones derived from flavone that often occur in plants as glycosides. List of flavanones * Blumeatin * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperidin
Hesperidin is a flavanone glycoside found in citrus fruits. Its aglycone is hesperetin. Its name is derived from the word "hesperidium", for fruit produced by citrus trees. Hesperidin was first isolated in 1828 by French chemist M. Lebreton from the white inner layer of citrus peels (mesocarp, albedo). Hesperidin is believed to play a role in plant defense. Sources ''Rutaceae'' * 700–2,500 ppm in fruit of ''Citrus aurantium'' (bitter orange, petitgrain) * in orange juice (''Citrus sinensis'') * in '' Zanthoxylum gilletii'' * in lemon * in lime * in leaves of '' Agathosma serratifolia'' ''Lamiaceae'' Peppermint contains hesperidin. Content in foods Approximate hesperidin content per 100 ml or 100 g * 481 mg peppermint, dried * 44 mg blood orange, pure juice * 26 mg orange, pure juice * 18 mg lemon, pure juice * 14 mg lime, pure juice * 1 mg grapefruit, pure juice Metabolism Hesperidin 6-''O''-α--rhamnosyl-β--glucosidase, an en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
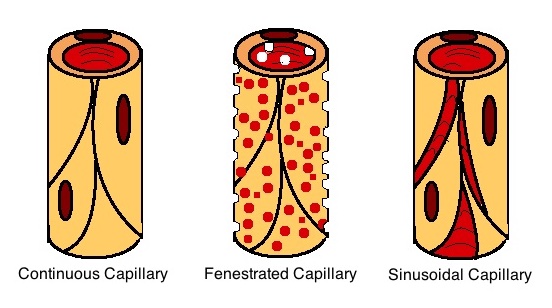
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease (state of malnutrition) resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, fatigue, and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding from the skin may occur. As scurvy worsens, there can be poor wound healing, personality changes, and finally death from infection or bleeding. It takes at least a month of little to no vitamin C in the diet before symptoms occur. In modern times, scurvy occurs most commonly in people with mental disorders, unusual eating habits, alcoholism, and older people who live alone. Other risk factors include intestinal malabsorption and Kidney dialysis, dialysis. While many animals produce their vitamin C, humans and a few others do not. Vitamin C, an antioxidant, is required to make the building blocks for collagen, carnitine, and catecholamines, and assists the intestines in the absorption of iron from foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription dietary supplement. As a therapy, it is used to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Vitamin C may be taken by mouth or by intramuscular, subcutaneous or intravenous injection. Various health claims exist on the basis that moderate vitamin C deficiency increases disease risk, such as for the common cold, cancer or COVID-19. There are also claims of benefits from vitamin C supplementation in excess of the recommended d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Szent-Györgyi
Albert Imre Szent-Györgyi de Rapoltu Mare, Nagyrápolt (; September 16, 1893 – October 22, 1986) was a Hungarian biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1937. He is credited with first isolating vitamin C and discovering many of the components and reactions of the citric acid cycle and the molecular basis of muscle contraction. He was also active in the Hungarian resistance movement, Hungarian Resistance during World War II, and entered Hungarian politics after the war. Early life Szent-Györgyi was born in Budapest, Kingdom of Hungary, on September 16, 1893. His father, Miklós Szent-Györgyi, was a landowner, born in Târgu Mureş, Marosvásárhely, Transylvania (today Târgu Mureş, Romania), a Calvinism, Calvinist, and could trace his ancestry back to 1608 when Sámuel, a Calvinist Wiktionary:predicant, predicant, was ennobled. At the time of Szent-Györgyi's birth, being of the nobility was considered important and created opportunities that o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phloroglucinol
Phloroglucinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a colorless solid. It is used in the organic synthesis, synthesis of pharmaceuticals and explosives. Phloroglucinol is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The other two isomers are hydroxyquinol (1,2,4-benzenetriol) and pyrogallol (1,2,3-benzenetriol). Phloroglucinol, and its benzenetriol isomers, are still defined as "natural phenol, phenols" according to the IUPAC official nomenclature rules of chemical compounds. Many such monophenolics are often termed polyphenols. The enzyme is biosynthesized by phloroglucinol synthase. Synthesis and occurrence In 1855, phloroglucinol was first prepared from phloretin by the Austrian chemist Heinrich Hlasiwetz (1825–1875). A modern synthesis of phloroglucinol involves hydrolysis of benzene-1,3,5-triamine and its derivatives. Representative is the following route from 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene, trinitrobenzene. : The synthesis is noteworthy because ordinary aniline deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |