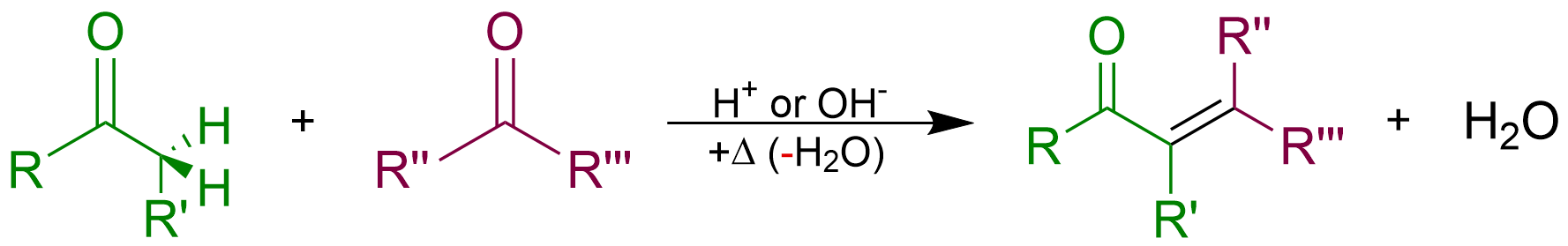|
Flavones
Flavones (from Latin ''flavus'' "yellow") are a class of flavonoids based on the backbone of 2-phenylchromen-4-one (2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one) (as shown in the first image of this article). Flavones are common in foods, mainly from spices, and some yellow or orange fruits and vegetables. Common flavones include apigenin (4',5,7-trihydroxyflavone), luteolin (3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone), tangeritin (4',5,6,7,8-pentamethoxyflavone), chrysin (5,7-dihydroxyflavone), and 6-hydroxyflavone. Intake and elimination The estimated daily intake of flavones is about 2 mg per day. Following ingestion and metabolism, flavones, other polyphenols, and their metabolites are absorbed poorly in body organs and are rapidly excreted in the urine, indicating mechanisms influencing their presumed absence of metabolic roles in the body. Drug interactions Flavones have effects on CYP (P450) activity, which are enzymes that metabolize most drugs in the body. Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into: *flavonoids or bioflavonoids *isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenylchromone, chromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyran, benzopyrone) structure *neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarin (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyran, benzopyrone) structure The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavon Num
Flavon is a ''frazione'' of the ''comune'' (municipality) of Contà in Trentino in the northern Italian region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, located about north of Trento Trento ( or ; Ladin language, Ladin and ; ; ; ; ; ), also known in English as Trent, is a city on the Adige, Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the Trentino, autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th .... It was an independent commune until 1 January 2016. References {{Authority control Frazioni of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luteolin
Luteolin is a flavone, a type of flavonoid, with a yellow crystalline appearance. Luteolin is the main yellow dye from the '' Reseda luteola'' plant, used for dyeing since at least the first millennium B.C. Luteolin was first isolated in pure form, and named, in 1829 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. The luteolin empirical formula was determined by the Austrian chemists Heinrich Hlasiwetz and Leopold Pfaundler in 1864. In 1896, the English chemist Arthur George Perkin proposed the correct structure for luteolin. Perkin's proposed structure for luteolin was confirmed in 1900 when the Polish-Swiss chemist Stanislaw Kostanecki (1860–1910) and his students A. Różycki and J. Tambor synthesized luteolin. Natural occurrences Luteolin is most often found in leaves, but it is also present in rinds, barks, clover blossoms, and ragweed pollen. It has also been isolated from the aromatic flowering plant, ''Salvia tomentosa'' in the mint family, ''Lamiaceae''. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangeritin
Tangeretin is an O- polymethoxylated flavone that is found in tangerine and other citrus ''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the family Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. ''Citrus'' is nativ ... peels. Tangeretin strengthens the cell wall and acts as a plant's defensive mechanism against disease-causing pathogens.Uckoo, RM; et al. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011. It has also been used as a marker compound to detect contamination in citrus juices. The following is a list of methods used to extract tangeretin from citrus peels: * column chromatography * preparative-high performance liquid chromatography * super critical fluid chromatography * high speed counter current chromatography * a combination of vacuum flash silica gel chromatography and flash C8 column chromatography * flash chromatography * isolation using ionic liquids and a cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Coumarate-CoA Ligase
In enzymology, a 4-coumarate—CoA ligase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :ATP + 4-coumarate + CoA \rightleftharpoons AMP + diphosphate + 4-coumaroyl-CoA The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, 4-coumarate, and CoA, whereas its 3 products are AMP, diphosphate, and 4-coumaroyl-CoA. This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, to be specific those forming carbon-sulfur bonds as acid-thiol ligases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (AMP-forming). Other names in common use include 4-coumaroyl-CoA synthetase, ''p''-coumaroyl CoA ligase, ''p''-coumaryl coenzyme A synthetase, ''p''-coumaryl-CoA synthetase, ''p''-coumaryl-CoA ligase, feruloyl CoA ligase, hydroxycinnamoyl CoA synthetase, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase, caffeoyl coenzyme A synthetase, ''p''-hydroxycinnamoyl coenzyme A synthetase, feruloyl coenzyme A synthetase, sinapoyl coenzyme A synthetase, 4-coumaryl-CoA synthetase, hydroxycinnamate:CoA ligase, ''p''-coumaryl- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase
In enzymology, a trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :trans-cinnamate + NADPH + H+ + O2 \rightleftharpoons 4-hydroxycinnamate + NADP+ + H2O The 4 substrates of this enzyme are trans-cinnamate, NADPH, H+, and O2, whereas its 3 products are 4-hydroxycinnamate, NADP+, and H2O. This enzyme participates in phenylalanine metabolism and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. It employs one cofactor, heme. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on paired donors, with O2 as oxidant and incorporation or reduction of oxygen. The oxygen incorporated need not be derived from O2 with NADH or NADPH as one donor, and incorporation of one atom o oxygen into the other donor. Nomenclature The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-Coumaric Acid
''p''-Coumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CH=CHCO2H. It is one of the three isomers of coumaric acid. It is a white solid that is only slightly soluble in water but very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether. Natural occurrences It is a precursor to many natural products, especially Monolignol, lignols, precursors to the woody mass that comprise many plants. Of the myriad occurrences, ''p''-coumaric acid can be found in ''Gnetum cleistostachyum''. In food ''p''-Coumaric acid can be found in a wide variety of edible plants and fungi such as peanuts, navy beans, tomatoes, carrots, basil and garlic. It is found in wine and vinegar. It is also found in barley grain. ''p''-Coumaric acid from pollen is a constituent of honey. Derivatives p-Coumaric acid glucoside, ''p''-Coumaric acid glucoside can also be found in commercial breads containing flaxseed. Diesters of ''p''-coumaric acid can be found in carnauba wax. Biosynthesis It is biosynthesized from c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the Fatty acid metabolism#Synthesis, synthesis and Fatty acid metabolism#.CE.B2-Oxidation, oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvic acid, pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a Substrate (chemistry), substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenic acid, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In acetyl-CoA, its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the Anabolism, anabolic and Catabolism, catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of Pyruvic acid, pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylate
In organic chemistry, a carboxylate is the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid, (or ). It is an anion, an ion with negative charge. Carboxylate salts are salts that have the general formula , where M is a metal and ''n'' is 1, 2,.... Carboxylate esters have the general formula (also written as ), where R and R′ are organic groups. Synthesis Carboxylate ions can be formed by deprotonation of carboxylic acids. Such acids typically have p''K''a of less than 5, meaning that they can be deprotonated by many bases, such as sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate. : Resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion Carboxylic acids easily dissociate into a carboxylate anion and a positively charged hydrogen ion (proton), much more readily than alcohols do (into an alkoxide ion and a proton), because the carboxylate ion is stabilized by resonance. The negative charge that is left after deprotonation of the carboxyl group is delocalized between the two electronegat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reactions
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coumaroyl-CoA
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids. Biosynthesis and significance It is generated in nature from phenylalanine, which is converted by PAL to trans- cinnamate. Trans-cinnamate is hydroxylated by trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase to give 4-hydroxycinnamate (i.e, coumarate). Coumarate is condensed with coenzyme-A in the presence of 4-coumarate-CoA ligase: :ATP + 4-coumarate + CoA \rightleftharpoons AMP + diphosphate + 4-coumaroyl-CoA. Enzymes using Coumaroyl-Coenzyme A * Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6''-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase * Anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase * Chalcone synthase Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcone Synthase
Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ubiquitous to higher plants and belongs to a family of polyketide synthase enzymes (PKS) known as type III PKS. Type III PKSs are associated with the production of chalcones, a class of organic compounds found mainly in plants as natural defense mechanisms and as synthetic intermediates. CHS was the first type III PKS to be discovered. It is the first committed enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to naringenin chalcone. Function CHS catalysis serves as the initial step for flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are important plant secondary metabolites that serve various functions in higher plants. These include pigmentation, UV protection, fertility, antifungal defense and the recruitment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. CHS is believed to act as a central hub for the enzymes involved in the flavonoid pathway. Studies have shown that these enzymes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |