|
Fish Physiology
Fish physiology is the scientific study of how the component parts of fish function together in the living fish. It can be contrasted with fish anatomy, which is the study of the form or Morphology (biology), morphology of fishes. In practice, fish anatomy and physiology complement each other, the former dealing with the structure of a fish, its organs or component parts and how they are put together, such as might be observed on the dissecting table or under the microscope, and the latter dealing with how those components function together in the living fish. Respiration Most fish exchange gases using gills on either side of the pharynx (throat). Gills are tissues which consist of threadlike structures called Protein filament, filaments. These filaments have many functions and "are involved in ion and water transfer as well as oxygen, carbon dioxide, acid and ammonia exchange. Each filament contains a capillary network that provides a large surface area for exchanging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccal Cavity
The buccal space (also termed the buccinator space) is a fascial space of the head and neck (sometimes also termed fascial tissue spaces or tissue spaces). It is a potential space in the cheek, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle and deep to the platysma muscle and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe. Structure Boundaries The boundaries of each buccal space are: * the angle of the mouth anteriorly, * the masseter muscle posteriorly, * the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the zygomaticus muscles superiorly, * the depressor anguli oris muscle and the attachment of the deep fascia to the mandible inferiorly, * the buccinator muscle medially (the buccal space is superficial to the buccinator), * the platysma muscle, subcutaneous tissue and skin laterally (the space is deep to platysma). Communications * to the pterygomandibular space, infratemporal space, submasseter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourami
Gouramis, or gouramies , are a group of fresh water, freshwater Anabantiformes, anabantiform fish that comprise the family (biology), family Osphronemidae. The fish are native to Asia—from the Indian Subcontinent to Southeast Asia and northeasterly towards Korea. The name "gourami", of Indonesian language, Indonesian origin from Sundanese language, Sundanese word the name "gurame", is also used for fish of the families Helostomatidae and Anabantidae. Many gouramis have an elongated, feeler-like ray at the front of each of their pelvic fins. All living species show parental care until fry are free swimming: some are mouthbrooders, like the Krabi mouth-brooding betta (''Betta simplex''), and others, like the Siamese fighting fish (''Betta splendens''), build bubble nests. Currently, about 133 species are recognised, placed in four subfamilies and about 15 Genus, genera. The name Polyacanthidae has also been used for this family. Some fish now classified as gouramis were previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers", with some seemingly not having them. Siluriformes as a whole are Fish scale, scale-less, with neither the Armoured catfish, armour-plated nor the naked species having scales. This order of fish are Autapomorphy, defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish range in size and behavior from the three List of largest fish, largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivorous and scavenging bottom feeders, down to tiny ectoparasitic species known as the Candiru (fish), candirus. In the Southern United States, catfish species may be known by a variety of slang names, such as "mud cat", " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrinidae
The Erythrinidae are a family of fishes found in rivers and other freshwater habitats from Costa Rica south as far as Argentina. They are common and are caught with hooks by fishermen, partially because of their voracious behaviour. They are sometimes called ''trahiras'' (also spelled trairas) or ''tarariras''. The Erythrinidae include cylindrical fish with blunt heads, and prey on other fish. They can reach lengths up to . Some species can breathe air, enabling them to survive in water low in oxygen, and even to move over land between ponds. The earliest definitive remains of the family are of '' Hoplias'' from the Middle Miocene of Colombia. Potential fossil remains are known from the Early Paleocene-aged Tenejapa-Lacandón Formation of Mexico. The three genera in this family appear to have diverged from one another over the Paleogene. However, most species within the family are relatively young, their evolution influenced by major tectonic changes in South America over the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypriniformes
Cypriniformes is an order of ray-finned fish, which includes many families and genera of cyprinid ( carps and their kin) fish, such as barbs, loaches, botias, and minnows (among others). Cypriniformes is an "order-within-an-order", placed under the superorder Ostariophysi—which is also made up of cyprinid, ostariophysin fishes. The order contains 11–12 families (with some authorities having listed as many as 23), over 400 genera, and more than 4,250 named species; new species are regularly described, and new genera are recognized frequently.Eschmeyer, W.N., Fong, J.D. (2015Species by family/subfamilyin the Catalog of Fishes, California Academy of Sciences (retrieved 2 July 2015) Cyprinids are most diverse in South and Southeast Asia and are entirely absent from Australia and South America.Nelson (2006) At 112 years old, the longest-lived cypriniform fish documented is the bigmouth buffalo. Their closest living relatives are the Characiformes ( characins, tetras a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
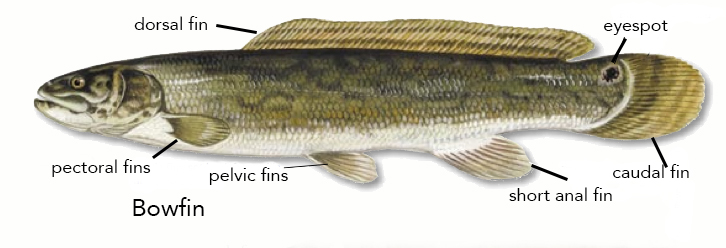
Bowfin
The ruddy bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a ray-finned fish native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being one of only two surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "living fossil" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. It is one of two species in the genus ''Amia,'' along with '' Amia ocellicauda'', the eyespot bowfin. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei. Bowfins are demersal freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once widespread in both freshwater and marine environments across North and South America, Europe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant and Extinction, extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn Evolution, evolving into two major clades, the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct pelycosaur, "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including Homo sapiens, humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming Limbless vertebrate, limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, Bipedidae, some lizards, kiwi (bird), kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
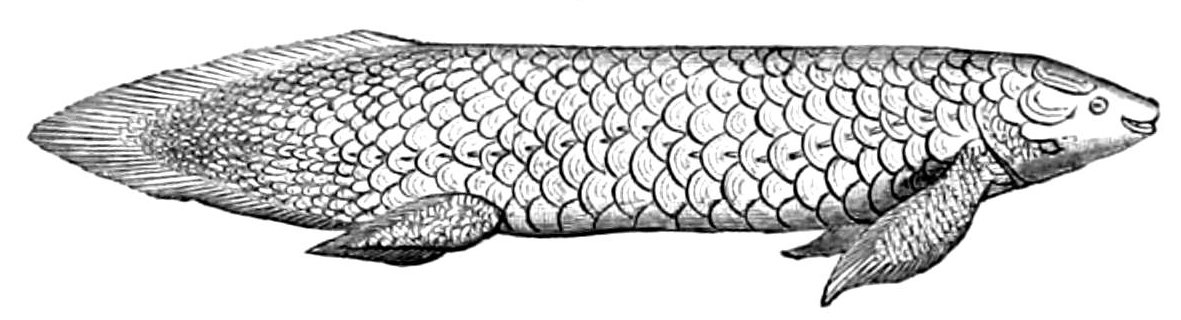
Bichir
Bichirs and the reedfish comprise Polypteridae , a family (biology), family of archaic Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes and the only family in the order (biology), order Polypteriformes .Helfman GS, Collette BB, Facey DE, Bowen BW. 2009. The Diversity of Fishes. West Sussex, UK: Blackwell Publishing. 720 p. All the species occur in freshwater habitats in tropical Africa and the Nile River system, mainly swampy, shallow floodplains and estuary, estuaries. Cladistia, polypterids and their fossil relatives, are considered the sister group to all other extant ray-finned fishes (Actinopteri).Dai Suzuki, Matthew C. Brandley, Masayoshi Tokita: ''CORRECTION: The mitochondrial phylogeny of an ancient lineage of ray-finned fishes (Polypteridae) with implications for the evolution of body elongation, pelvic fin loss, and craniofacial morphology in Osteichthyes.'' BMC Evolutionary Biology. Bd. 10, Art.-Nr. 209, 2010, They likely diverged from Actinopteri at least 330 million ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the class Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods (which includes living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals). The mouths of lungfish typically bear tooth plates, which are used to crush hard shelled organisms. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia, though they were formerly globally distributed. The fossil record of the group extends into the Early Devonian, over 410 million years ago. The earliest known members of the group were marine, while almost all post-Carboniferous representatives inhabit freshwater environments. Etymology Dipnoi is Modern Latin derived from the Greek δίπν ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copeia
''Ichthyology & Herpetology'' (formerly ''Copeia'') is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in ichthyology and herpetology that was originally named after Edward Drinker Cope, a prominent American researcher in these fields. It is the official journal of the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Copeia'' has a 2021 impact factor of 1.857, ranking it 65th out of 176 journals in the category "Zoology". History On December 27, 1913, John Treadwell Nichols published the first issue of ''Copeia''. This issue consisted of a single piece of paper folded to form four pages of information with five articles. The cover of the pamphlet bore the inscription: "Published by the contributors to advance the science of coldblooded vertebrates." In 2020, the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists voted to rename the journal, ''Ichthyology & Herpetology''. Name change The journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoloplacidae
''Scoloplax'' is the only genus in the catfish (order Siluriformes) family Scoloplacidae, the spiny dwarf catfishes. Species The six currently recognized species in this genus are: * '' Scoloplax baileyi'' Rocha, Lazzarotto & Rapp Py-Daniel, 2012Rocha, R., Lazzarotto, H. & Rapp Py-Daniel, L. (2012): A New Species of ''Scoloplax'' with a Remarkable New Tooth Morphology within Loricarioidea (Siluriformes: Scoloplacidae). ''Copeia, 2012 (4): 670–677.'' * '' Scoloplax baskini'' Rocha, de Oliveira & Rapp Py-Daniel, 2008 * '' Scoloplax dicra'' Bailey & Baskin, 1976 * '' Scoloplax distolothrix'' Schaefer, Weitzman & Britski, 1989 * '' Scoloplax dolicholophia'' Schaefer, Weitzman & Britski, 1989 * '' Scoloplax empousa'' Schaefer, Weitzman & Britski, 1989 (Pantanal dwarf catfish) Distribution ''Scoloplax'' is distributed in South America in Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay. ''S. baskini'' is from the small tributaries of Rio Aripuanã, Rio Madeira drainage, Amazon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |