|
Ferrosilicon
Ferrosilicon is an ferroalloy, alloy of iron and silicon. It has a typical silicon content of 15–90% by weight and a high proportion of iron silicides. Production and reactions Ferrosilicon is produced by reduction of silica or sand with coke (fuel), coke in the presence of iron. Typical sources of iron are scrap iron or millscale. Ferrosilicons with silicon content up to about 15% are made in blast furnaces lined with acid fire bricks. Ferrosilicons with higher silicon content are made in electric arc furnaces. The usual formulations on the market are ferrosilicons with 15%, 45%, 75%, and 90% silicon. The remainder is iron, with about 2% consisting of other elements like aluminium and calcium. An overabundance of silica is used to prevent formation of silicon carbide. Microsilica is a useful byproduct. A mineral perryite is similar to ferrosilicon, with its composition Fe5Si2. In contact with water, ferrosilicon may slowly produce hydrogen. The reaction, which is accelerate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferroalloy
Ferroalloy refers to various alloys of iron with a high proportion of one or more other elements such as manganese (Mn), aluminium (Al), or silicon (Si). They are used in the production of steels and alloys. The alloys impart distinctive qualities to steel and cast iron or serve important functions during production and are, therefore, closely associated with the iron and steel industry, the leading consumer of ferroalloys. The leading producers of ferroalloys in 2014 were China, South Africa, India, Russia and Kazakhstan, which accounted for 84% of the world production. World production of ferroalloys was estimated as 52.8 million tonnes in 2015. Compounds The main ferroalloys are: *FeAl – ferroaluminum *FeB – ferroboron – 12–20% of boron, max. 3% of silicon, max. 2% aluminium, max. 1% of carbon *FeCe – ferrocerium *FeCr – ferrochromium *FeMg – ferromagnesium *FeMn – ferromanganese *FeMo – ferromolybdenum – min. 60% Mo, max. 1% Si, max. 0.5% Cu *Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Silicon is a significant element that is essential for several physiological and metabolic processes in plants. Silicon is widely regarded as the predominant semiconductor material due to its versatile applications in various electrical devices such as transistors, solar cells, integrated circuits, and others. These may be due to its significant band gap, expansive optical transmission range, extensive absorption spectrum, surface roughening, and effective anti-reflection coating. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
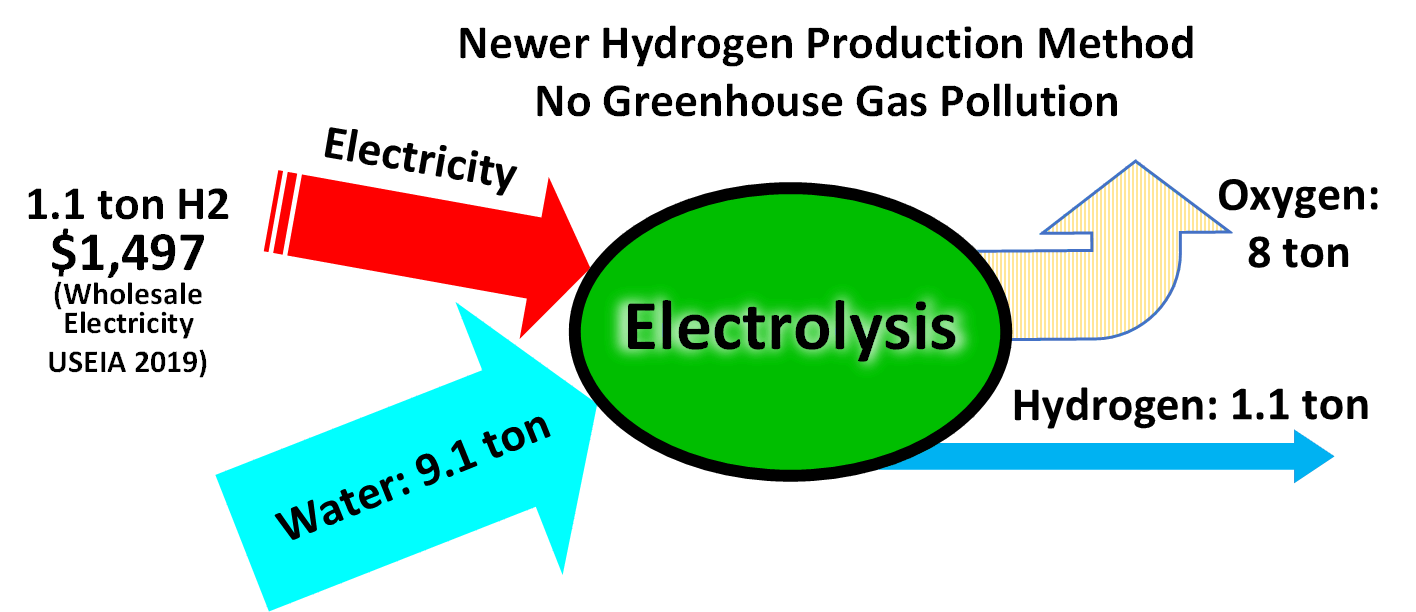
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen gas is produced by several industrial methods. Nearly all of the world's current supply of hydrogen is created from fossil fuels. Article in press. Most hydrogen is ''gray hydrogen'' made through steam methane reforming. In this process, hydrogen is produced from a chemical reaction between steam and methane, the main component of natural gas. Producing one tonne of hydrogen through this process emits 6.6–9.3 tonnes of carbon dioxide. When carbon capture and storage is used to remove a large fraction of these emissions, the product is known as ''blue hydrogen''. ''Green hydrogen'' is usually understood to be produced from Renewable energy, renewable electricity via electrolysis of water. Less frequently, definitions of ''green hydrogen'' include hydrogen produced from other low-emission sources such as Biomass (energy), biomass. Producing green hydrogen is currently more expensive than producing gray hydrogen, and the efficiency of energy conversion is inherently low. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is usually defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class of soil or soil type; i.e., a soil containing more than 85 percent sand-sized particles by mass. The composition of sand varies, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal settings is silica (silicon dioxide, or SiO2), usually in the form of quartz. Calcium carbonate is the second most common type of sand. One such example of this is aragonite, which has been created over the past 500million years by various forms of life, such as coral and shellfish. It is the primary form of sand apparent in areas where reefs have dominated the ecosystem for millions of years, as in the Caribbean. Somewhat more rarely, sand may be composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solidus (chemistry)
While chemically pure materials have a single melting point, chemical mixtures often partially melt at the temperature known as the solidus (''T''S or ''T''sol), and fully melt at the higher liquidus temperature (''T''L or ''T''liq). The solidus is always less than or equal to the liquidus, but they need not coincide. If a gap exists between the solidus and liquidus it is called the freezing range, and within that gap, the substance consists of a mixture of solid and liquid phases (like a slurry). Such is the case, for example, with the olivine ( forsterite- fayalite) system, which is common in Earth's mantle. Definitions In chemistry, materials science, and physics, the liquidus temperature specifies the temperature above which a material is completely liquid, and the maximum temperature at which crystals can co-exist with the melt in thermodynamic equilibrium. The solidus is the locus of temperatures (a curve on a phase diagram) below which a given substance is completely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphitization
Graphitization is a process of transforming a carbonaceous material, such as coal or the carbon in certain forms of iron alloys, into graphite. Process The graphitization process involves a restructuring of the molecular structure of the carbon material. In the initial state, these materials can have an amorphous structure or a crystalline structure different from graphite. Graphitization generally occurs at high temperatures (up to ), and can be accelerated by catalysts such as iron or nickel. When carbonaceous material is exposed to high temperatures for an extended period of time, the carbon atoms begin to rearrange and form layered crystal planes. In the structure of graphite, carbon atoms are arranged in flat hexagonal sheets that are stacked on top of each other. These crystal planes give graphite its characteristic flake structure, giving it specific properties such as good electrical and thermal conductivity, low friction and excellent lubrication. Interest Graphiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cast Iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its carbon appears: Cast iron#White cast iron, white cast iron has its carbon combined into an iron carbide named cementite, which is very hard, but brittle, as it allows cracks to pass straight through; Grey iron, grey cast iron has graphite flakes which deflect a passing crack and initiate countless new cracks as the material breaks, and Ductile iron, ductile cast iron has spherical graphite "nodules" which stop the crack from further progressing. Carbon (C), ranging from 1.8 to 4 wt%, and silicon (Si), 1–3 wt%, are the main alloying elements of cast iron. Iron alloys with lower carbon content are known as steel. Cast iron tends to be brittle, except for malleable iron, malleable cast irons. With its relatively low melting point, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force, electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change Alternating current, AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromotor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate Laplace force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may also be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be brushed or brushless, single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase, axial or radial flux, and may be air-cooled or liquid-cooled. Standardized electric motors provide power for industrial use. The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicide
A silicide is a type of chemical compound that combines silicon and a usually more electropositive element. Silicon is more electropositive than carbon. In terms of their physical properties, silicides are structurally closer to borides than to carbides. Because of size differences however silicides are not isostructural with borides and carbides. Bonds in silicides range from conductive metal-like structures to covalent or ionic. Silicides of all non-transition metals have been described except beryllium. Silicides are used in interconnects. Structure Silicon atoms in silicides can have many possible organizations: *Isolated silicon atoms: electrically conductive (or semiconductive) CrSi, MnSi, FeSi, CoSi, , , , , , *Si2 pairs: , hafnium and thorium silicides *Si4 tetrahedra: KSi, RbSi, CsSi *Si''n'' chains: USi, , CaSi, SrSi, YSi *Planar hexagonal graphite-like Si layers: β-USi2, silicides of other lanthanoids and actinoids *Corrugated hexagonal Si layers: C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |