|
First Navy Jack
The First Navy Jack was the Jack of the United States, naval jack of the United States from 1975 to 1976 and again from 2002 to 2019. It was authorized by the United States Navy, U.S. Navy and was flown from the jackstaff of commissioned vessels of the U.S. Navy while moored pierside or at anchor. Since then, it is used only as a naval jack by the oldest active warship in the U.S. Navy. The design is purported to be that of the first U.S. naval Jack (flag), jack, flown soon after independence. The First Navy Jack was replaced as the U.S. naval jack by the U.S. Jack of the United States, Union Jack (consisting of white stars on a blue field, not to be confused with the flag of the United Kingdom, also commonly called "the Union Jack") on June 4, 2019, by order of the Chief of Naval Operations. History In late 1775, as the first ships of the Continental Navy readied in the Delaware River, Commodore Esek Hopkins issued an instruction directing his vessels to fly a "striped" jack an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
USS Blue Ridge (LCC-19)
USS ''Blue Ridge'' (LCC-19) is the lead ship of the two amphibious command ships of the United States Navy, and is the third Navy ship named after the Blue Ridge Mountains, a range of mountains in the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern United States. As the flagship of the United States Seventh Fleet, Seventh Fleet, her primary role is to provide command, control, communications, computers, and intelligence (C4I) support to the commander and staff of the Fleet. She is currently Forward-basing, forward-deployed to United States Fleet Activities Yokosuka, U.S. Navy Fleet Activities, Yokosuka in Japan. ''Blue Ridge'' is the oldest deployed warship of the U.S. Navy, following the decommissioning of . ''Blue Ridge'', as the U.S. Navy's active commissioned ship having the longest total period as active, flies the First Navy Jack instead of the jack of the United States. ''Blue Ridge'' is expected to remain in service until 2039. History ''Blue Ridge'' was put "in commission spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kingdom Of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of southern Italy, Norman conquest of the southern peninsula. The island was divided into Three valli of Sicily, three regions: Val di Mazara, Val Demone and Val di Noto. After a brief rule by Charles of Anjou, a revolt in 1282 known as the Sicilian Vespers threw off Capetian House of Anjou, Angevin rule in the island of Sicily. The Angevins managed to maintain control in the mainland part of the kingdom, which became a separate entity also styled ''Kingdom of Sicily'', although it is retroactively referred to as the Kingdom of Naples. Sicily (officially known as the Kingdom of Trinacria between 1282 and 1442) at the other hand, remained a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Raising The First Naval Jack
{{disambiguation ...
Raising may refer to: *Raising (syntax), a syntactic construction *Raising (sound change), a sound change *Raising (metalworking), a metalworking technique *Barn raising, a community event to erect the wooden framework for a building *Fundraising, a method of raising money, usually for non-profits and schools See also *Raise (other) * **Raising Hell (other) **Raising the Bar (other) **Raising the Wind (other) Raising the Wind may refer to: * ''Raising the Wind'', an 1803 farce by James Kenney in which the character Jeremy Diddler appears * Raising the Wind (1925 film), ''Raising the Wind'' (1925 film), a British short comedy film directed by Leslie S. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gadsden Flag
The Gadsden flag is a historical American flag with a yellow field depicting a timber rattlesnake coiled and ready to strike. Beneath the rattlesnake are the words Dont Tread on Me. Some modern versions of the flag include an apostrophe in the word "don't". The flag is named after Christopher Gadsden, a South Carolinian delegate to the Continental Congress and brigadier general in the Continental Army, who designed the flag in 1775 during the American Revolution. He gave the flag to Commodore Esek Hopkins, and it was unfurled on the main mast of Hopkins' flagship USS ''Alfred'' on December 20, 1775. Two days later, Congress made Hopkins commander-in-chief of the Continental Navy. He adopted the Gadsden banner as his personal flag, flying it from the mainmast of the flagship while he was aboard. The Continental Marines also flew the flag during the early part of the war. The rattlesnake was a symbol of the unity of the Thirteen Colonies at the start of the Revolutionary W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America. The Thirteen Colonies in their traditional groupings were: the New England Colonies (New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut); the Middle Colonies ( New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware); and the Southern Colonies (Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia). These colonies were part of British America, which also included territory in The Floridas, the Caribbean, and what is today Canada. The Thirteen Colonies were separately administered under the Crown, but had similar political, constitutional, and legal systems, and each was dominated by Protestant English-speakers. The first of the colonies, Virginia, was established at Jamestown, in 1607. Maryland, Pennsylvania, and the New England Colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American Revolutionary War, which was launched on April 19, 1775, in the Battles of Lexington and Concord. Leaders of the American Revolution were Founding Fathers of the United States, colonial separatist leaders who, as British subjects, initially Olive Branch Petition, sought incremental levels of autonomy but came to embrace the cause of full independence and the necessity of prevailing in the Revolutionary War to obtain it. The Second Continental Congress, which represented the colonies and convened in present-day Independence Hall in Philadelphia, formed the Continental Army and appointed George Washington as its commander-in-chief in June 1775, and unanimously adopted the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Timber Rattlesnake
The timber rattlesnake (''Crotalus horridus''), also known Common name, commonly as the canebrake rattlesnake and the banded rattlesnake,Albert Hazen WWright AH, species:Anna Allen WWright AA (1957). ''Handbook of Snakes of the United States and Canada''. Ithaca and London: Comstock Publishing Associates, a division of Cornell University Press. (7th printing, 1985). 1,105 pp. (in two volumes). . (''Crotalus horridus'', pp. 956–966.) is a species of Crotalinae, pit viper in the Family (biology), family Viperidae. The species is native to the eastern United States. Like all other pit vipers, it is Venomous snake, venomous, with a very toxic bite. Its venom is extremely potent, both hemorrhagic and neurotoxic venom are present depending on population and location. ''C. horridus'' is the only rattlesnake species in most of the populous Northeastern United States and is second only to its relatives to the west, the Crotalus viridis, prairie rattlesnake, as the most northerly distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
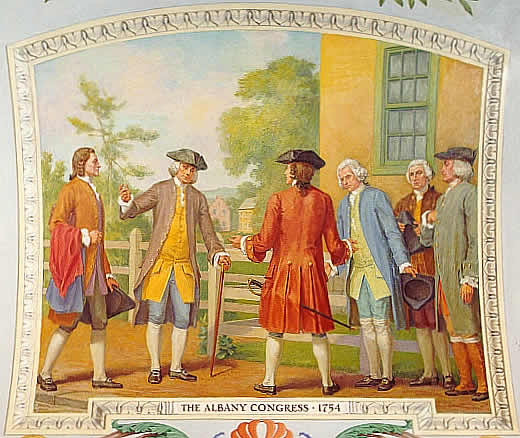
Albany Congress
The Albany Congress (June 19 – July 11, 1754), also known as the Albany Convention of 1754, was a meeting of representatives sent by the legislatures of seven of the British colonies in British America: Connecticut Colony, Connecticut, Province of Maryland, Maryland, Province of Massachusetts Bay, Massachusetts, Province of New Hampshire, New Hampshire, Province of New York, New York, Province of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, and Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Rhode Island. Those not in attendance included Newfoundland Colony, Newfoundland, History of Nova Scotia, Nova Scotia, Province of New Jersey, New Jersey, Colony of Virginia, Virginia, Colony of Georgia, Georgia, Colony of North Carolina, North Carolina, and Colony of South Carolina, South Carolina. Representatives met daily at the Albany City Hall, City Hall () in Albany, New York, from June 19 to July 11, 1754, to discuss better relations with the Native Americans in the United States, Native America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Political Cartoon
A political cartoon, also known as an editorial cartoon, is a cartoon graphic with caricatures of public figures, expressing the artist's opinion. An artist who writes and draws such images is known as an editorial cartoonist. They typically combine artistic skill, hyperbole and satire in order to either question authority or draw attention to corruption, political violence and other social ills. Developed in England in the latter part of the 18th century, the political cartoon was pioneered by James Gillray, although his and others in the flourishing English industry were sold as individual prints in print shops. Founded in 1841, the British periodical '' Punch'' appropriated the term ''cartoon'' to refer to its political cartoons, which led to the term's widespread use. History Origins The pictorial satire has been credited as the precursor to the political cartoons in England: John J. Richetti, in ''The Cambridge history of English literature, 1660–1780'', states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pennsylvania Gazette
''The Pennsylvania Gazette'' was one of the United States' most prominent newspapers from 1728 until 1800. In the years leading up to the American Revolution, the newspaper served as a voice for colonial opposition to Kingdom of Great Britain, British colonial rule, especially to the Stamp Act (1765), Stamp Act and the Townshend Acts. The newspaper was headquartered in Philadelphia. History 18th century The newspaper was first published in 1728 by Samuel Keimer and was the second newspaper to be published in the colonial Province of Pennsylvania under the name ''The Universal Instructor in all Arts and Sciences: and Pennsylvania Gazette'', a reference to Keimer's intention to print out a page of Ephraim Chambers' ''Cyclopaedia, or Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences'' in each edition. On October 2, 1729, Samuel Keimer, the owner of ''The Gazette'', fell into debt and before fleeing to Barbados sold the newspaper to Benjamin Franklin and his partner Hugh Meredith, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Join, Or Die
''Join, or Die.'' is a political cartoon showing the disunity in the American colonies, originally in the context of the French and Indian War in 1754. Attributed to Benjamin Franklin, the original publication by ''The Pennsylvania Gazette'' on May 9, 1754, is the earliest known pictorial representation of colonial union produced by an American colonist in Thirteen Colonies, Colonial America. It was based on a superstition that if a snake was cut in pieces and the pieces were put together before sunset, the snake would return to life. The cartoon is a woodcut showing a snake cut into eighths, with each segment labeled with the initials of one of the Thirteen Colonies, American colonies or regions. New England Colonies, New England was represented as one segment, rather than the four colonies it was at that time. Delaware Colony, Delaware was not listed separately as it was part of Province of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania. Province of Georgia, Georgia, however, was omitted com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which American Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces organized as the Continental Army and commanded by George Washington defeated the British Army during the American Revolutionary War, British Army. The conflict was fought in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. The war's outcome seemed uncertain for most of the war. However, Washington and the Continental Army's decisive victory in the Siege of Yorktown in 1781 led King George III and the Kingdom of Great Britain to negotiate an end to the war in the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris two years later, in 1783, in which the British monarchy acknowledged the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, leading to the establishment of the United States as an independent and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |