|
Flannel
Flannel is a soft woven fabric, of varying fineness. Flannel was originally made from carded wool or worsted yarn, but is now often made from either wool, cotton, or synthetic fiber. Flannel is commonly used to make tartan clothing, blankets, bed sheets, sleepwear, and several other uses. Flannel may be brushed to create extra softness or remain unbrushed. Brushing is a mechanical process wherein a fine metal brush rubs the fabric to raise fine fibres from the loosely spun yarns to form a nap on one or both sides. If the flannel is not napped, it gains its softness through the loosely spun yarn in its woven form. The term "flannel shirt" is often mistakenly used to refer to any shirt with a plaid or tartan pattern. However, 'flannel' refers simply to the fabric; not all flannel shirts are plaid and not all plaid shirts are flannel. History The word's origin is uncertain, but a Welsh origin has been suggested as fabric similar to flannel can be traced back to Wales, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
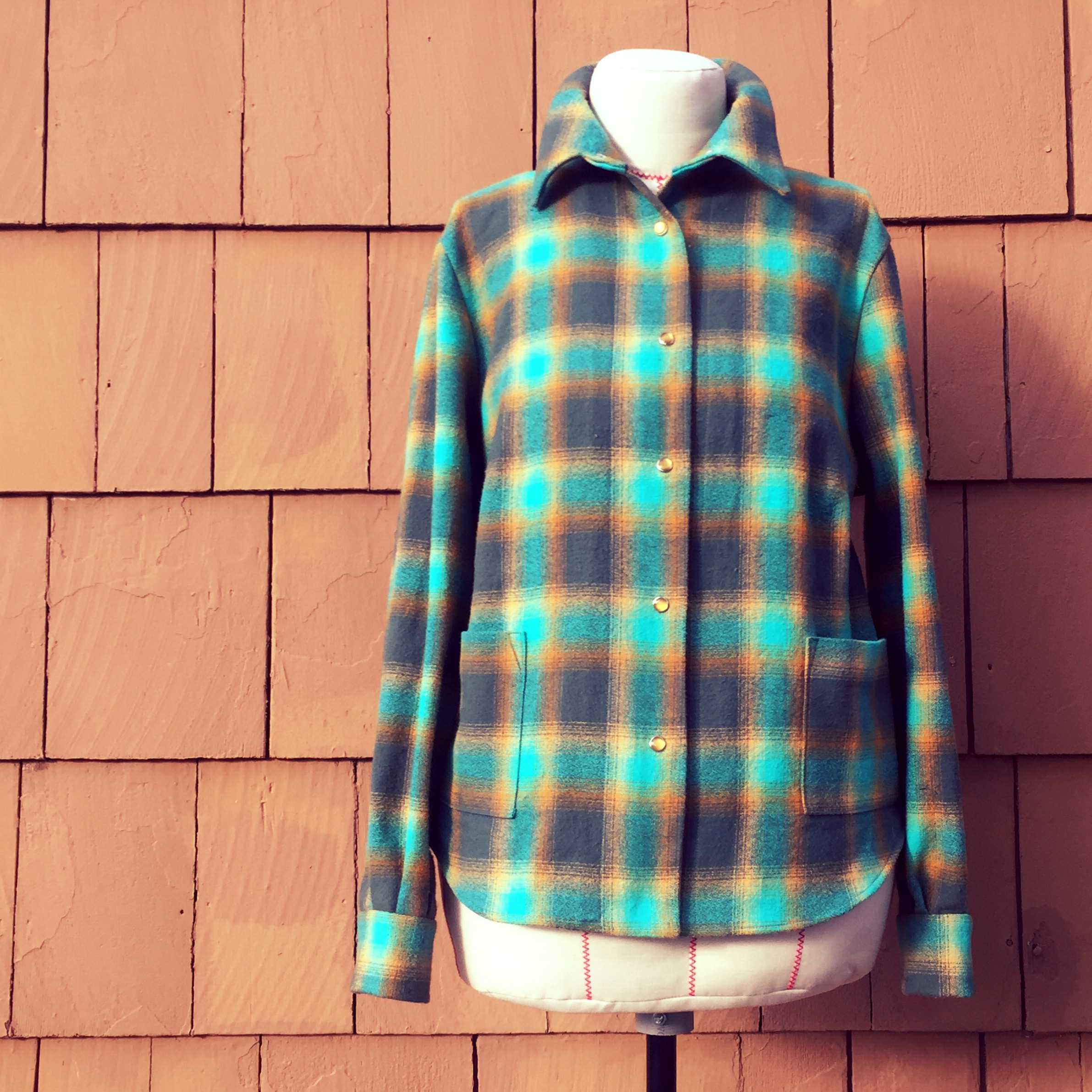
Flannel Shirt For Abi
Flannel is a soft #Weave, woven fabric, of varying fineness. Flannel was originally made from carding, carded wool or worsted yarn, but is now often made from either wool, cotton, or synthetic fiber. Flannel is commonly used to make tartan clothing, blankets, bed sheets, sleepwear, and several other uses. Flannel may be brushed to create extra softness or remain unbrushed. Brushing is a mechanical process wherein a fine metal brush rubs the fabric to raise fine fibres from the loosely spun yarns to form a nap (textile), nap on one or both sides. If the flannel is not napped, it gains its softness through the loosely spun yarn in its woven form. The term "flannel shirt" is often mistakenly used to refer to any shirt with a Plaid (pattern), plaid or tartan pattern. However, 'flannel' refers simply to the fabric; not all flannel shirts are plaid and not all plaid shirts are flannel. History The word's origin is uncertain, but a Welsh origin has been suggested as fabric similar to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanidloes
Llanidloes () is a town and community on the A470 and B4518 roads in Powys, within the historic county boundaries of Montgomeryshire (), Wales. The population in 2011 was 2,929, of whom 15% could speak Welsh. It is the third largest settlement in Montgomeryshire, after Newtown and Welshpool. It is the first town on the River Severn (), counting from the source. The town's Member of Parliament is Steve Witherden of the Labour Party (MP since 2024) and its Member of the Senedd is Russell George of the Conservatives (MS since 2011). Surroundings The town is close to the large dam and reservoir Llyn Clywedog. There is a scenic mountain road connecting Machynlleth and Llanidloes. Llanidloes is popular with hikers who walk on the scenic footpaths surrounding the town, including Glyndŵr's Way, which in conjunction with the Offa's Dyke path forms a 160-mile circuit around Mid Wales and local passage over the spine of the Cambrian Mountains. The Sarn Sabrina Walk – a 25 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nap (textile)
Primarily, nap is the raised (fuzzy) surface on certain kinds of cloth, such as velvet or moleskin. Nap can refer additionally to other surfaces that look like the surface of a napped cloth, such as the surface of a felt or beaver hat. Starting around the 14th century, the word referred originally to the roughness of woven cloth before it was sheared."nap". ''The Oxford English Dictionary''. 2nd ed. 1989. When cloth, especially woollen cloth, is woven, the surface of the cloth is not smooth, and this roughness is the nap. Generally the cloth is then "sheared" to create an even surface, and the nap is thus removed. A person who trimmed the surface of cloth with shears to remove any excess nap was known as a shearman. Nap typically has a direction in which it feels smoothest. In garments, nap direction is often matched across seams, because cloth will not only feel but look different depending on the direction of the nap. For this reason, sewing patterns frequently show the nap d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woollen Industry In Wales
The woollen industry in Wales was at times the country's most important industry, though it often struggled to compete with the better-funded woollen mills in the north of England, and almost disappeared during the 20th century. There is continued demand for quality Welsh woollen products. Wool processing includes removing the fleece by shearing, classing the wool by quality, untangling, carding and spinning it into yarn, which may be knitted or woven into cloth, then finishing the cloth by fulling, napping and pressing. Spinning and weaving of sheep's wool dates to prehistoric times in Wales, but only became an important industry when Cistercian monasteries were established in the 12th century. Water-powered fulling mills to finish the cloth enabled rapid expansion of the industry in the 13th century, although spinning and weaving continued to be a cottage industry. In the early 16th century, production shifted from south Wales to mid and north Wales. The Shrewsbury Drapers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drapers Company Of Shrewsbury
The Shrewsbury Drapers Company was a trade organisation founded in 1462 in the town of Shrewsbury, Shropshire, England. The members were wholesale dealers in wool and later woollen cloth. The Company dominated the trade in Welsh cloth and in 1566 was given a regional monopoly in the Welsh Wool trade. In the seventeenth century the trade had difficulties particularly during the English Civil war and then further declined in the eighteenth century with the industrialisation of cloth production and the improvement of transport infrastructure. This made it practical for merchants from Liverpool and elsewhere to travel into Wales and purchase cloth directly from the producers. The Reform Acts of the early nineteenth century took away the power of the trade guilds and the trade ceased. Since that time the Shrewsbury Drapers Company has survived and continues as a charity that runs almshouses in Shrewsbury. ''Please note'' ''The image shown in the infobox on the right is not Drapers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaid (pattern)
Tartan or plaid ( ) is a patterned cloth consisting of crossing horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours, forming repeating symmetrical patterns known as ''setts''. Originating in woven wool, tartan is most strongly associated with Scotland, where it has been used for centuries in traditional clothing such as the kilt. Historically, specific tartans were linked to Scottish clans, families, or regions, with patterns and colours derived from local dyes. The earliest surviving samples of tartan-style cloth are around 3,000 years old and were discovered in Xinjiang, China. Tartan became a symbol of Scottish identity, especially from the 16th century onward, despite bans following the Jacobite rising of 1745 under the Dress Act 1746. The 19th-century Highland Revival popularized tartan globally, associating it with Highland dress and the Scottish diaspora. Today, tartan is used worldwide in clothing, accessories, and design, transcending its traditional roots. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
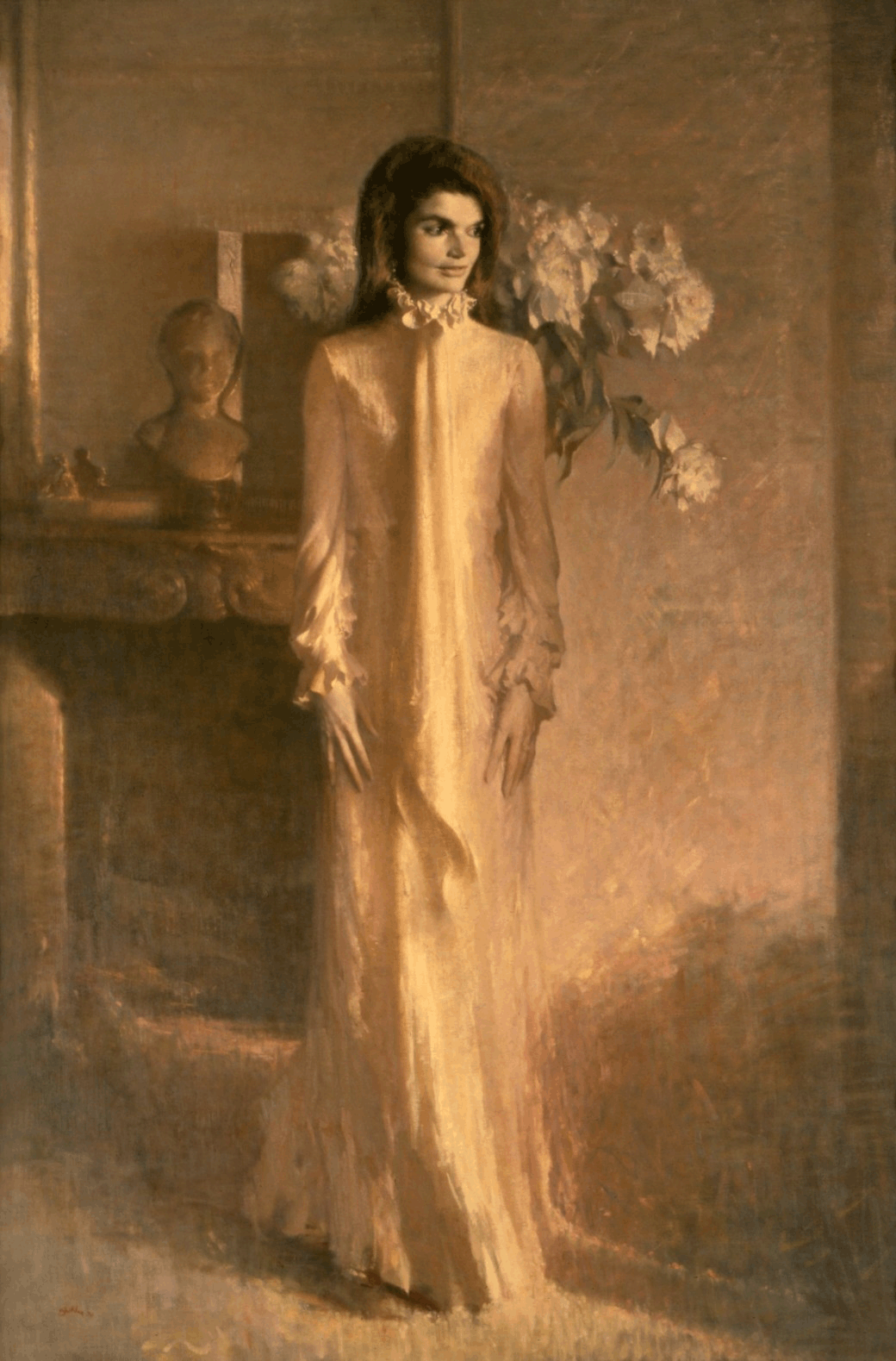
Sybil Connolly
Sybil Connolly (24 January 1921 – 6 May 1998) was a celebrated fashion designer and global icon known for her innovative use of traditional Irish textiles in haute couture. Often described as "Dublin's Dior", she achieved international repute and success, making her one of the first Irish designers to do so. She was a member of the "Big Three" Irish fashion designers (along with Irene Gilbert and Raymond Kenna/Kay Peterson), and was described by former Taoiseach (prime minister) Jack Lynch as "a national treasure." She worked with brands such as Tiffany & Co. and Bloomingdale's. Among her fashion label's famous clients were American First Lady and style icon Jacqueline Kennedy, Elizabeth Taylor, the Rockefellers, and the Mellons. Her activities were covered in both the fashion press and the social columns of publications such as the ''Hollywood Reporter''. Described by Bettina Ballard, the influential editor of American ''Vogue'', as a "personable milk-skinned Irish charm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washer Woman Skirt 1957 By Sybil Connolly
Washer most commonly refers to: *Washer (hardware), a thin usually disc-shaped plate with a hole in the middle typically used with a bolt or nut *Washing machine, for cleaning clothes Washer may also refer to: *Dishwasher, a machine for cleaning dishware, cookware and cutlery * Dishwasher (occupation), a person who cleans dishware, cookware and cutlery *Washer, a person with obsessive-compulsive disorder who washes her/his hands compulsively * Washer method, a mathematical formula for finding volume * Washer pitching, an outdoor game involving tossing discs at a target People with the surname * Arthur Washer (1855–1910), New Zealand cricketer * Buck Washer (1882–1955), American baseball pitcher * Jean Washer (1894–1972), Belgian tennis player *Mal Washer (born 1945), Australian politician * Paul Washer (born 1961), American Christian preacher *Philippe Washer (1924–2015), Belgian tennis player and son of Jean Washer * Thomas Washer, Virginia colonist and politician in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newtown, Montgomeryshire
Newtown () is a town in Powys, Wales. It lies on the River Severn in the community of Newtown and Llanllwchaiarn, within the historic boundaries of Montgomeryshire. It was designated a new town in 1967 and saw population growth as firms settled, changing its market town character. Its 2001 population of 10,780 rose to 11,357 in the 2011 census, and rose again to 11,362 in the 2021 census. Newtown was the birthplace of Robert Owen in 1771, whose house stood on the present site of the HSBC Bank.BiographRetrieved 15 September 2018./ref> The town has a theatre, Theatr Hafren,Theatre sitRetrieved 15 September 2018./ref> and a public gallery, Oriel Davies, displaying contemporary arts and crafts.Gallery sitRetrieved 15 September 2018./ref> It is the largest town in Powys and Mid Wales. Etymology The ancient parish and commote are named Cedewain, and Newtown was home to a Llan dedicated to St Mary. As such, the first recorded name for the town was Llanfair-yng-Nghedewain. Both the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staple (wool)
A wool staple is a cluster or lock of wool fibres and not a single fibre. For other textiles, the staple, having evolved from its usage with wool, is a measure of the quality of the fibre with regard to its length or fineness. Etymology Of uncertain origin but possibly a back-formation arising because part of the business of a wool-stapler was to sort and class the wool according to quality. Staple strength Staple strength is calculated as the force required to break per unit staple thickness, expressed as newtons per kilotex. The staple strength of wool is one of the major determining factors of the sale price of greasy wool. Virtually all fleece and better grade wool skirtings sold at auction in Australia are objectively measured prior to the sale with the average results printed in a catalogue. At least 40 staples must be measured to in order to conform to the Australian Standard. Wools under 30 newtons per kilotex are considered tender. Currently wools over 40 newtons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulling
Fulling, also known as tucking or walking ( Scots: ''waukin'', hence often spelt waulking in Scottish English), is a step in woollen clothmaking which involves the cleansing of woven cloth (particularly wool) to eliminate ( lanolin) oils, dirt, and other impurities, and to make it shrink by friction and pressure. The work delivers a smooth, tightly finished fabric that is insulating and water-repellent. Well-known examples are duffel cloth, first produced in Flanders in the 14th century, and loden, produced in Austria from the 16th century on. Waulking could be done with the hands and feet. In medieval Europe, it was done in water-powered fulling mills. After the Industrial Revolution, coal and electric power were used. Felting refers more generally to the interlocking of loose wool fibers; they need not be spun and woven first. Process Fulling involves two processes: scouring (cleaning) and milling (thickening). Removing the oils encourages felting, and the cloth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |