|
Fixed-point Ocean Observatory
A fixed-point ocean observatory is an ocean observing autonomous system of automatic sensors and samplers that continuously gathers data from deep sea, water column and lower atmosphere, and transmits the data to shore in real or near real-time. Infrastructure Fixed-point ocean observatories are typically composed of a cable anchored to the sea floor to which several automatic sensors and samplers are attached. The cable ends with a buoy at the ocean surface that may have some more sensors attached. Most observatories have communicating buoys that transmit data to shore, and which allow changes to the acquisition method of the sensors, as required. These unmanned platforms can be linked via a cable to the shore transmitting data via an internet connection, or they can transmit data to relay buoys which are able to provide a satellite link to the shore. An example for a network of observatories is the Ocean Observatories Initiative. Instrumentation A typical multi-disciplinar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
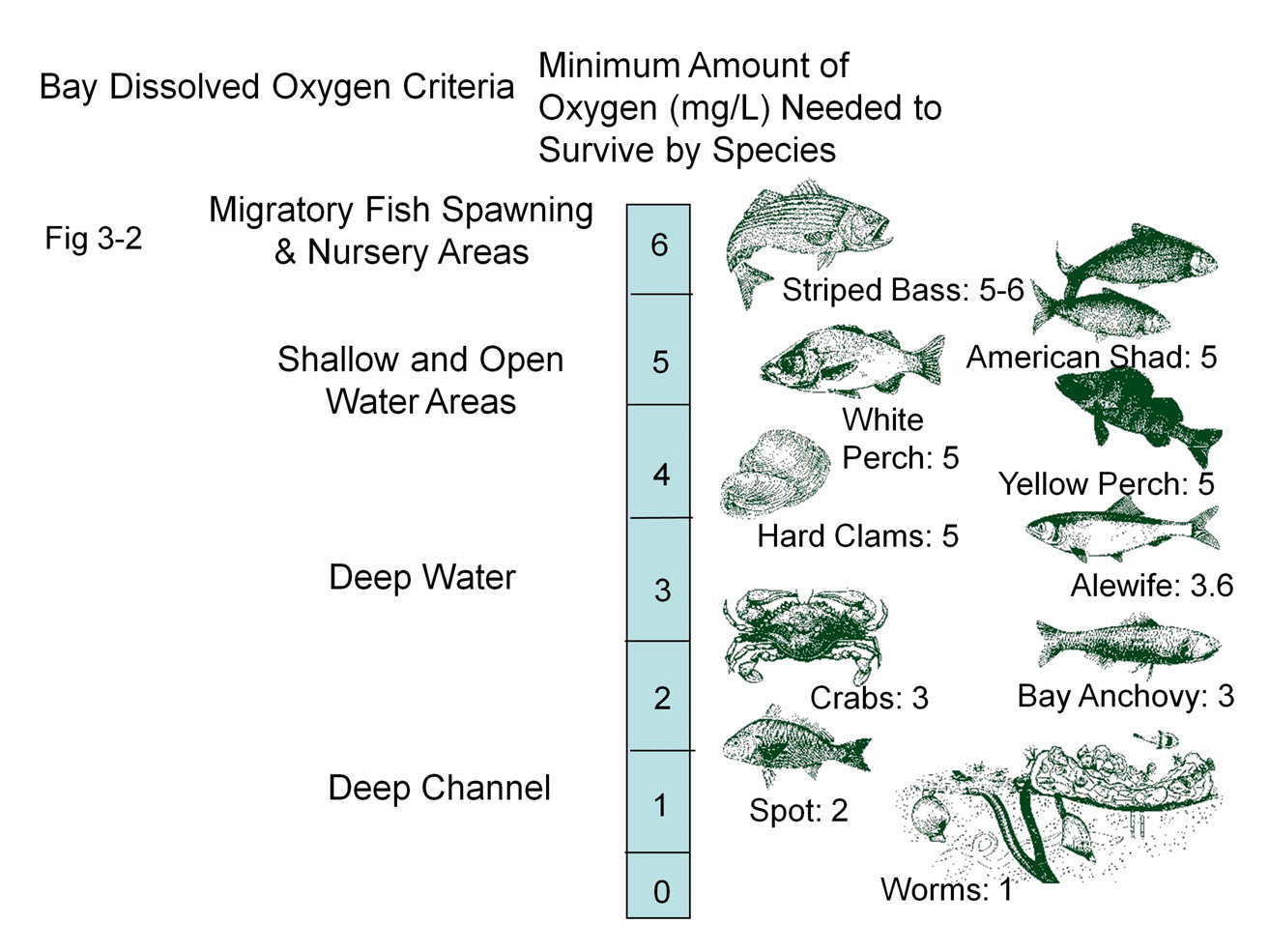
Dissolved Oxygen
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water. The standard unit of oxygen saturation is percent (%). Oxygen saturation can be measured regionally and noninvasively. Arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is commonly measured using pulse oximetry. Tissue saturation at peripheral scale can be measured using NIRS. This technique can be applied on both muscle and brain. In medicine In medicine, oxygen saturation refers to ''oxygenation'', or when oxygen molecules () enter the tissues of the body. In this case blood is oxygenated in the lungs, where oxygen molecules travel from the air into the blood. Oxygen saturation (() sats) measures the percentage of hemoglobin bindin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismometer
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground displacement and shaking such as caused by quakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output of such a device—formerly recorded on paper (see picture) or film, now recorded and processed digitally—is a ''seismogram''. Such data is used to locate and characterize earthquakes, and to study the internal structure of Earth. Basic principles A simple seismometer, sensitive to up-down motions of the Earth, is like a weight hanging from a spring, both suspended from a frame that moves along with any motion detected. The relative motion between the weight (called the mass) and the frame provides a measurement of the vertical ground motion. A rotating drum is attached to the frame and a pen is attached to the weight, thus recording any ground motion in a seismogram. Any movement from the ground moves the frame. The mass tends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camera
A camera is an instrument used to capture and store images and videos, either digitally via an electronic image sensor, or chemically via a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. As a pivotal technology in the fields of photography and videography, cameras have played a significant role in the progression of visual arts, media, entertainment, surveillance, and scientific research. The invention of the camera dates back to the 19th century and has since evolved with advancements in technology, leading to a vast array of types and models in the 21st century. Cameras function through a combination of multiple mechanical components and principles. These include exposure control, which regulates the amount of light reaching the sensor or film; the lens, which focuses the light; the viewfinder, which allows the user to preview the scene; and the film or sensor, which captures the image. Several types of camera exist, each suited to specific uses and offering unique cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment Trap
Sediment traps are instruments used in oceanography and limnology to measure the quantity of sinking particulate Organic material, organic (and inorganic) material in aquatic ecosystem, aquatic systems, usually oceans, Lake, lakes, or Reservoir, reservoirs. This flux of material is the product of biology, biological and ecology, ecological processes typically within the surface euphotic zone, and is of interest to scientists studying the role of the biological pump in the carbon cycle. Sediments traps normally consist of an upward-facing funnel that directs sinking Particulates, particulate matter (e.g. marine snow) towards a mechanism for collection and preservation. Typically, traps operate over an extended period of time (weeks to months) and their collection mechanisms may consist of a series of sampling vessels that are cycled through to allow the trap to record the changes in sinking flux with time (for instance, across a season, seasonal cycle). Preservation of collecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophone
A hydrophone () is a microphone designed for underwater use, for recording or listening to underwater sound. Most hydrophones contains a piezoelectric transducer that generates an electric potential when subjected to a pressure change, such as a sound wave. A hydrophone can also detect airborne sounds but is insensitive of them because it is designed to match the acoustic impedance of water, a denser fluid than air. Sound travels 4.3 times faster in water than in air, and a sound wave in water exerts a pressure 60 times more than what is exerted by a wave of the same amplitude in air. Similarly, a standard microphone can be buried in the ground, or immersed in water if it is put in a waterproof container but will give poor performance because of the similarly-bad acoustic impedance match. History The first hydrophones consisted of a tube with a thin membrane covering the submerged end and the observer's ear of the equipment. The design of effective hydrophones must take into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTD (instrument)
CTD stands for ''conductivity'', ''temperature'', and ''depth''. A ''CTD'' instrument is an oceanography ''sonde'' (French for probe) used to measure the electrical conductivity, temperature, and pressure of seawater. The ''pressure'' is closely related to ''depth''. ''Conductivity'' is used to determine salinity. The CTD may be incorporated into an array of Nansen bottle, Niskin bottles referred to as a carousel or Rosette sampler, rosette. The sampling bottles close at predefined depths, triggered either manually or by a computer, and the water samples may subsequently be analyzed further for biological and chemical parameters. The CTD may also be used for the calibration of sensors. Measured properties The instrument is a cluster of sensors which measure conductivity, temperature, and pressure. Sensors commonly scan at a rate of 24 Hz. Depth measurements are derived from measurement of hydrostatic pressure, and salinity is measured from electrical conductivity. Sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler
An acoustic doppler current profiler (ADCP) is a hydroacoustic current meter similar to a sonar, used to measure water current velocities over a depth range using the Doppler effect of sound waves scattered back from particles within the water column. The term ADCP is a generic term for all acoustic current profilers, although the abbreviation originates from an instrument series introduced by RD Instruments in the 1980s. The working frequencies range of ADCPs range from 38 kHz to several megahertz. A similar device is a ''SODAR'', which works in the air and uses the same principles for wind speed profiling. Working principle ADCPs contain piezoelectric transducers to transmit and receive sound signals. The traveling time of sound waves gives an estimate of the distance. The frequency shift of the echo is proportional to the water velocity along the acoustic path. To measure 3D velocities, at least three beams are required. In rivers, only the 2D velocity is relevant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolved Oxygen
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water. The standard unit of oxygen saturation is percent (%). Oxygen saturation can be measured regionally and noninvasively. Arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is commonly measured using pulse oximetry. Tissue saturation at peripheral scale can be measured using NIRS. This technique can be applied on both muscle and brain. In medicine In medicine, oxygen saturation refers to ''oxygenation'', or when oxygen molecules () enter the tissues of the body. In this case blood is oxygenated in the lungs, where oxygen molecules travel from the air into the blood. Oxygen saturation (() sats) measures the percentage of hemoglobin bindin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Partial Pressure
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |